Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Stimulants have been used to increase alertness and productivity for centuries, but do they come with a risk of addiction? In this article, we’ll explore the potential for stimulant addiction and what you should know if you’re considering taking them. From the dangers of addiction to the potential benefits, we’ll uncover the truth about stimulants and their effects on the body.
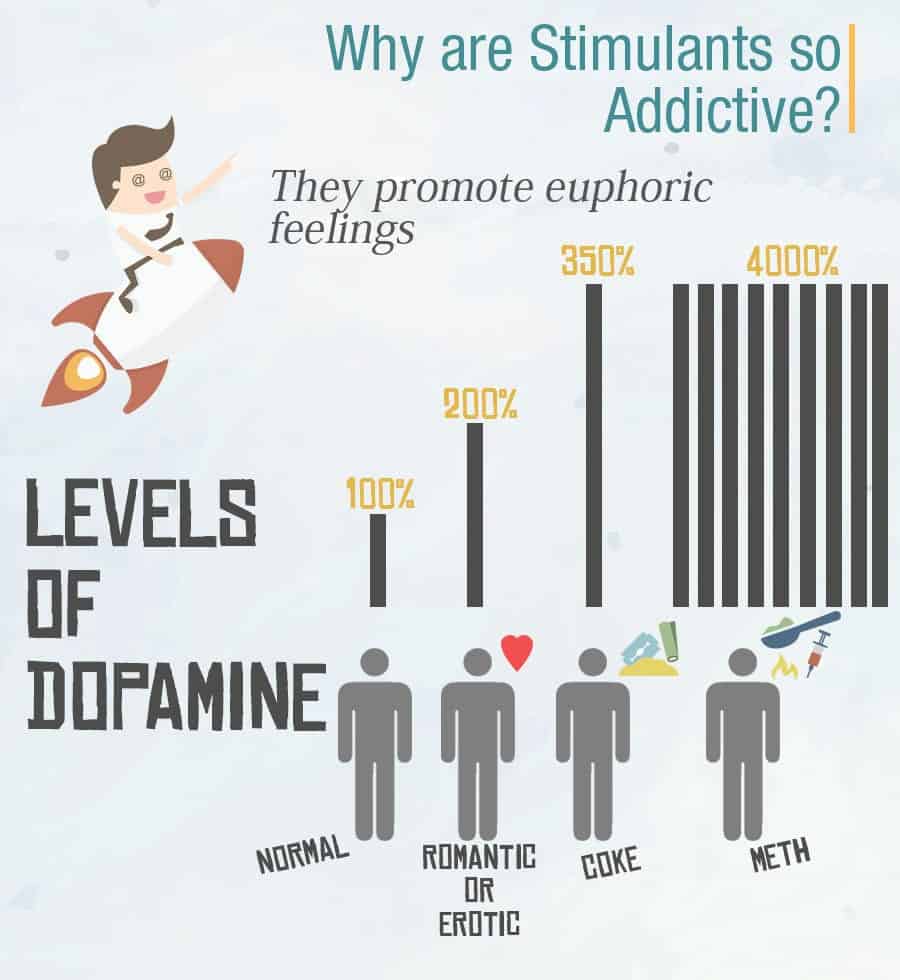
Yes, stimulants can be addictive when they are abused. Stimulants increase dopamine levels in the brain, creating feelings of pleasure. Over time, the brain may become dependent on the drug to achieve these feelings, leading to addiction.
Contents
Are Stimulants Addictive?
What Are Stimulants?
Stimulants are drugs that increase alertness, attention, and energy. These drugs are used to treat conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. Stimulants can be prescribed medications, such as Ritalin or Adderall, or they can be illegal drugs, such as cocaine or methamphetamine. Stimulants increase the activity of noradrenaline, dopamine, and serotonin in the brain, which can lead to feelings of euphoria, alertness, and increased energy.
Prescription Stimulants
Prescription stimulants are commonly used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. These medications can be effective in treating the symptoms of these conditions, but they can also be addictive. Some of the most commonly abused prescription stimulants are Adderall and Ritalin. These drugs can cause physical and psychological dependence and can be difficult to quit.
Illegal Stimulants
Illegal stimulants, such as cocaine and methamphetamine, are highly addictive and can have severe physical and psychological side effects. These drugs can cause intense cravings and can be difficult to stop using. Cocaine and methamphetamine are also extremely dangerous and can lead to serious health complications and even death.
The Effects Of Stimulant Abuse
Stimulants can have a range of short-term and long-term effects. Short-term effects may include increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased body temperature. Long-term effects may include changes in mental health, such as anxiety and depression, and physical health problems, such as heart disease and stroke.
The Risk Of Addiction
Stimulants can be addictive, even when taken as prescribed. People who misuse stimulants are at an increased risk of developing an addiction. Signs of addiction include changes in behavior, such as lying or stealing to get the drug, and physical symptoms, such as increased tolerance or withdrawal.
Treatment For Stimulant Addiction
Stimulant addiction is a serious condition and requires professional treatment. Treatment usually involves a combination of medication and counseling. Medication can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while counseling can help identify and address the underlying causes of addiction.
Preventing Stimulant Abuse
The best way to prevent stimulant abuse is to be aware of the risks associated with these drugs and to avoid taking them without a prescription. If you are prescribed stimulants, make sure to take them as prescribed and to talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
Educating Others
It’s important to educate yourself and others about the risks of stimulant abuse. Talking to friends and family members about the dangers of stimulants can help prevent abuse. Additionally, talking to young people about the risks of taking stimulants without a prescription is essential to help prevent substance abuse.
Seeking Help
If you or someone you know is struggling with stimulant abuse, it’s important to seek help. Treatment programs can help people with stimulant addiction to get back on track and recover. Treatment should be tailored to the individual and may include medication, counseling, and lifestyle changes.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Are Stimulants?
A1. Stimulants are a type of drug that increases activity in the central nervous system, leading to increased alertness, energy, and focus. Stimulants are typically used to treat conditions such as ADD/ADHD, narcolepsy, and obesity. Common stimulants include amphetamines (Adderall, Ritalin), caffeine, nicotine, and cocaine.
Q2. Are Stimulants Addictive?
A2. Yes, stimulants can be addictive. Stimulants can produce feelings of pleasure and euphoria, leading to increased use and abuse. People who use stimulants for a prolonged period of time can develop physical and psychological dependence, which can lead to addiction.
Q3. What Are the Signs of Stimulant Addiction?
A3. Signs of stimulant addiction can include changes in behavior, such as isolation, mood swings, and irritability; physical changes, such as weight loss or changes in sleeping patterns; and financial or legal problems. Other signs of addiction include cravings for the drug and an inability to control how much of the drug is being used.
Q4. What Are the Risks of Stimulant Abuse?
A4. Stimulant abuse can lead to a range of serious health issues, including heart attack, stroke, and seizures. Other risks include increased risk for mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and paranoia. Stimulant abuse can also lead to physical dependence and addiction.
Q5. How Is Stimulant Addiction Treated?
A5. Stimulant addiction is typically treated with a combination of medication, counseling, and lifestyle changes. Medications can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while counseling can help address underlying mental health issues. Lifestyle changes, such as improving diet and exercise, can help reduce cravings and improve overall health.
Q6. What Are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Addiction?
A6. Long-term effects of stimulant addiction can include physical and mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and paranoia. Stimulant addiction can also lead to financial and legal issues, as well as strained relationships with family and friends. Long-term use can also lead to tolerance, meaning more of the drug is needed to achieve the same effects.
Stimulants: Everything You Should Know
The answer to the question of whether stimulants are addictive is a resounding yes. Stimulants can cause physical and psychological dependence, lead to addiction, and be difficult to quit. While stimulants can be beneficial in many ways, they should always be used with caution and under the supervision of a qualified medical professional. Ultimately, when it comes to stimulants, the risks of addiction can be significant and should be taken into consideration before beginning any type of stimulant regimen.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts