Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
The opiate family is one of the most widely-used and abused classes of drugs in the world. From the highly-addictive heroin to the powerful and often-abused prescription painkillers, these drugs are known to have a profound effect on the brain and body. But what exactly are the drugs in the opiate family and how do they work? In this article, we’ll explore the different drugs in the opiate family and discuss the risks and effects associated with them.
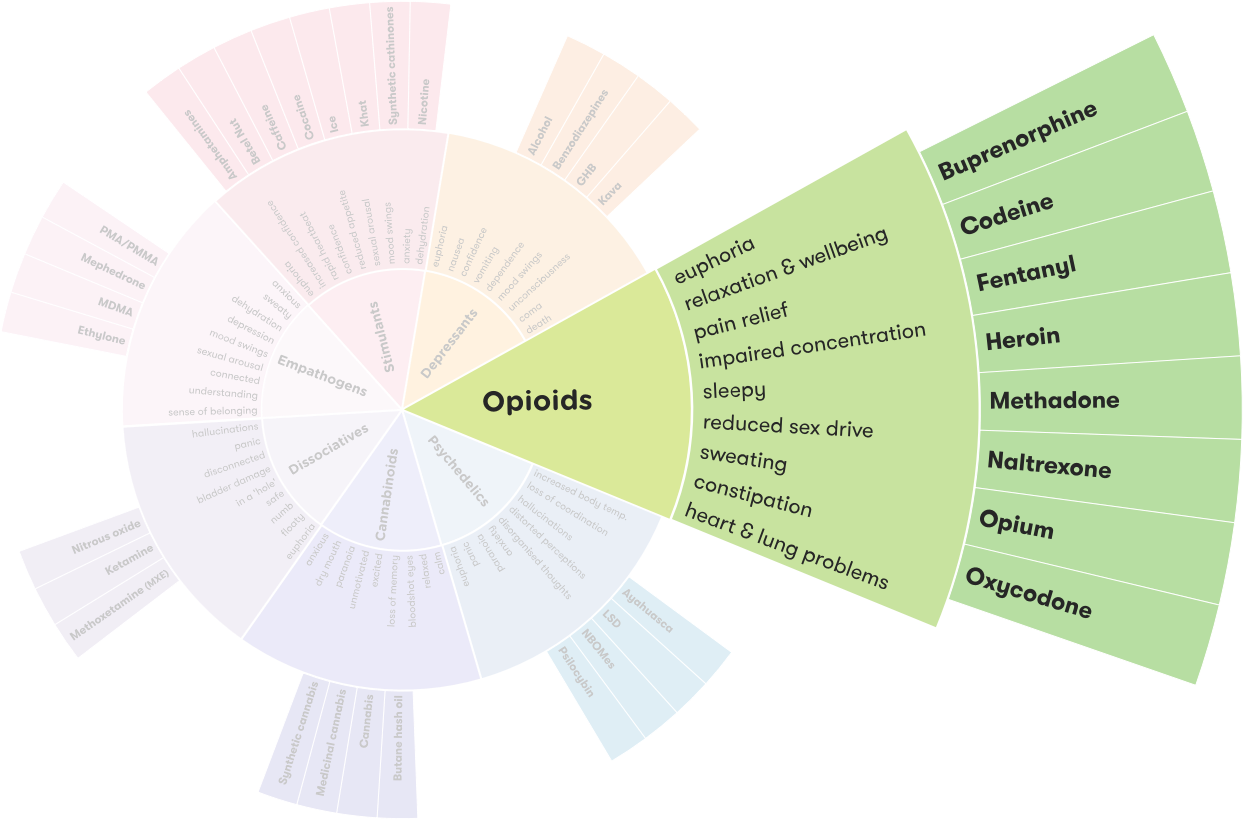
Opiate drugs are substances derived from the opium poppy plant. Examples of drugs in the opiate family include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydromorphone, buprenorphine, fentanyl, and methadone. These drugs are used to treat moderate to severe pain, as well as relieve coughing and diarrhea.
Contents
- What Are Drugs in the Opiate Family?
- What Are the Effects of Opiates?
- What Are the Risks of Opiate Use?
- What Are the Treatment Options for Opiate Addiction?
- What Are the Prevention Strategies for Opiate Abuse?
- What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opiate Use?
- What Are the Alternatives to Opiates?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Drugs in the Opiate Family?
Opiate drugs are a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant. These drugs are used to treat pain, but they can also be abused and lead to addiction. Opiates have several psychoactive effects, including sedation, euphoria, and relaxation. In the United States, opiate drugs are regulated by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
The opiate family includes several different drugs, including both natural and synthetic substances. Natural opiates include morphine and codeine, while synthetic opiates include fentanyl and oxycodone. All opiates work to reduce pain, but they can also cause physical and psychological dependence.
In addition to the drugs in the opiate family, there are also synthetic opioids. Synthetic opioids are laboratory-created drugs that are chemically similar to opiates. These drugs are often used to treat pain, but they can also be abused and lead to addiction. Common synthetic opioids include hydrocodone, oxycodone, and methadone.
What Are the Effects of Opiates?
The main effect of opiates is to reduce pain. Opiates work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, which then reduces the perception of pain. Opiates can also cause a feeling of euphoria and relaxation, which can lead to abuse and addiction.
In addition to their pain-relieving effects, opiates can also cause dangerous side effects. These include nausea, vomiting, constipation, drowsiness, confusion, and respiratory depression. Long-term use of opiates can also lead to tolerance, which means that the user needs to take more and more of the drug to get the same effects.
Opiate use can also lead to physical and psychological dependence. Physical dependence occurs when the body becomes used to the drug and needs it to function normally. Psychological dependence occurs when the user feels like they need the drug to cope with daily life.
What Are the Risks of Opiate Use?
The use of opiates carries a number of risks, including addiction, overdose, and death. Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior and use despite adverse consequences. Overdose can occur when too much of the drug is taken, which can lead to respiratory depression and death.
In addition to the risks associated with opiate use, there are also legal risks. Opiates are regulated by the DEA and possession of these drugs without a prescription is considered a crime. Selling or distributing opiates without a license is also illegal.
What Are the Treatment Options for Opiate Addiction?
Treatment for opiate addiction is available and effective. Treatment typically begins with detox, which is the process of removing the drug from the body. Detox can be done in a hospital, residential facility, or at home with the help of medication.
After detox, the patient will typically enter into a rehabilitation program. This program can involve individual counseling, group therapy, or a combination of both. The goal of the program is to help the patient develop healthy coping skills and learn how to manage cravings and triggers.
What Are the Prevention Strategies for Opiate Abuse?
The best way to prevent opiate abuse is to reduce the risk of addiction. This can be done by limiting access to opiates and educating people about the risks of opiate use. Health care providers can also play an important role in preventing opiate abuse by monitoring patients’ use of the drugs and providing support and education.
In addition to these strategies, it is also important to promote awareness of the dangers of opiates. This includes educating people about the risks of opiate abuse and addiction, as well as the resources available to help those struggling with addiction.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opiate Use?
The long-term effects of opiate use include physical and psychological dependence, tolerance, and organ damage. Opiate use can also lead to reduced cognitive functioning and memory problems.
Long-term use of opiates can also lead to respiratory depression, which can be fatal. In addition, long-term use of opiates can lead to hormonal imbalances, depression, anxiety, and an increased risk of infections.
Opiate use can also lead to financial problems due to the cost of the drug. In addition, legal problems can arise due to the possession and use of opiates without a prescription.
What Are the Alternatives to Opiates?
There are a number of alternatives to opiates that can be used to treat pain. These include over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as non-opioid pain medications, such as tramadol.
In addition, there are a number of alternative therapies that can be used to treat pain, such as massage, acupuncture, yoga, and meditation. These therapies can help to reduce pain without the use of drugs.
Finally, there are a number of lifestyle changes that can be made to reduce pain. These include getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are Opiates?
Opiates are a class of drugs that are derived from the poppy plant and are used to relieve pain. These drugs work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, and can produce a feeling of euphoria and relaxation. Opiates are often prescribed by doctors to treat pain, but they can also be obtained illegally and can be highly addictive and dangerous.
What Drugs are in the Opiate Family?
There are a wide variety of drugs that are in the opiate family. The most commonly known are morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, fentanyl, and methadone. Morphine and codeine are the two most widely used opiate drugs and are found naturally in the poppy plant. Oxycodone, hydrocodone, and fentanyl are synthetic opioids that are made in a lab and are often used to treat severe pain. Methadone is a synthetic opioid that is used to help individuals who are addicted to opioids to manage their withdrawal symptoms.
What are the Effects of Opiate Use?
The effects of opiate use can vary depending on the type of opiate being used, the amount of the drug taken, and the individual’s personal tolerance level. Generally, opiate drugs produce feelings of relaxation and euphoria as well as pain relief. Other effects can include sleepiness, nausea, confusion, constipation, and drowsiness. Opiate abuse can also lead to physical and psychological dependence, overdose, and death.
What are the Risks of Opiate Use?
The risks of opiate use can be serious and can include physical and psychological dependence, overdose, and death. Long-term use of opioids can lead to tolerance, meaning that the user needs more and more of the drug to feel the same effects. This can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as an increased risk of overdose. Additionally, opiates can interact with other drugs and can have dangerous and even fatal consequences.
How is Opiate Addiction Treated?
Opiate addiction is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that requires professional treatment. Treatment for opiate addiction typically involves a combination of medication and therapy. Medications, such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone, are used to help individuals manage their withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and group therapy, can help individuals understand and address the underlying causes of their addiction.
What Are the Warning Signs of Opiate Abuse?
The warning signs of opiate abuse can vary depending on the individual, but some common signs to look out for include a sudden change in behavior, such as becoming more secretive or withdrawn, a noticeable increase in mood swings, changes in sleeping and eating habits, an inability to control the amount of opiates being taken, and an increased tolerance for the drug. If these signs are present, it is important to seek help from a professional as soon as possible.
The Opioid Effect: An Ohio Family Rebuilds After Addiction
The opiate family of drugs is one of the oldest and most widely used classes of drugs in the world. They are highly effective at relieving pain, but they can have serious side effects, including addiction and overdose. Understanding the different types of drugs in the opiate family is essential to making informed decisions about their use. Knowing the risks and potential benefits of using opiates can help ensure that people make the best decisions for their own health and safety.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts