Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Stimulants are substances that can increase alertness, energy, and focus. For many people, stimulants are a part of everyday life. But how do these substances work? In this article, we will explore the science behind stimulants and discuss how they affect the body and mind. We will also look at the potential risks associated with using stimulants. With this knowledge, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions about their use. Let’s get started!
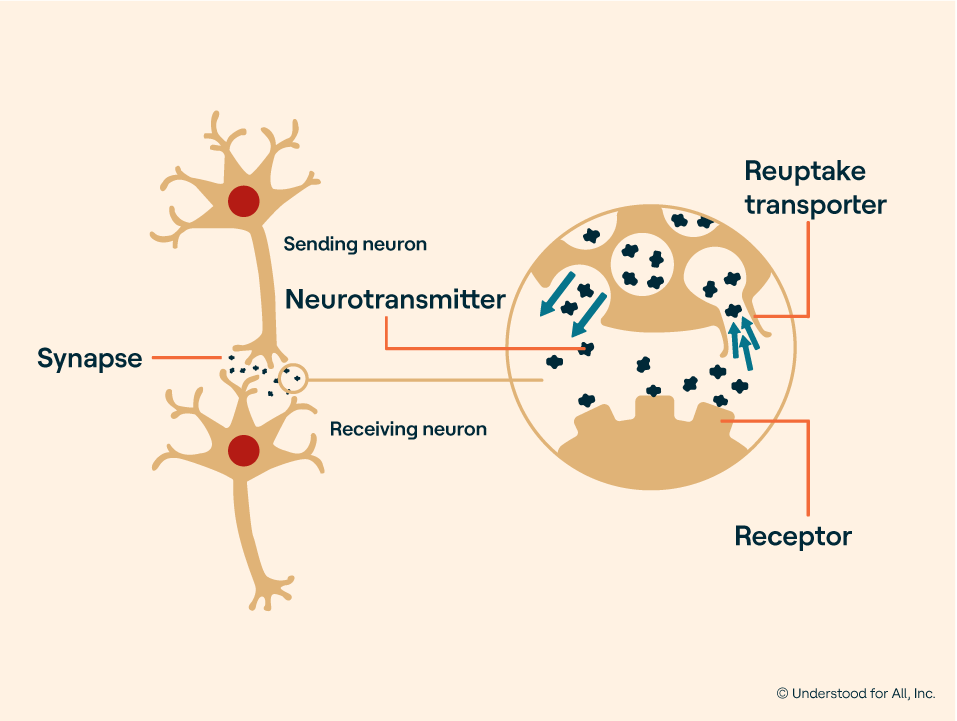
Stimulants work by increasing the level of neurotransmitters like dopamine, epinephrine, and norepinephrine in the brain. This action increases alertness, attention, and energy, while decreasing the need for sleep. Stimulants can improve memory and focus, while also reducing fatigue and irritability.
Stimulants have been used to treat ADHD, narcolepsy, and depression. They can also be used to treat chronic fatigue syndrome, and some types of learning disabilities. Stimulants can help improve concentration, focus, and motivation.
Contents
What Are Stimulants?
Stimulants are drugs or substances that increase mental and physical energy, alertness, and concentration. They are often used to treat conditions such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Stimulants can also be used recreationally to increase energy, alertness, and euphoria. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines, such as Adderall and Ritalin.
How Stimulants Work on the Brain
Stimulants work by increasing the activity of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure and reward, and norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that is associated with alertness and focus. Stimulants increase the amount of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to feelings of pleasure, alertness, and focus.
Short and Long-Term Effects of Stimulants
Stimulants can produce both short-term and long-term effects. Short-term effects include increased alertness, energy, focus, and euphoria. Long-term effects can include changes in brain chemistry, increased tolerance, and dependence. Stimulants can also lead to physical side effects, such as insomnia, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and weight loss.
Types of Stimulants
Stimulants can be divided into two categories: legal and illegal. Legal stimulants include caffeine and nicotine, which are found in coffee, tea, and cigarettes. Illegal stimulants include amphetamines, such as Adderall and Ritalin, and cocaine.
Legal Stimulants
Caffeine is the most widely used legal stimulant. It is found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and even chocolate. Caffeine works by blocking the action of adenosine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with sleepiness. Caffeine can increase alertness, energy, and focus, and can also improve mood.
Nicotine is another legal stimulant that is found in cigarettes and other tobacco products. Nicotine works by increasing the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to feelings of pleasure and focus.
Illegal Stimulants
Amphetamines are illegal stimulants that are often used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. Amphetamines work by increasing the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to feelings of pleasure, alertness, and focus.
Cocaine is an illegal stimulant that is derived from the coca plant. It works by increasing the release of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, leading to feelings of euphoria, alertness, and focus.
Risks of Stimulant Use
Stimulants can be dangerous if used in excess or if used without supervision. Stimulants can lead to physical side effects, such as insomnia, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and weight loss. They can also lead to psychological side effects, such as mood swings, anxiety, and paranoia. Stimulants can also lead to addiction and dependence.
Physical Risks
Stimulants can have physical side effects, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, insomnia, and weight loss. Long-term use of stimulants can lead to serious health problems, such as heart disease and stroke.
Psychological Risks
Long-term use of stimulants can lead to psychological side effects, such as mood swings, anxiety, and paranoia. Stimulants can also lead to addiction and dependence.
Conclusion
Stimulants are drugs or substances that increase mental and physical energy, alertness, and concentration. Stimulants work by increasing the activity of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. Stimulants can produce both short-term and long-term effects, such as increased alertness, energy, focus, and euphoria. Stimulants can be divided into two categories: legal and illegal. Legal stimulants include caffeine and nicotine, while illegal stimulants include amphetamines, such as Adderall and Ritalin, and cocaine. Stimulants can be dangerous if used in excess or if used without supervision, and can lead to physical and psychological side effects, such as insomnia, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and addiction.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What are Stimulants?
Stimulants are drugs that increase alertness, attention, and energy. They are also known as “uppers” as they increase dopamine and norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters that regulate mood and motivation. Stimulants can come in many forms, including caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and cocaine. They can be found in both legal and illegal forms.
How do Stimulants Work?
Stimulants work by increasing the activity of the central nervous system, specifically the dopamine and norepinephrine neurotransmitters. When these neurotransmitters are activated, they increase alertness, attention, and energy. Stimulants can also increase heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration, as well as cause feelings of euphoria.
Are Stimulants Addictive?
Yes, stimulants can be addictive. Stimulants are known to create a “high” that can lead to abuse and dependence. Over time, the body becomes tolerant to the drug, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect. This can be dangerous, as stimulants can have serious side effects such as insomnia, irritability, and anxiety.
What are the Side Effects of Stimulants?
The side effects of stimulants vary depending on the type and dose of the drug taken. Common side effects include insomnia, irritability, anxiety, increased heart rate, high blood pressure, and increased respiratory rate. Long-term use of stimulants can also lead to psychological and physical dependence.
How Can Stimulant Abuse be Treated?
Treatment for stimulant abuse typically involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. Medications can help reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms, while psychotherapy can help individuals understand and manage their motivations for using stimulants. Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and developing healthy coping skills, can also help people recovering from stimulant abuse.
What is the Long-Term Outlook for Stimulant Abuse?
The long-term outlook for people recovering from stimulant abuse is optimistic. With proper treatment, individuals can learn to manage their cravings and develop healthier coping skills. Recovery is a process that takes time, but with effort and dedication, individuals can achieve lasting sobriety and improved quality of life.
Why Stimulants Help ADHD
In conclusion, stimulants are a type of medication that work to enhance the body’s central nervous system, allowing the body to become more alert and active. Stimulants act on the brain specifically, triggering an increase in neurotransmitters, like dopamine and norepinephrine, which are responsible for increasing focus and alertness. While stimulants are most commonly used to treat conditions such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), they can also be used to treat certain mental health conditions and narcolepsy. Stimulants are powerful drugs that should be used only under the supervision of a medical professional.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts