Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Nicotine is one of the most widely used and abused drugs in the world. Although it is widely known for its addictive properties, the exact nature of what makes nicotine so addictive is still unknown. Nicotine addiction is caused by a variety of factors, such as its effects on the brain, the rewarding and reinforcing properties it possesses, and its easy accessibility.
Contents
- How Much Nicotine Does It Take To Get Addicted?
- Is Nicotine Actually Addictive?
- Is Nicotine Physically Or Mentally Addictive?
- Why Do Smokers Crave Nicotine?
- Smokeless Tobacco
- Cigarette
- Cigars & Cigarillos
- Beedi
- See More
- Feedback
- How Long Does It Take To Get Addicted To Nicotine
- Why Am I Not Addicted To Nicotine
How Much Nicotine Does It Take To Get Addicted?
It is difficult to determine exactly how much nicotine it takes to become addicted because everyone’s body responds differently to nicotine. However, research has shown that it generally takes about three to four weeks for a person to become addicted to nicotine after regular use.
Nicotine is a powerful stimulant and is found in tobacco products such as cigarettes and chewing tobacco. It is highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence. When nicotine is inhaled, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, where it binds to receptors in the brain and stimulates the release of neurotransmitters. This triggers a number of physiological effects, including an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as well as an increase in alertness and energy.
Heavy smokers and more frequent users of tobacco products are more likely to become addicted to nicotine faster than occasional smokers. People who are more sensitive to nicotine may also become addicted more quickly. Additionally, certain genetic factors can increase the risk of addiction. People with a family history of addiction are more likely to become addicted to nicotine.
Overall, it is difficult to determine exactly how much nicotine it takes to become addicted. However, research has shown that it generally takes about three to four weeks for a person to become addicted to nicotine after regular use. Heavy smokers and more frequent users of tobacco products are more likely to become addicted to nicotine faster than occasional smokers. People who are more sensitive to nicotine may also become addicted more quickly. Additionally, certain genetic factors can increase the risk of addiction.
Is Nicotine Actually Addictive?
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance found in tobacco products. It is responsible for many of the adverse health effects associated with smoking. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that tobacco use kills up to half a million people each year.
Nicotine is a stimulant that affects the brain, heart, and lungs. It triggers the release of the chemical dopamine, which produces a feeling of pleasure and relaxation. Over time, users develop a tolerance to nicotine, requiring more and more of it to get the same effect. This can lead to addiction, making it difficult to quit.
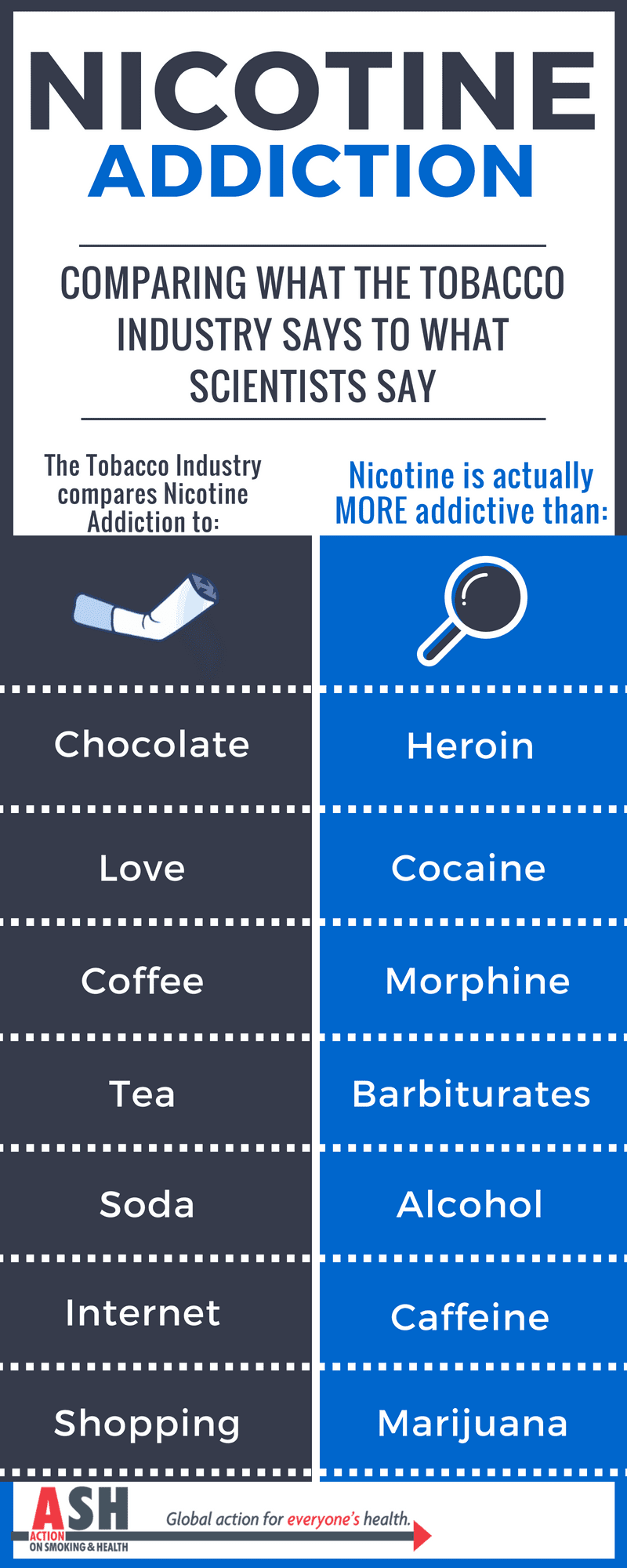
Studies have shown that nicotine is as addictive as heroin and cocaine. Withdrawal symptoms can include irritability, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, and cravings for cigarettes. The best way to quit smoking is to seek help from a healthcare provider who can provide nicotine replacement therapy or other medications to help reduce cravings. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health and decrease your risk of developing cancers or other diseases.
Is Nicotine Physically Or Mentally Addictive?
Nicotine is one of the most widely used and abused drugs in the world. It is widely known as the active ingredient in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. Nicotine is highly addictive and can have both physical and mental effects on the body.
Physically, nicotine is absorbed through the lungs when smoking, or through the mucous membrane of the mouth when chewing tobacco. It is then quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, affecting the central nervous system. Nicotine increases levels of dopamine and other chemicals in the brain, resulting in a feeling of pleasure and satisfaction. This feeling of pleasure also causes physical addiction, as the body begins to crave more nicotine in order to maintain a feeling of pleasure. Over time, the body builds up a tolerance to nicotine, requiring more and more nicotine to achieve the same effect.
Mentally, nicotine can have a powerful effect on the user. Nicotine stimulates the release of epinephrine, which creates a feeling of alertness and focus. This can be beneficial in some situations, but it can also lead to an increased risk of anxiety and depression. Nicotine also affects the brain’s reward system, leading to a feeling of pleasure and satisfaction when nicotine is consumed. This feeling can also lead to psychological addiction, as the brain begins to crave more nicotine in order to maintain this pleasure.
Overall, nicotine is both physically and mentally addictive. It is important to remember that nicotine addiction is a serious problem and should be treated as such. If you or someone you know is struggling with nicotine addiction, it is important to seek professional help.
Why Do Smokers Crave Nicotine?
Smoking is a habit that many people have difficulty quitting. One of the most powerful aspects of smoking is nicotine, which is the addictive substance in cigarettes. Nicotine is responsible for many of the cravings that smokers experience and can be difficult to resist. Understanding why smokers crave nicotine can help people to better manage their cravings and quit smoking.
Nicotine affects the brain in a way that makes it highly addictive. When nicotine enters the brain it triggers the release of a chemical called dopamine. Dopamine is often referred to as the “feel good” chemical as it causes a feeling of pleasure and relaxation. This feeling is short lived, however, and as the dopamine levels drop, smokers begin to experience cravings for another cigarette in order to “top up” their dopamine levels and experience the pleasure again.
Over time, smoking can lead to a physical dependency on nicotine, which can make it difficult to quit. The body becomes used to the presence of nicotine and begins to expect it, leading to withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety and irritability when a smoker attempts to quit. This is why many smokers find quitting much more difficult than expected.
In order to successfully quit smoking, it is important to understand why smokers crave nicotine and the effects it has on the body. Quitting smoking is a difficult process and requires dedication and perseverance. However, with the right support and motivation, it is possible to break the addiction and lead a healthier and happier life.
Smokeless Tobacco
Smokeless tobacco is also known as “spit tobacco” and its use has been increasing in recent years. It is a form of nicotine delivery that does not involve burning and inhaling smoke. This makes it attractive to those who want to avoid the risks associated with smoking. Despite this, smokeless tobacco is still addictive and can be just as dangerous as smoking.
The main active ingredient in smokeless tobacco is nicotine. Nicotine is a highly addictive substance that stimulates the reward center in the brain. This is why nicotine is so addictive, as it creates a feeling of satisfaction and pleasure when used. Smokeless tobacco also contains hundreds of other chemicals, some of which are known to be carcinogenic. This is why it is important to be aware of the risks associated with smokeless tobacco and to seek medical advice if you are concerned about your health.
Cigarette
Cigarette smoking is one of the most common forms of tobacco use. It contains nicotine, a chemical that is known to be highly addictive. Nicotine is both physically and psychologically addictive because it stimulates the release of dopamine in the brain, resulting in a feeling of pleasure and relaxation. This reward pathway is what makes nicotine addictive, as it reinforces the behavior of smoking.
The addictive properties of nicotine are further increased by the fact that it quickly enters the bloodstream and is rapidly removed from the body. This means that the user experiences a “crash” when their nicotine levels drop, and the cravings for more nicotine become stronger. Additionally, nicotine has a high tolerance level, so smokers need to increase their dose over time in order to achieve the same high. This further increases the user’s dependence on cigarettes.
Cigars & Cigarillos
Nicotine is the main active chemical in cigars and cigarillos, and it is what makes them addictive. Nicotine is a stimulant and it can have a variety of effects on the body, including increasing alertness, boosting energy levels, and improving mood. It also acts as a depressant, reducing stress and anxiety. When nicotine is inhaled, it reaches the bloodstream quickly, and its effects can last up to several hours.
Most people become addicted to nicotine due to its psychoactive effects. The nicotine in cigars and cigarillos causes a release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of pleasure and reward. This can lead to a habit of smoking as a way to get a rush of dopamine. Additionally, nicotine has physical effects that contribute to its addictiveness. It increases heart rate, respiration, and blood pressure, and it can also be calming, leading to a feeling of relaxation. With long-term use, the body develops a dependence on nicotine and can experience withdrawal symptoms when deprived of it.
Beedi
Beedi is a type of cigarette common in India and other parts of Asia. It is made of a mixture of tobacco and other ingredients such as cloves and cardamom. Beedis contain more nicotine than regular cigarettes, which makes them more addictive. This is due to the way in which nicotine is absorbed by the body. When nicotine is inhaled through smoking, it is absorbed by the lungs and then rapidly enters the bloodstream. This causes the brain to release dopamine, which produces feelings of pleasure and satisfaction.
Nicotine addiction is a physical and psychological dependence on nicotine, which makes it difficult to stop smoking. The physical dependence is caused by the body’s need for nicotine to maintain its normal functioning. The psychological dependence is caused by the effects of nicotine on the brain, which cause the smoker to feel pleasure and satisfaction when smoking. This feeling of pleasure and satisfaction reinforces the desire to smoke and keeps the smoker addicted.
See More
Nicotine is an addictive substance found in tobacco products such as cigarettes, cigars, snuff and chewing tobacco. People who use nicotine experience a wide range of physical and psychological effects, including feelings of pleasure, relaxation and alertness. The addictive properties of nicotine are due to its ability to act on the brain’s reward system and stimulate the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which can lead to pleasure and relaxation.
Nicotine can be absorbed through the skin, lungs, and digestive system, making it easy to become addicted. Research has shown that nicotine is as addictive as alcohol and cocaine, and it can be even harder to quit than those drugs. Nicotine activates the brain’s reward system, making it difficult to break the addiction. It also increases the level of dopamine in the brain, which is the same chemical released when people use other drugs, such as cocaine and heroin. Nicotine also has the ability to increase the release of other neurotransmitters like serotonin and endorphins, which can lead to feelings of pleasure and relaxation. Additionally, nicotine increases heart rate and blood pressure, which can make people feel more energized.
The effects of nicotine addiction can be devastating. Nicotine is linked to a range of serious health problems, including cancer, heart disease, stroke, and lung disease. It can also lead to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the risks associated with nicotine addiction.
Feedback
The main factor that makes nicotine addictive is the feedback loop it creates in the brain. When nicotine is consumed, it triggers the release of dopamine, which is a natural reward chemical. This creates a pleasurable feeling, which encourages the user to consume more nicotine and repeat the cycle. In addition, nicotine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and produces a calming effect. This makes it difficult for those that are addicted to nicotine to quit as the withdrawal effects can be too difficult to bear.
Apart from the psychological effects, nicotine also has physical effects on the body. Nicotine can increase heart rate, raise blood pressure, and constrict blood vessels. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Additionally, nicotine can also disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and insomnia.
Overall, nicotine produces a wide range of effects, both psychological and physical, that contribute to its addictive properties. The effects of nicotine are powerful, and it can be difficult for those who are addicted to quit. However, with the right support and a strong will to quit, it is possible to break the cycle of nicotine addiction and lead a healthier life.
How Long Does It Take To Get Addicted To Nicotine
Nicotine is one of the most addictive substances known to humans and is found in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. The exact amount of time it takes to become addicted to nicotine varies from person to person, but it can take as little as two weeks for someone to become dependent on the drug. In general, nicotine addiction develops quickly and can be difficult to break.
When nicotine is ingested, it binds to receptors in the brain, resulting in the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that causes feelings of pleasure. The constant release of dopamine encourages people to continue using nicotine, and over time, the brain develops a tolerance to the drug. This means that people must use more nicotine in order to achieve the same pleasurable effects. As people begin to rely on nicotine to feel good, they become physically and psychologically dependent on the drug, and it quickly becomes a habit.
The best way to avoid becoming addicted to nicotine is to avoid tobacco products altogether. If you have already begun using nicotine and are trying to quit, seek help from healthcare professionals or support groups. Quitting nicotine can be difficult, but it is possible and the health benefits are worth the effort.
Why Am I Not Addicted To Nicotine
Nicotine is the primary addictive substance in tobacco products, and it is responsible for the intense craving and compulsive use that characterizes tobacco addiction. Nicotine triggers the release of dopamine, a chemical in the brain associated with pleasure, reward and motivation. It also activates the brain’s “reward system” and floods it with pleasure-inducing chemicals, such as serotonin and endorphins. This reward system reinforces the behavior, making it difficult to quit smoking.
The body quickly builds up a tolerance to nicotine, so people need to smoke more over time to get the same effects they experienced before. Additionally, the body can become physically dependent on nicotine, making it difficult to quit without experiencing withdrawal symptoms such as cravings, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. The combination of psychological and physical addiction makes it challenging to quit smoking, but not impossible.
How do you know if you’re addicted to Nicotine
In conclusion, nicotine is a highly addictive substance that can cause serious physical and mental health issues. It is one of the most addictive drugs available, and it is important to understand why so that you can make an informed decision about whether or not to use it. Nicotine is a powerful stimulant that affects the brain and body in ways that make it extremely difficult to quit, and it can be extremely difficult for those who are addicted to break the cycle of addiction. Understanding the addictive properties of nicotine is essential for anyone considering using it, and it is important to remember that it can have devastating consequences if used in excess.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts