Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Opiate addiction is a serious condition that can cause devastating consequences for individuals, families, and communities. Fortunately, there are a variety of medications available to help those addicted to opiates to effectively manage their cravings and withdrawal symptoms. In this article, we will discuss the various drugs that are used to treat opiate addiction and how they can help individuals to overcome their addiction. We will also examine the potential risks and benefits of each drug and the available evidence to support their use.
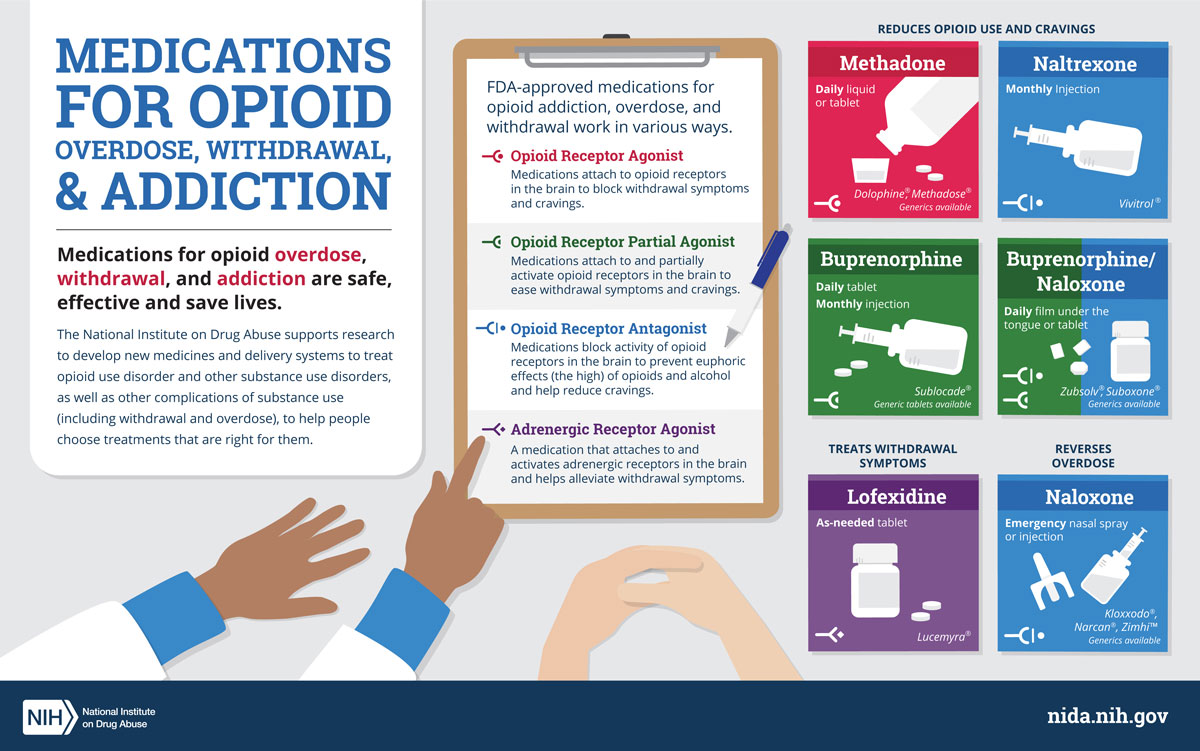
Medications used to treat opiate addiction include methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone. Methadone is a long-acting opioid agonist medication that works to reduce opioid cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist that helps to reduce cravings, while naltrexone is an opioid antagonist that blocks the effects of opioids.
Contents
Medication-Assisted Treatment for Opiate Addiction
Opiate addiction is a serious medical condition caused by the abuse of opioids, including prescription painkillers, heroin, and fentanyl. Treatment for opiate addiction involves medication-assisted treatment (MAT) and behavioral therapy. MAT is a combination of medications and therapies that help reduce the physical and psychological symptoms of opioid addiction, minimize the risk of relapse, and improve patient outcomes. The medications used in MAT are methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone.
Methadone is an opioid agonist and is used to treat opioid addiction. It works by binding to the same brain receptors as opioids and reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Methadone is usually taken in liquid form, administered in a clinic, and closely monitored by medical providers.
Methadone’s Effects on Opiate Addiction
Methadone is an effective treatment for opioid addiction because it reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, decreases the risk of relapse, and can be used in combination with counseling and other therapies. It can also reduce cravings for other drugs, including alcohol, and can help patients stay in treatment longer.
Methadone is not without risks, however. It can cause side effects, including nausea, headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, and constipation. It can also be addictive if misused and has the potential for abuse or overdose.
Buprenorphine for Opiate Addiction
Buprenorphine is an opioid partial agonist and is used to treat opioid addiction. It works by binding to the same brain receptors as opioids, but to a lesser degree, and can reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Buprenorphine is usually taken in pill or film form and is administered in a clinic or by a doctor.
Buprenorphine is an effective treatment for opioid addiction because it reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, decreases the risk of relapse, and can be used in combination with counseling and other therapies. It can also reduce cravings for other drugs, including alcohol, and can help patients stay in treatment longer.
Buprenorphine’s Effects on Opiate Addiction
Buprenorphine is an effective treatment for opioid addiction because it reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, decreases the risk of relapse, and can be used in combination with counseling and other therapies. It can also reduce cravings for other drugs, including alcohol, and can help patients stay in treatment longer.
Buprenorphine is not without risks, however. It can cause side effects, including nausea, headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, and constipation. It can also be addictive if misused and has the potential for abuse or overdose.
Naltrexone for Opiate Addiction
Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist and is used to treat opioid addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opioids on the brain and reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Naltrexone is usually taken in pill form and can be administered in a clinic or by a doctor.
Naltrexone is an effective treatment for opioid addiction because it reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, decreases the risk of relapse, and can be used in combination with counseling and other therapies. It can also reduce cravings for other drugs, including alcohol, and can help patients stay in treatment longer.
Naltrexone’s Effects on Opiate Addiction
Naltrexone is an effective treatment for opioid addiction because it reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms, decreases the risk of relapse, and can be used in combination with counseling and other therapies. It can also reduce cravings for other drugs, including alcohol, and can help patients stay in treatment longer.
Naltrexone is not without risks, however. It can cause side effects, including nausea, headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, and constipation. It can also be addictive if misused and has the potential for abuse or overdose.
Combined Medication and Behavioral Therapies for Opiate Addiction
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is a combination of medications and therapies that help reduce the physical and psychological symptoms of opioid addiction, minimize the risk of relapse, and improve patient outcomes. MAT involves medications such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone, as well as behavioral therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational interviewing (MI). These therapies help patients develop the skills and strategies to cope with triggers, cravings, and stress, and to make positive changes in their lives.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychotherapy that helps patients identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors. CBT helps patients identify and manage triggers and cravings, develop coping skills, and build confidence in their ability to stay in recovery.
Motivational Interviewing
Motivational interviewing (MI) is a form of counseling that helps patients explore and resolve ambivalence about changing their behavior. MI helps patients understand the benefits of recovery, develop commitment to their goals, and develop the skills and strategies to stay in recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Drugs Are Used to Treat Opiate Addiction?
What Is Methadone?
Methadone is a synthetic opioid medication that is used to treat opiate addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opiate drugs, reducing cravings and helping to prevent relapse. Methadone is usually prescribed in the form of a liquid or tablet, and is taken orally. It is usually taken once a day, and it can be taken for a period of up to 12 months.
What Is Buprenorphine?
Buprenorphine is a partial opioid agonist that is used to treat opiate addiction. It works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and blocking the effects of other opiates, reducing cravings and helping to prevent relapse. Buprenorphine is usually prescribed in the form of a tablet or film, and is taken orally. It is usually taken once a day, and it can be taken for a period of up to 12 months.
What Is Naltrexone?
Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist that is used to treat opiate addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opiate drugs, reducing cravings and helping to prevent relapse. Naltrexone is usually prescribed in the form of an injection or tablet, and is taken orally or injected into the muscle. It is usually taken once a day, and it can be taken for a period of up to 12 months.
What Is Suboxone?
Suboxone is a combination medication that is used to treat opiate addiction. It combines buprenorphine and naloxone, which are both opioid medications. Buprenorphine helps to block the effects of opiate drugs, while naloxone helps to prevent relapse. Suboxone is usually prescribed in the form of a film, and is taken orally. It is usually taken once a day, and it can be taken for a period of up to 12 months.
What Is Vivitrol?
Vivitrol is an extended-release formula of naltrexone that is used to treat opiate addiction. It works by blocking the effects of opiate drugs, reducing cravings and helping to prevent relapse. Vivitrol is usually prescribed in the form of an injection, and is injected into the muscle. It is usually taken once a month, and it can be taken for a period of up to 12 months.
What Is Narcan?
Narcan is a brand name for naloxone, an opioid antagonist that is used to treat opioid overdoses. It works by quickly reversing the effects of opiate drugs, allowing the person to breathe normally and preventing them from dying of an overdose. Narcan is usually prescribed in the form of a nasal spray or injection, and is administered directly to the person who has overdosed. It is usually given as soon as possible, and it can be taken for a period of up to 12 months.
What drugs are used to treat opiate use disorder?
The use of drugs to treat opiate addiction is a complex and difficult process, and requires the expertise of a physician and team of medical professionals. However, with proper treatment, opiate-addicted individuals can be successfully treated, and have the opportunity to lead healthier, happier lives. With the right combination of medications, counseling, and support, opiate addicts can begin to reclaim their lives, and move forward to a brighter future.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts