Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
We all know that there is a significant problem with drug addiction all over the world. As a result, many employers, schools, and other organizations require drug testing in order to ensure that their members are not consuming illegal substances. One of the drugs that is commonly tested for is opiates, which can be anything from heroin to prescription painkillers. But what drugs will show up as opiates on a drug test? In this article, we will discuss the different drugs that are commonly tested for and which ones will show up as opiates in a drug test.
Contents
What Drugs Test Positive for Opiates?
Opiate drug tests are used to detect the presence of one or more opiates or opiate metabolites in a person’s system. Opiates are powerful drugs derived from the opium poppy plant and can be used to treat pain, but are also highly addictive and can be abused. Commonly tested drugs that are considered opiates include heroin, oxycodone, codeine, morphine, hydrocodone, and hydromorphone.
The most common way to test for opiates is through a urine or blood sample, which will detect the presence of opiates or their metabolites, which are the chemical byproducts created by the body when it processes the drug. The test results will indicate whether a person has recently used an opiate. In some cases, a saliva or hair sample can also be used to detect the presence of opiates.
Prescription Opiates
Prescription opiates, such as oxycodone, codeine, and morphine, are commonly prescribed by doctors to treat pain. These drugs are highly addictive and can be abused, so they are monitored closely by doctors and drug testing is often used to ensure that they are being used as prescribed.
If a person tests positive for a prescription opiate, it can indicate that they are using the drug without a prescription or taking more than the prescribed dose. A positive test result could also mean that the person has recently used a drug containing a synthetic form of an opiate, such as fentanyl.
Heroin
Heroin is an illegal, highly addictive drug derived from the opium poppy plant. Heroin use is increasing in the United States, and it is one of the most commonly abused drugs. Heroin is usually injected, snorted, or smoked, and it produces a powerful high that can lead to addiction.
Heroin use can be detected through a urine or blood test, as the drug and its metabolites will show up in the test results. A positive test result can indicate recent use of heroin or other opiates, such as oxycodone or codeine.
Synthetic Opiates
Synthetic opiates, such as fentanyl, are increasingly being used as a substitute for heroin and other opiates. These drugs are more powerful than other opiates and can be more dangerous, as they can cause an overdose more easily. Synthetic opiates are usually manufactured in labs and are often mixed with other drugs, such as heroin, to increase their potency.
Synthetic opiates can be detected with a urine or blood test, just like other opiates. A positive test result can indicate recent use of fentanyl or other synthetic opiates, as well as other opiates such as heroin or oxycodone.
Over-the-Counter Opiates
Over-the-counter (OTC) opiate drugs, such as codeine, are available without a prescription and are sometimes abused. OTC opiates can be found in cough syrups and other medications, and can be detected with a urine or blood test.
A positive test result can indicate recent use of an OTC opiate or other opiate drugs, such as heroin or oxycodone. It is important to note that OTC medications containing codeine are not considered opiates, as they do not produce the same euphoric effects as other opiates.
Other Opiates
In addition to the drugs mentioned above, there are other opiates that can be detected with a urine or blood test. These include hydrocodone, hydromorphone, buprenorphine, meperidine, and tramadol.
A positive test result can indicate recent use of one or more of these drugs, as well as other opiates, such as heroin or oxycodone. It is important to note that some of these drugs, such as buprenorphine, are sometimes prescribed to treat addiction and should only be taken as prescribed.
How Long do Opiates Stay in Your System?
The length of time that opiates stay in your system depends on a variety of factors, such as the type of drug used, your age, weight, metabolism, and other health factors. Generally, opiates can be detected in urine for up to four days, in blood for up to two days, and in saliva for up to two days.
However, some opiates, such as heroin and fentanyl, can be detected in urine for up to seven days, in blood for up to four days, and in saliva for up to four days. Additionally, chronic opiate use can be detected in hair for up to 90 days.
Factors that Affect Detection Times
There are several factors that can affect the length of time that opiates stay in your system and can be detected on a drug test. These include your age, weight, metabolism, and health factors. Additionally, the type of drug used can also affect the detection time, as some drugs are more quickly metabolized than others.
Testing for Opiates
Drug tests for opiates are commonly used by employers, doctors, and law enforcement to detect the presence of one or more opiates or opiate metabolites in a person’s system. Commonly tested drugs that are considered opiates include heroin, oxycodone, codeine, morphine, hydrocodone, and hydromorphone.
The most common way to test for opiates is through a urine or blood sample, which will detect the presence of opiates or their metabolites. In some cases, a saliva or hair sample can also be used to detect the presence of opiates.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Opiate Drugs?
Opiate drugs are a type of medication derived from the opium poppy plant. Common opiate drugs include heroin, morphine, codeine, and oxycodone. These drugs are used to treat pain, but they are also highly addictive and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Additionally, opiate drugs can cause dangerous side effects, including respiratory depression and increased risk of overdose.
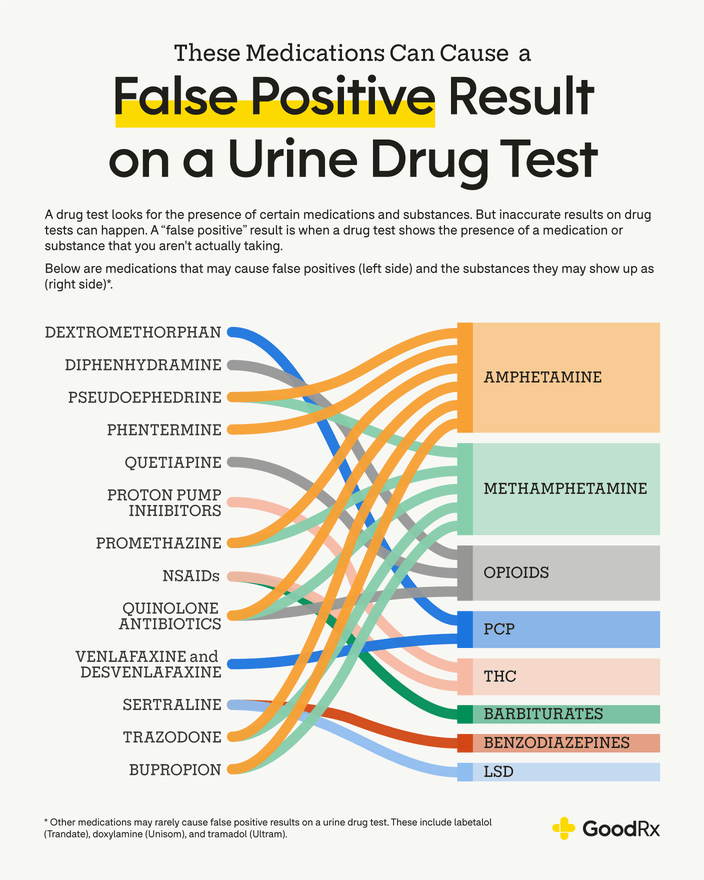
What Drugs Show Up as Opiates on a Drug Test?
Drug tests that screen for opiates typically detect the presence of morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone in the body. However, some tests may also be able to detect other opiates, such as hydromorphone, oxymorphone, and buprenorphine. Additionally, some drug tests may be able to detect synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl and tramadol.
How Accurate Are Opiate Drug Tests?
Opiate drug tests are generally accurate and reliable when they are conducted correctly. However, the accuracy of the results may be affected by factors such as the type of test that is used, how recently the drug was used, and the amount of the drug in the body.
What Is the Detection Window for Opiate Drugs?
The detection window for opiate drugs varies depending on the type of drug and how often it is used. Generally, opiate drugs can be detected in a drug test for up to three days after they are used. However, some drugs may be detectable for longer periods of time, such as codeine, which can be detected for up to four days.
What Are the Signs of Opiate Abuse?
Signs of opiate abuse include euphoria, sedation, changes in mood, impaired coordination, slowed breathing, and constricted pupils. Additionally, individuals who are abusing opiates may also suffer from physical and psychological dependence and experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking the drug.
Can Opiates Be Used Safely?
Yes, opiates can be used safely when they are prescribed by a doctor and taken as directed. It is important to take these drugs exactly as prescribed in order to avoid the risk of addiction and overdose. It is also important to talk to a doctor about any potential side effects and to never share opiate medications with others.
The Different Drug Testing Panels And What They Screen For
In conclusion, it is important to be aware of the drugs that can show up as opiates on a drug test. While there are some prescription medications that may cause a false positive for opiates, there are also many illegal drugs that can lead to a positive result. It is important to not only understand the drugs that are being looked for in a drug test but also to be aware of the laws and regulations concerning the possession and use of these drugs. Being aware of the laws and regulations can help ensure that individuals are not unknowingly putting themselves at risk of being found in violation.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts