Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
When it comes to drug testing, one of the most important tests to administer is the opiate test. This test is used to detect the presence of opiates in a person’s body and can be used to determine if the person has been using illegal opiates or has been prescribed opiates by a doctor. Unfortunately, there are instances where a false positive can occur and lead to undesired consequences. In this article, we will discuss what can cause a false positive opiate test and how to avoid them.
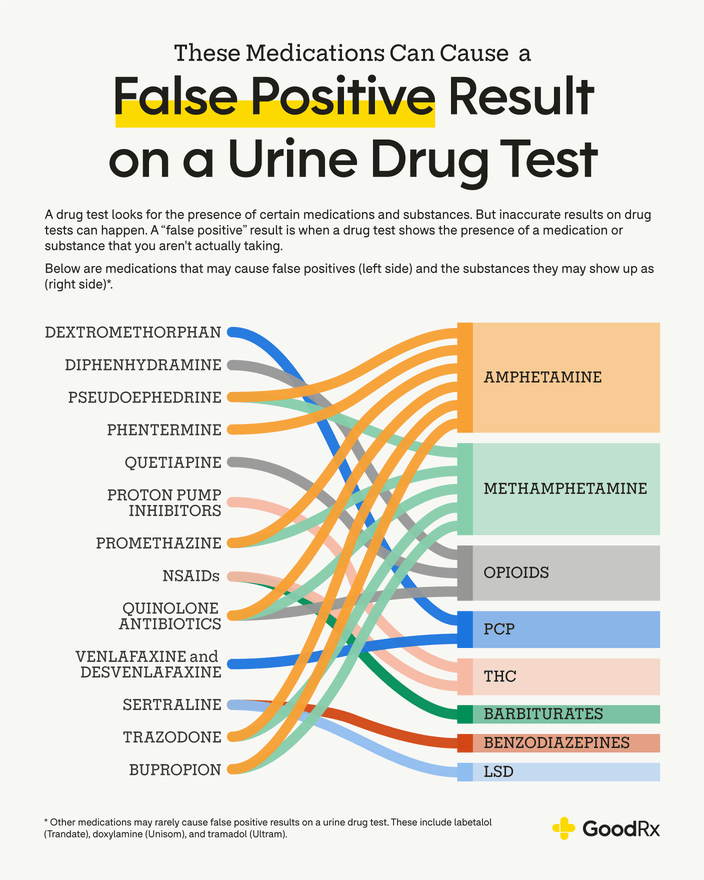
False positives on opiate drug tests are rare but can occur. Certain prescription medications, such as codeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and morphine, can be confused with opiates in some tests. Other non-opiate drugs, such as certain kinds of antidepressants and antihistamines, may also produce false positive results.
Contents
- What Can Lead to False Positive Opiate Test Results?
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What is an Opiate Test?
- What Can Cause a False Positive Opiate Test?
- How Can False Positives Be Avoided?
- What Are the Consequences of a False Positive Opiate Test?
- Can Opiate Tests Distinguish Between Natural Opiates and Synthetic Opiates?
- What is the Difference Between a Screening Test and a Confirmatory Test?
- Can certain foods, drinks, and meds cause a false positive on a drug test?
What Can Lead to False Positive Opiate Test Results?
A false positive opiate test result can be caused by a number of factors. These include cross-reactivity of medications, laboratory errors, and eating certain foods that contain opiates. It is important to understand the causes of false positives in order to avoid them.
When a person is tested for opiates, the test is designed to detect the presence of opiates in the system. However, there are certain medications, foods, and laboratory errors that can lead to false positives. This can lead to a person being incorrectly diagnosed with opiate use, which can have serious implications for the individual’s health, employment, and legal status.
Cross-Reactivity of Medications
Cross-reactivity is a phenomenon in which certain medications can have a similar chemical structure to opiates and can therefore produce a false positive result. This is particularly common among medications such as codeine and oxycodone, as these are both opioids. Other medications that can produce false positives include certain antibiotics, antihistamines, and antifungals.
It is important to be aware of any medications that could potentially produce a false positive when taking an opiate test. If possible, the patient should mention any medications they are taking to the doctor or the laboratory technician administering the test. This will allow them to take the necessary steps to avoid a false positive result.
Laboratory Errors
Laboratory errors can also lead to false positives in opiate tests. These errors can be caused by a variety of factors, including incorrect sample handling, incorrect laboratory procedures, or incorrect interpretation of the results. It is important for laboratories to follow strict procedures in order to minimize the chances of errors occurring.
Consumption of Certain Foods
Certain foods can also lead to false positives in opiate tests. Poppy seeds, for example, contain trace amounts of opiates and can produce a false positive. It is important to note that poppy seeds are not the same as opium, which is a much more potent opiate. However, consuming poppy seeds can still lead to a false positive result.
In addition, certain medicines used in Chinese and Indian traditional medicine can also contain opiates, which can lead to a false positive result. It is important to be aware of these medicines and to mention them to the doctor or laboratory technician if they are being taken.
Take-Home Message
False positives can occur in opiate tests due to cross-reactivity of medications, laboratory errors, and consumption of certain foods. It is important to be aware of these factors and to mention any medications being taken or foods consumed to the doctor or laboratory technician administering the test. This will help to avoid a false positive result.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Opiate Test?
An opiate test is a type of drug test used to detect the presence of opiates, such as codeine, heroin, and morphine, in a person’s system. Opiates are drugs derived from the opium poppy plant and are commonly prescribed to treat severe pain. Opiate tests are often used to determine if a person has used opiates recently or if they have a drug addiction.
What Can Cause a False Positive Opiate Test?
A false positive opiate test occurs when a person tests positive for opiates even though they have not recently used them. False positives can be caused by a variety of factors, including cross-reactivity with other substances, improper storage and handling of the test sample, or laboratory error. Cross-reactivity occurs when a substance in the sample triggers a false positive response in the test, such as the presence of poppy seeds or ibuprofen. Improper storage and handling of the sample can cause contamination, leading to a false positive. Finally, laboratory error can result in incorrect interpretation of the test results.
How Can False Positives Be Avoided?
False positives can be avoided by ensuring that the test sample is collected and handled properly, stored in the correct conditions, and tested in a reliable laboratory. Additionally, it is important to let the laboratory know if the person being tested is taking any medications, as this can affect the test results.
What Are the Consequences of a False Positive Opiate Test?
The consequences of a false positive opiate test can be serious, as it can lead to incorrect diagnoses, inappropriate treatments, and legal repercussions. It is important to ensure that any test results are accurate and that the laboratory is reliable before any action is taken based on the results.
Can Opiate Tests Distinguish Between Natural Opiates and Synthetic Opiates?
Yes, opiate tests can distinguish between natural and synthetic opiates. Most opiate tests use antibodies that can detect the presence of specific opiates or opiate metabolites, allowing the laboratory to differentiate between natural and synthetic opiates.
What is the Difference Between a Screening Test and a Confirmatory Test?
A screening test is a preliminary test used to detect the presence of a specific drug or drug metabolite in a sample. It is typically less expensive and faster than a confirmatory test, but it may not be as accurate. A confirmatory test is a more reliable test used to confirm the results of a screening test. It typically uses more advanced technology and is more accurate and reliable than a screening test.
Can certain foods, drinks, and meds cause a false positive on a drug test?
A false positive opiate test can have major implications for individuals, so it is important to understand what can cause a false positive result. Common causes include cross-reactivity with other substances, improper testing techniques, and the presence of naturally occurring opiates. As with any medical test, it is essential to make sure that the testing is done correctly and that the sample is accurately analyzed. If you have any doubts about a positive opiate test result, you should consult with a health care provider to confirm the finding. With the right knowledge and care, you can ensure that you get the most accurate results from your opiate testing.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts