Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Tobacco has been a contentious issue for many years now. Since its inception, it has been the subject of debate, with some claiming that it is a stimulant and others arguing that it is a depressant. In this article, we will explore the science behind the effects of tobacco on the body, and whether it is truly a stimulant or depressant. By looking at the physiological effects of tobacco, we can gain insight into its overall impact on the body. So, is tobacco a stimulant or depressant? Let’s find out.
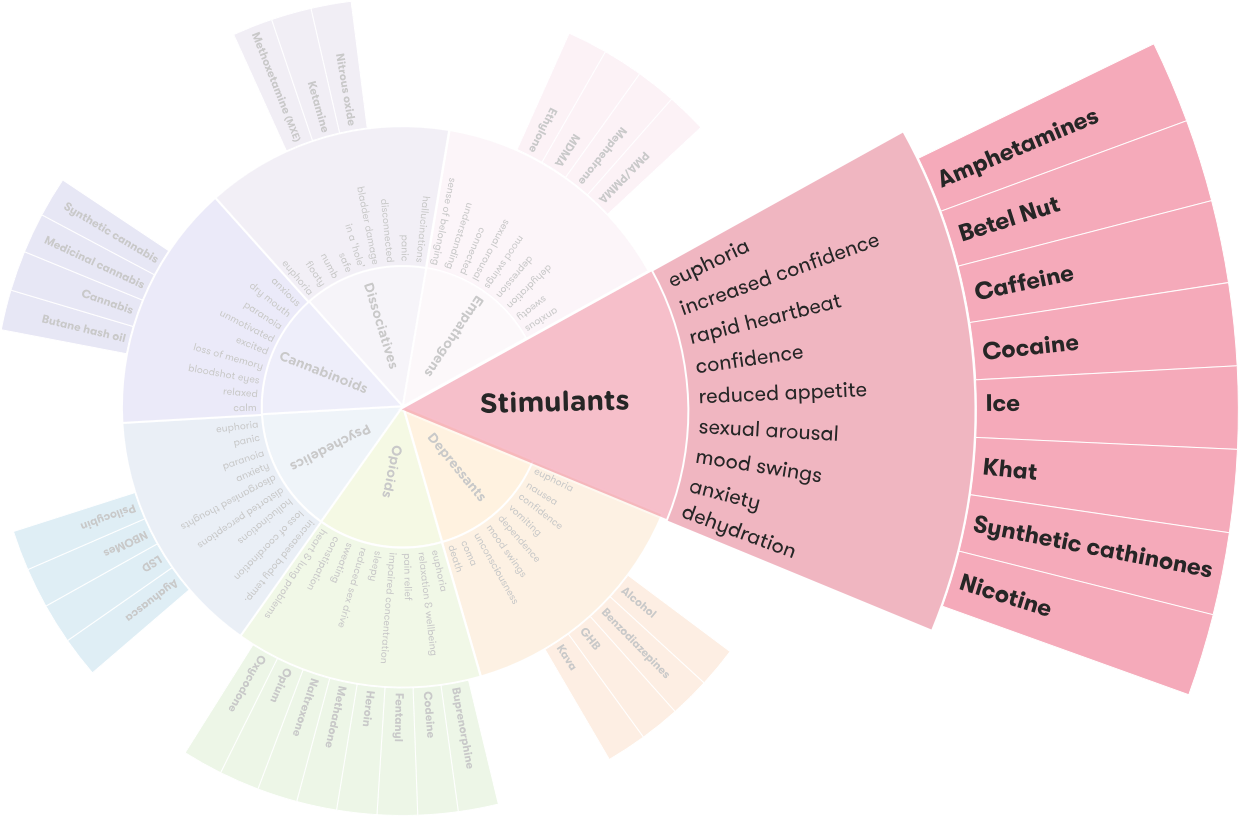
Tobacco is a stimulant. It contains the stimulant nicotine, which can increase alertness, heart rate, and blood pressure. Tobacco also contains other chemicals that can act as stimulants, such as caffeine and theobromine. Tobacco use can also lead to dependence on nicotine, which can cause withdrawal symptoms when stopped.
Contents
- Is Tobacco a Stimulant or Depressant?
- The Effects of Smoking Cigars and Pipes
- Conclusion
- Related Faq
- Question 1: Is Tobacco a Stimulant or Depressant?
- Question 2: How does Tobacco affect the body?
- Question 3: Are there any other drugs in Tobacco?
- Question 4: What are the short-term effects of Tobacco use?
- Question 5: What are the long-term effects of Tobacco use?
- Question 6: What are the alternatives to using Tobacco?
- Is nicotine a stimulant or a depressant?
Is Tobacco a Stimulant or Depressant?
Tobacco has long been used as a stimulant and depressant, depending on the kind of tobacco and the way it is consumed. Stimulants work to increase arousal, alertness, and energy, while depressants work to lower these things. As with many drugs, the effects of tobacco are complex and depend on how it is consumed.
Tobacco is most often smoked, either in cigarettes or cigars. The nicotine in cigarettes is a stimulant, and it increases alertness, heart rate, and blood pressure. It also leads to an increased release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure. The effects of nicotine may fade after just a few minutes, leading to withdrawal symptoms such as irritability and difficulty concentrating.
The Effects of Cigarette Smoking
Cigarette smoking is the most common form of tobacco consumption, and it has a variety of short- and long-term effects. In the short term, nicotine in cigarettes produces a stimulating effect, leading to improved alertness and concentration. Smokers may also experience improved mood and a sense of wellbeing. In the long term, however, smoking cigarettes leads to a variety of health problems, including increased risk of heart disease, stroke, cancer, and respiratory diseases.
The Effects of Chewing Tobacco
Chewing tobacco is another form of tobacco consumption. The nicotine in chewing tobacco is absorbed through the lining of the mouth and into the bloodstream, leading to a stimulating effect. Chewing tobacco may also have an antidepressant effect, as the nicotine can increase levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood. However, like cigarette smoking, chewing tobacco can lead to long-term health problems, including increased risk of oral cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
The Effects of Smoking Cigars and Pipes
Smoking cigars and pipes is another form of tobacco consumption. Cigars and pipes contain higher levels of nicotine than cigarettes, so they produce a more pronounced stimulating effect. In addition, smoking cigars and pipes can lead to a variety of health problems, including increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and lung cancer.
The Effects of Snuff
Snuff is a form of smokeless tobacco, and it is absorbed through the lining of the nose. The nicotine in snuff produces a stimulating effect, and it may also lead to an antidepressant effect. However, snuff can also lead to long-term health problems, including increased risk of cancer and other respiratory diseases.
The Effects of E-Cigarettes
E-cigarettes are a relatively new form of tobacco consumption, and they contain nicotine in the form of a vapor. The nicotine in e-cigarettes produces a stimulating effect, and it may also lead to an antidepressant effect. However, e-cigarettes can also lead to long-term health problems, including increased risk of cancer and other respiratory diseases.
Conclusion
Tobacco has a variety of effects on the body, depending on the form in which it is consumed. Cigarettes and cigars contain nicotine, which is a stimulant, and can lead to an increased sense of alertness and wellbeing. Chewing tobacco, snuff, and e-cigarettes also contain nicotine and produce a stimulating effect. However, all forms of tobacco use can lead to long-term health problems, including increased risk of cancer and other serious diseases.
Related Faq
Question 1: Is Tobacco a Stimulant or Depressant?
Answer: Tobacco is considered a stimulant. It contains nicotine, which is a stimulant drug that can cause alertness, increased energy levels, and increased heart rate. Nicotine also affects the brain, making it more difficult to concentrate and causing mood changes. Nicotine is highly addictive, and when consumed in large amounts, it can have a depressant effect on the body.
Question 2: How does Tobacco affect the body?
Answer: When tobacco is consumed, nicotine enters the bloodstream and travels to the brain. There, it stimulates the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is associated with pleasure and reward. Nicotine also affects the brain in other ways, causing it to become less sensitive to the effects of other drugs, such as alcohol. Tobacco also affects the lungs, heart, and immune system. Smoking can cause chronic coughing, and long-term use of tobacco is associated with an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
Question 3: Are there any other drugs in Tobacco?
Answer: Yes, in addition to nicotine, tobacco contains a variety of other drugs and chemicals, including tar, carbon monoxide, and ammonia. Tar is a black, sticky substance that coats the lungs, and it contributes to the development of lung cancer. Carbon monoxide decreases the amount of oxygen in the blood, which can lead to heart and respiratory problems. Ammonia is a toxic chemical that can irritate the lungs and cause breathing problems.
Question 4: What are the short-term effects of Tobacco use?
Answer: The short-term effects of using tobacco include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, increased alertness, and increased energy levels. Other short-term effects include increased appetite, increased risk of developing mouth and throat cancer, and increased risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
Question 5: What are the long-term effects of Tobacco use?
Answer: The long-term effects of using tobacco include an increased risk of lung cancer, coronary heart disease, stroke, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Other long-term effects include an increased risk of developing other cancers, such as throat and mouth cancer, as well as an increased risk of developing chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and other respiratory diseases.
Question 6: What are the alternatives to using Tobacco?
Answer: Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the health risks associated with tobacco use. For those who are unable to quit, there are other methods of reducing the amount of tobacco consumed, such as using nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) products, or using less-harmful forms of tobacco, such as cigars or pipes. Other alternatives include exercising, meditating, and spending time in nature, which can help to reduce stress and cravings.
Is nicotine a stimulant or a depressant?
Tobacco is a complex substance with many properties and effects on the body. As a stimulant, it can provide a pick-me-up and a burst of energy, but this can be short-lived. As a depressant, tobacco can lead to feelings of relaxation, but it can also have long-term negative effects on mental and physical health. The decision to use tobacco is not one to be taken lightly, and individuals should weigh the pros and cons before making any decisions.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts