Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Opiate addiction can be one of the most difficult addictions to break free from. Withdrawal from opiates can be unbearable and can lead to many negative physical and mental consequences. Fortunately, there are a few methods that can help ease the discomfort of opiate withdrawal and make the transition to recovery much smoother. In this article, we will explore the various methods that can be used to help with opiate withdrawal and how they can help make the process much easier.
The best way to manage opiate withdrawal is to seek professional help. Medical detox programs can provide medication to help reduce withdrawal symptoms and provide emotional support. Additionally, therapy and counseling can help individuals learn how to cope with their cravings and manage their recovery. Other methods of supporting opiate withdrawal include finding support through a 12-step program, engaging in alternative therapies such as yoga and acupuncture, and keeping a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and exercise.
Contents
- Treatment for Opiate Withdrawal
- Self-Care For Opiate Withdrawal
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What are Opiates?
- What are the Symptoms of Opiate Withdrawal?
- What are the Treatments for Opiate Withdrawal?
- What Natural Remedies can Help with Opiate Withdrawal?
- What is the Role of Exercise in Opiate Withdrawal?
- Are there Support Groups for People in Opiate Withdrawal?
- Opioid Withdrawal: What It’s Like to Detox from Opiates | MedCircle
Treatment for Opiate Withdrawal
Opiate withdrawal can be difficult, but with the right treatment, it can be managed. Treatment for opiate withdrawal can involve medications, therapies, and lifestyle changes that help lessen the severity of withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. It is important to consult a doctor to determine the best plan of treatment for each individual.
Medications
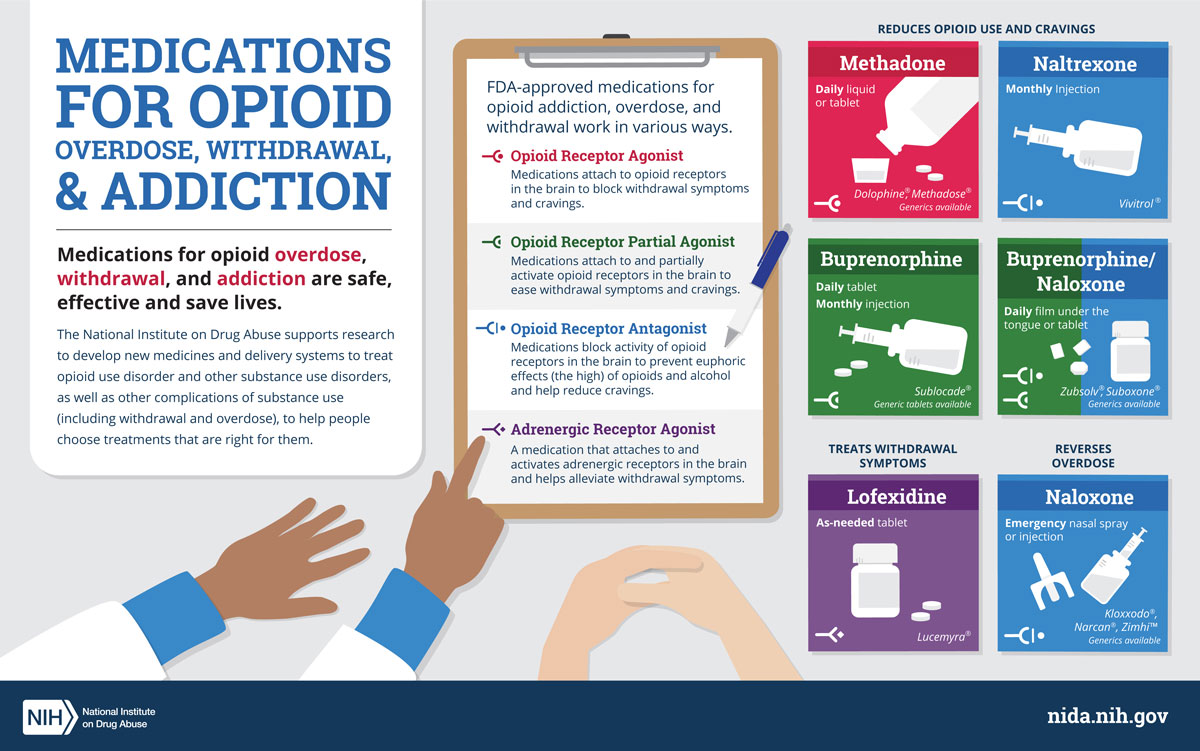
Medications are often used to help ease opiate withdrawal symptoms. The most common medications used to treat opiate withdrawal are methadone, buprenorphine, naltrexone, and clonidine. These medications can help lessen the symptoms of withdrawal, reduce cravings, and prevent relapse. It is important to consult a doctor to determine which medications may be best for each individual.
Therapies
Therapies can be an important part of treatment for opiate withdrawal. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of therapy that can help an individual identify and change negative thinking patterns and behaviors. Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is another type of therapy that can be used to help manage emotions, reduce stress, and improve relationships. Other types of therapies, such as group therapy, can provide support and help individuals cope with withdrawal symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help an individual manage opiate withdrawal. Eating a balanced diet and getting plenty of rest can help to reduce withdrawal symptoms. Exercise can also help reduce stress, improve mood, and increase energy levels. Additionally, avoiding triggers such as people or places associated with opiate use can help prevent relapse.
Self-Care For Opiate Withdrawal
Self-care is an important part of managing opiate withdrawal. Taking time to relax, journal, practice mindfulness, and engage in other activities that help reduce stress can be beneficial. Additionally, engaging in activities that are enjoyable, such as listening to music, reading, or spending time outdoors, can help to improve mood and reduce cravings.
Support Groups
Support groups can be a helpful resource for individuals going through opiate withdrawal. Participating in a support group can provide emotional support, help build motivation, and provide a safe space to talk about struggles and successes. Most support groups are facilitated by professionals who can provide guidance and resources.
Seeking Professional Help
Seeking professional help is an important part of managing opiate withdrawal. A doctor or therapist can provide individualized care and help to identify the best plan of treatment. They can also provide support and guidance for individuals as they work to manage their withdrawal symptoms.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are Opiates?
Opiates are a class of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant and are used to relieve pain. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, heroin, and hydrocodone. They can be taken orally, injected, or inhaled. Opiates are highly addictive, and withdrawal symptoms can occur when someone stops taking them.
What are the Symptoms of Opiate Withdrawal?
The symptoms of opiate withdrawal are varied and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle aches and pains, insomnia, sweating, and anxiety. More severe symptoms include abdominal cramps, fever, and goosebumps.
What are the Treatments for Opiate Withdrawal?
The most common approach to treating opiate withdrawal is to gradually reduce the dose of opiates over time. This is done in combination with medications to ease the symptoms of withdrawal and reduce cravings. Medications commonly used include methadone and buprenorphine. Inpatient detoxification may be necessary in some cases.
What Natural Remedies can Help with Opiate Withdrawal?
There are a number of natural remedies that can help with opiate withdrawal. These include getting adequate rest and sleep, eating a healthy diet, drinking plenty of fluids, and taking supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and B vitamins. Herbal remedies such as kava, passionflower, and valerian root may also help.
What is the Role of Exercise in Opiate Withdrawal?
Exercise is an important part of recovering from opiate addiction. It can help to reduce stress, improve mood, and reduce cravings. Regular exercise can also help to improve sleep and reduce anxiety. It is important to start slowly and build up gradually to avoid injury.
Are there Support Groups for People in Opiate Withdrawal?
Yes, there are support groups available for people going through opiate withdrawal. These groups provide a safe and supportive environment to discuss feelings and provide emotional support. They are also a great resource for finding resources and information on opiate addiction and withdrawal.
Opioid Withdrawal: What It’s Like to Detox from Opiates | MedCircle
Opiate withdrawal is not something to take lightly. It can be a difficult and uncomfortable experience. However, there are a number of strategies that can help to reduce the severity of symptoms. These include lifestyle changes, medications, alternative therapies, and support networks. With the right combination of treatments, you can find relief and ultimately overcome opiate withdrawal and addiction.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts