Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Tobacco has long been a part of human culture, yet its effects on the body are still largely debated. Is tobacco a stimulant? This is an important question to consider, as the use of tobacco has been linked to health issues such as cancer, heart disease and stroke. In this article, we will explore the effects of tobacco on the body and the role of stimulation in relation to its use. We will look at the scientific evidence and discuss the potential implications of using tobacco as a stimulant.
Tobacco is a stimulant drug that contains nicotine. It is primarily used as a recreational drug and is also used as a sedative and antidepressant. Nicotine activates the brain’s reward system, leading to feelings of pleasure and improved mood. This can lead to addiction and other health risks.
However, it is important to note that while nicotine is a stimulant, it is not the only active ingredient in tobacco. Tobacco also contains other drugs, such as tar and carbon monoxide, which can be harmful to one’s health.
The use of tobacco is known to increase the risk of cancer, heart disease, and other serious health conditions. For this reason, it is important to avoid smoking or using any form of tobacco.
Contents
- What is Stimulant?
- Effects of Tobacco Stimulant
- Is Tobacco a Stimulant?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Tobacco?
- Is Tobacco a Stimulant?
- What are the Effects of Nicotine?
- What are the Health Risks Associated with Tobacco Use?
- What are the Benefits of Quitting Tobacco Use?
- What are Some Ways to Quit Using Tobacco?
- Smart drugs: All-natural brain enhancers made by mother nature | Dave Asprey | Big Think
What is Stimulant?
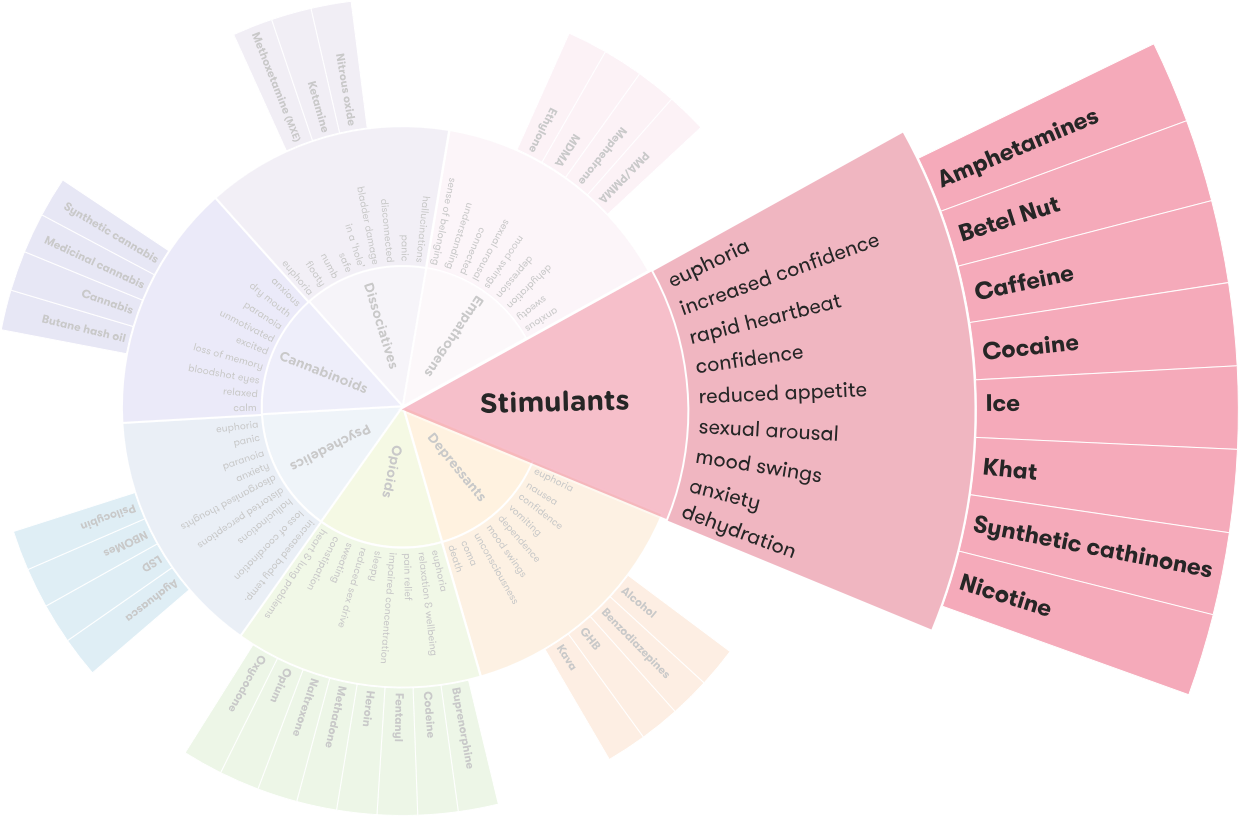
A stimulant is a drug or substance that can cause physical and mental stimulation in the body. Stimulants are usually used to increase energy, alertness, and concentration. They can also be used to improve physical performance, control appetite, or help with sleep or concentration problems. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and cocaine.
Types of Stimulants
Stimulants can be divided into two categories: natural and synthetic. Natural stimulants are those that come from plants or animals. Examples of natural stimulants include caffeine, theobromine, theophylline, and nicotine. Synthetic stimulants are those that are produced in a laboratory, such as amphetamines, cocaine, and methamphetamine.
How Does Tobacco Work as a Stimulant?
Tobacco contains nicotine, a natural stimulant. When people smoke tobacco, the nicotine is absorbed into the bloodstream and produces a stimulant effect. Nicotine increases alertness, concentration, and energy levels. It also causes a slight increase in blood pressure and heart rate, which can make a person feel more energized and awake.
Effects of Tobacco Stimulant
The effects of nicotine from tobacco can be both short-term and long-term. In the short-term, nicotine can cause a person to feel more alert, energetic, and focused. It can also lead to increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased respiration. In the long-term, nicotine can lead to addiction, increased risk of heart disease, and increased risk of cancer.
Short-Term Effects of Tobacco Stimulant
In the short-term, nicotine from tobacco can cause a person to feel more alert, energetic, and focused. Nicotine from tobacco can also cause a person to feel lightheaded, dizzy, or have a racing heart. Some people also experience a mild buzz or high from nicotine.
Long-Term Effects of Tobacco Stimulant
In the long-term, nicotine from tobacco can lead to addiction. Nicotine is a highly addictive drug, and it can be difficult to quit once a person is addicted. Nicotine can also increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, as well as increase the risk of certain types of cancer.
Is Tobacco a Stimulant?
Yes, tobacco can be considered a stimulant. Tobacco contains nicotine, a natural stimulant, which produces a stimulant effect when smoked. Nicotine can increase alertness, concentration, and energy levels. However, it can also lead to addiction, increased risk of heart disease, and increased risk of cancer.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Tobacco?
Tobacco is a plant grown for its leaves, which are smoked, chewed, or sniffed for a variety of effects. It is believed that tobacco originated in the Americas, and it has been used by many cultures for centuries. Tobacco leaves contain nicotine, which is a stimulant that acts on the central nervous system.
Is Tobacco a Stimulant?
Yes, tobacco is a stimulant. Nicotine, the main active ingredient in tobacco, is a stimulant drug that acts on the central nervous system. When tobacco is smoked, chewed, or sniffed, nicotine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and produces a variety of effects, including increased alertness and energy, as well as a feeling of relaxation.
What are the Effects of Nicotine?
Nicotine acts on the central nervous system, producing a variety of effects. These include increased alertness and energy, as well as a feeling of relaxation. Nicotine can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, and it can also cause anxiety and irritability. In addition, nicotine is highly addictive and can lead to physical dependence.
What are the Health Risks Associated with Tobacco Use?
Tobacco use can have serious health consequences. Smoking tobacco can lead to lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Chewing tobacco can lead to gum disease and mouth cancer. Long-term use of any form of tobacco can also lead to addiction, and it can be difficult to quit once addicted.
What are the Benefits of Quitting Tobacco Use?
Quitting tobacco use can have a number of benefits. After quitting, the risk of developing certain types of cancer and other health problems decreases. Quitting can also lead to an overall improvement in health, including better sleep, improved lung function, and a decrease in stress.
What are Some Ways to Quit Using Tobacco?
There are a number of ways to quit using tobacco. Quitting cold turkey is one option, although it can be difficult. Other options include using nicotine replacement therapy, such as patches or gum, or using medications, such as bupropion or varenicline. Counseling and support groups can also be helpful in quitting.
Smart drugs: All-natural brain enhancers made by mother nature | Dave Asprey | Big Think
Tobacco is a highly addictive substance that has been linked to numerous health issues and is considered a stimulant. There is no doubt that tobacco is a dangerous and harmful substance. However, it is important to remember that it is up to the individual to make their own decisions about the use of tobacco. While it is not recommended, it is ultimately the individual’s responsibility to weigh the risks and benefits of using tobacco and make an educated decision.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts