Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
It’s a frightening experience to experience a mental health crisis. Stimulant psychosis is a type of mental health crisis that can be caused by the use of psychostimulant drugs, and it can be a particularly scary experience. People who have stimulant psychosis can experience changes in their behavior, thoughts, and feelings, as well as hallucinations and delusions. But the good news is that it is treatable – the important question then becomes, how long does stimulant psychosis last? In this article, we explore this question and look at the factors that can affect the duration of stimulant psychosis.
Stimulant psychosis usually lasts for about 1 to 3 days, although it could be longer depending on the individual and the dose taken. It is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible if you or someone you know has taken a stimulant drug and is experiencing symptoms of psychosis.
The severity of psychosis can vary from mild to severe. Symptoms of stimulant psychosis include confusion, paranoia, delusions, and hallucinations. Treatment for stimulant psychosis usually involves supportive care and antipsychotic medications.
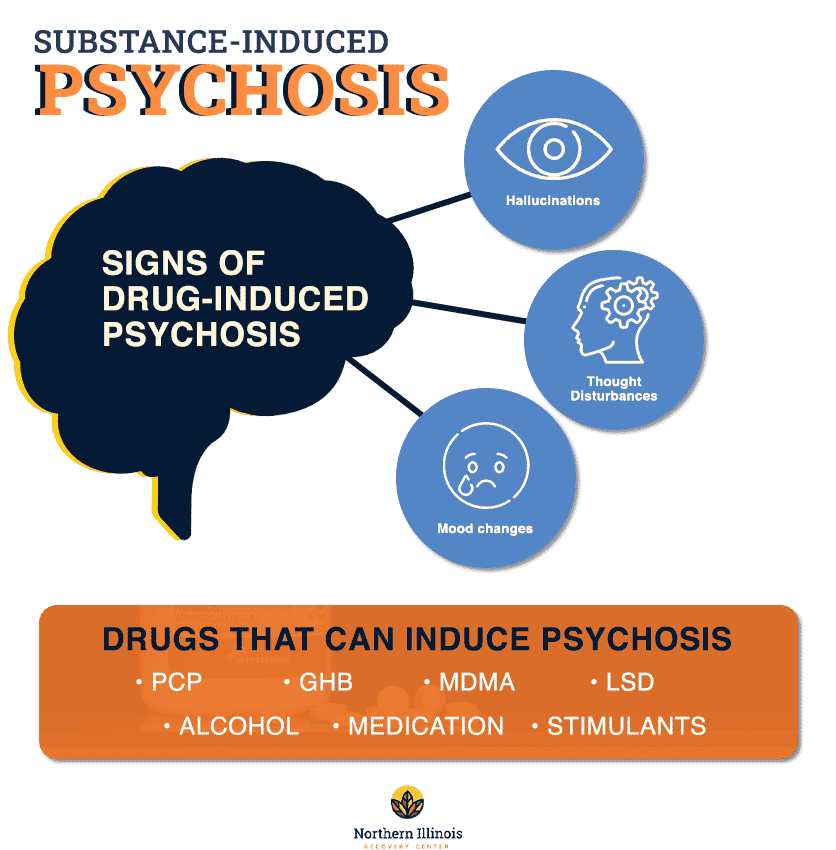
What is Stimulant Psychosis?
Stimulant psychosis is a mental disorder caused by the use of stimulant drugs like cocaine, methamphetamine, and prescription medications. It is characterized by hallucinations, delusions, paranoia, agitation, and other psychotic symptoms. Stimulant psychosis can occur in the short-term, or it can be a long-term effect of drug abuse or misuse.
Stimulant psychosis is believed to be caused by a combination of the drug’s effects on the brain and the individual’s own vulnerability to psychosis. For instance, people with a pre-existing mental health disorder may be more prone to stimulant psychosis. It is also believed that the longer someone uses stimulant drugs, the greater their risk of developing stimulant psychosis.
What Are the Symptoms of Stimulant Psychosis?
The symptoms of stimulant psychosis can vary depending on the type of stimulant used and the individual’s underlying mental health. Common symptoms of stimulant psychosis include delusions, paranoia, hallucinations, aggressive behavior, and disorganized thinking.
People experiencing stimulant psychosis may also experience changes in their mood, such as mania, depression, or anxiety. They may also experience changes in their sleep patterns, such as insomnia or sleeping too much. Stimulant psychosis can also cause physical symptoms, such as sweating, rapid heartbeat, and increased blood pressure.
How Long Does Stimulant Psychosis Last?
The length of time that stimulant psychosis lasts depends on the type of stimulant used and the individual’s underlying mental health. In most cases, stimulant psychosis is a short-term condition that resolves once the stimulant is out of the person’s system. However, in some cases, stimulant psychosis may persist for a longer period of time, even after the person has stopped using the drug.
What Factors Affect How Long Stimulant Psychosis Lasts?
A number of factors can affect how long stimulant psychosis lasts. These include the type of stimulant used, the individual’s underlying mental health, and the length of time that the stimulant was used. People who use stimulants for a longer period of time are more likely to experience longer-lasting stimulant psychosis.
How Is Stimulant Psychosis Treated?
Stimulant psychosis is typically treated with medications and psychotherapy. Medications are typically used to manage psychotic symptoms and help reduce the risk of relapse. Psychotherapy can help the individual understand their condition and develop coping strategies for managing their symptoms. It can also help them find ways to avoid using stimulants in the future.
In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage stimulant psychosis. This will typically involve the person being monitored and treated in a controlled environment. Treatment is typically tailored to the individual’s needs and may include medications, psychotherapy, and other therapeutic interventions.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Stimulant Psychosis?
Stimulant psychosis is a mental disorder that occurs when a person has been taking a stimulant medication for an extended period of time or in higher doses than prescribed. This can cause a person to experience symptoms such as delusions, hallucinations, and paranoia.
2. What Causes Stimulant Psychosis?
The most common cause of stimulant psychosis is the misuse or abuse of stimulant medications. This includes taking more of the drug than prescribed, taking it more often than prescribed, or taking it without a prescription. Other factors that may contribute to the development of stimulant psychosis include genetics, mental health problems, and stress.
3. What are the Symptoms of Stimulant Psychosis?
The symptoms of stimulant psychosis can vary, but typically include delusions, hallucinations, paranoia, disorganized thinking, and aggression. Other symptoms may include severe anxiety, impulsivity, and difficulty sleeping.
4. How is Stimulant Psychosis Diagnosed?
Stimulant psychosis is typically diagnosed based on a person’s symptoms, medical history, and psychological evaluation. A physical exam, lab tests, and imaging tests may also be used to rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
5. How is Stimulant Psychosis Treated?
Treatment for stimulant psychosis typically involves discontinuing or reducing the use of the drug, as well as medication to help manage the symptoms. Other treatments may include psychotherapy, support groups, and lifestyle changes.
6. How Long Does Stimulant Psychosis Last?
The length of time that stimulant psychosis will last depends on a variety of factors, including the severity of the symptoms and the individual’s response to treatment. Generally, stimulant psychosis can last anywhere from days to weeks, but in some cases, it can persist for months or even years.
Drug-Induced Psychosis – Steven Batki, M.D.
As a professional writer, I can confidently conclude that stimulant psychosis can last anywhere from days to months, depending on the individual and the severity of their condition. While the symptoms can be alarming, the good news is that with proper treatment and medication, people can make a full recovery. With the right support and care, stimulant psychosis can be managed effectively and individuals can go on to live happy and healthy lives.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts