Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
If you’re looking for information on what drugs are considered opiates, you’ve come to the right place. Opiates are a type of drug derived from the opium poppy plant or synthetically produced in a laboratory. They are usually prescribed to treat pain, but they can also be used recreationally. In this article, we will look at the different types of opiates and what makes them different from other drugs. We’ll also discuss the potential risks and side effects of using opiates and answer some common questions about them.
Contents
What are the Different Types of Opiates?
Opiate drugs are those derived from the opium poppy plant, or those that have similar effects to these drugs. Although they can be effective in relieving pain, they can also be highly addictive and have serious adverse health effects. It is important to be aware of what drugs are considered to be opiates and their risks before taking them.
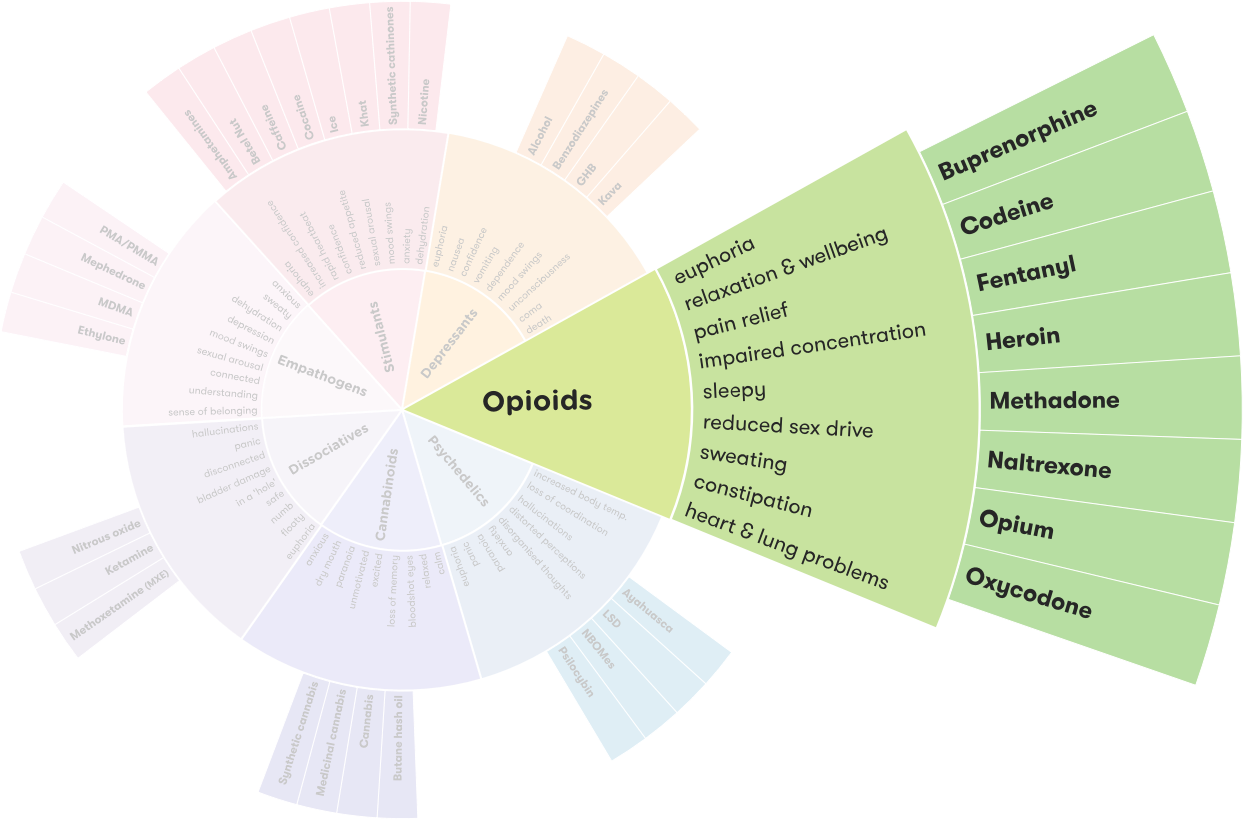
The most common type of opiates are opioids, which are synthetic derivatives of the opium poppy plant. These drugs include codeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and morphine. Opioids are used to treat moderate to severe pain and can be found in some over-the-counter medicines.
Another type of opiate is called an agonist, which is a drug that binds to the same receptor sites in the brain as opioids. Opioid agonists, such as methadone and buprenorphine, are used to treat opioid addiction and can also be used to treat pain.
What are the Side Effects of Opiates?
The most common side effects of opiate use include nausea, constipation, vomiting, and drowsiness. Other side effects can include confusion, dry mouth, itching, and difficulty breathing. Long-term use of opiates can also lead to psychological dependence and addiction.
Opiate use can also lead to tolerance, which means that the user will need to take increasing amounts of the drug to feel the same effects. This can increase the risk of overdose and other adverse health effects.
Are there Alternatives to Opiates?
There are many alternatives to opiate drugs that can be used to treat pain, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen. Other treatments, such as massage, physical therapy, and acupuncture, can also be used to manage pain.
In some cases, non-opioid drugs or non-drug treatments may be more effective than opiates for managing pain. It is important to speak with a doctor or healthcare provider before taking any drugs, including opiates.
What are Synthetic Opiates?
Synthetic opiates are drugs that are chemically similar to opiates, but are not derived from the opium poppy plant. These drugs are usually created in a laboratory and are designed to act like opiates.
Synthetic opiates include fentanyl, meperidine, and tramadol. These drugs are used to treat moderate to severe pain and can be found in some prescription medications. Synthetic opiates can be more potent than traditional opiates and can be particularly dangerous when used in combination with other drugs, such as alcohol or benzodiazepines.
What are the Risks of Synthetic Opiates?
The risks of synthetic opiates are similar to those of traditional opiates, including nausea, vomiting, constipation, and confusion. They can also lead to tolerance, addiction, and overdose. Synthetic opiates can be particularly dangerous when combined with other drugs or alcohol, which can increase the risk of overdose and other adverse effects.
Are there Alternatives to Synthetic Opiates?
Yes, there are alternative treatments to synthetic opiates that can be used to manage pain. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen are often used to treat mild to moderate pain. Other treatments, such as massage, physical therapy, and acupuncture, can also be used to manage pain.
In some cases, non-opioid drugs or non-drug treatments may be more effective than synthetic opiates for managing pain. It is important to speak with a doctor or healthcare provider before taking any drugs, including synthetic opiates.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What are Opiates?
Opiates are drugs derived from the opium poppy plant, which is mostly grown in Asia and South America. They are used medically to treat pain, but they can also be abused and lead to addiction. Opiates interact with the opioid receptors in the brain to produce feelings of euphoria, dulling pain and bringing on a sense of relaxation. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, and heroin.
What Are Some Examples of Opiates?
Common examples of opiates include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, meperidine, hydromorphone, and heroin. Morphine and codeine are both naturally-occurring opiates found in the opium poppy plant, while the other substances are semi-synthetic derivatives of those two substances. Oxycodone and hydrocodone are commonly prescribed for pain relief, while meperidine is used to treat moderate to severe pain. Hydromorphone and heroin are both highly addictive and are usually not prescribed for medical use.
What Are the Effects of Opiates?
When taken as prescribed, opiates can be effective in relieving pain and providing a sense of euphoria. However, when taken in higher doses or in higher frequencies, they can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Opiate use can cause a range of side effects, including drowsiness, confusion, constipation, nausea, and slowed breathing. It can also lead to a feeling of euphoria and a heightened sense of well-being.
What Are the Risks of Taking Opiates?
Taking opiates can be dangerous, especially when taken without a doctor’s supervision. Some of the risks associated with opiate use include physical dependence, overdose, and death. Long-term use can also lead to tolerance, meaning that the user needs to take higher and higher doses to achieve the same effects. Additionally, taking opiates can interfere with judgment and decision-making, leading to risky behaviors and accidents.
What Are the Treatments for Opiate Addiction?
Treatment for opiate addiction typically involves a combination of medication and counseling. Medications such as buprenorphine and methadone can be used to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while counseling can help the user identify underlying causes of their addiction and develop strategies for avoiding relapse. Detoxification is also an important part of treatment, as it helps the user rid their body of any remaining opiates.
Are There Any Natural Alternatives to Opiates?
Yes, there are several natural alternatives to opiates that can be used to manage pain. These include acetaminophen and ibuprofen, which are both available over-the-counter. Other natural remedies include massage, yoga, physical therapy, acupuncture, and herbal supplements such as turmeric and ginger. While these methods may not provide the same level of relief as opiates, they can help reduce pain and discomfort without the risk of addiction.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates are powerful drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant. Opiates include substances such as morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, heroin, and methadone. These drugs can be highly addictive and, if not taken as prescribed, can lead to severe physical and psychological dependence. For this reason, they should be taken with caution, and only by those individuals who have been prescribed them by a qualified medical professional.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts