Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Opioid addiction has become a major problem in our society. It affects people of all ages and backgrounds and can have devastating consequences. Despite the prevalence of opioid addiction, there is still a lot of misunderstanding about how best to treat it. In this article, we will explore the different options available for treating opioid addiction and discuss the importance of seeking professional help. We’ll also look at the importance of creating an individualized treatment plan that is tailored to the needs of the person struggling with opioid addiction. Finally, we will discuss the importance of long-term support and follow-up care to ensure successful recovery.
Opioid addiction is a serious condition that requires professional treatment and support. Treatment typically includes counseling, medication, and lifestyle changes. It may also involve support groups, family therapy, and alternative therapies.
- Step 1:Find a qualified doctor or treatment center to develop an individualized treatment plan.
- Step 2:Undergo detoxification, if necessary. This may involve medications to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
- Step 3:Participate in counseling and/or support groups to help build a support system and identify triggers for opioid use.
- Step 4:Take medications, if prescribed, to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms and help with long-term recovery.
- Step 5:Adopt lifestyle changes to help with recovery, such as exercising, eating healthy, and avoiding triggers.
Contents
Understanding Opioid Addiction
Opioid addiction is a serious condition that requires professional medical attention. Millions of people around the world suffer from this debilitating disorder, which is characterized by an uncontrollable craving for opioids and an inability to stop using them despite the negative consequences. Opioid addiction is a complex disorder and can be difficult to treat. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatments for opioid addiction in order to effectively manage it.
The most common cause of opioid addiction is the use of prescription painkillers. People who are prescribed opioids for chronic pain may become dependent on them in order to cope with their pain. Other causes of opioid addiction include recreational use, self-medicating for mental health issues, and using opioids to cope with stress.
The symptoms of opioid addiction include an intense craving for opioids, increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms when not using opioids, and problems with relationships, work, and finances due to opioid use. It is important to recognize the signs of opioid addiction in order to seek treatment.
Treatment Options for Opioid Addiction
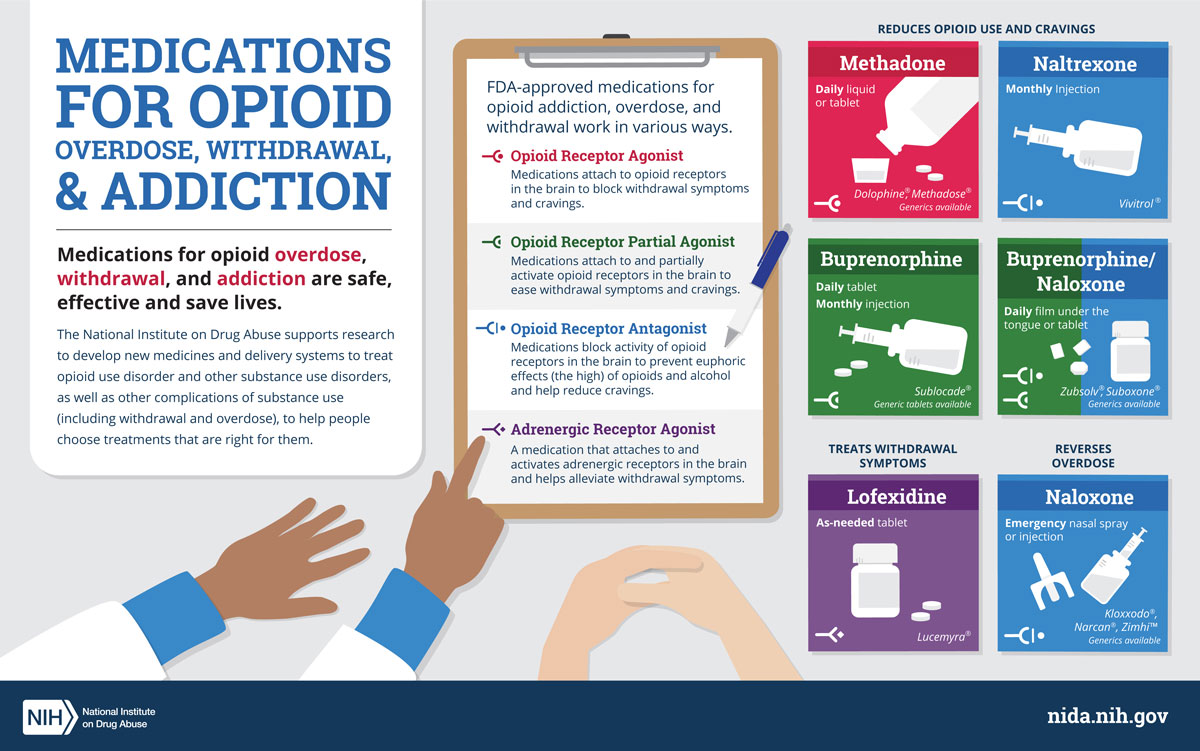
The most effective treatment for opioid addiction is a comprehensive approach that includes medication, counseling, and support groups. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is the use of medications such as buprenorphine and naltrexone to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Counseling can help individuals learn to cope with their addiction, understand the consequences of their actions, and develop healthy coping skills. Support groups provide an opportunity for individuals to share their experiences and receive support from others in similar situations.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is the use of medications to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Buprenorphine and naltrexone are two medications that are commonly used to treat opioid addiction. Buprenorphine is an opioid agonist, meaning it binds to opioid receptors in the brain and reduces cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Naltrexone is an opioid antagonist, meaning it blocks opioid receptors and prevents individuals from feeling the effects of opioids.
Individual and Group Counseling
Individual and group counseling can help individuals with opioid addiction learn to cope with their addiction, understand the consequences of their actions, and develop healthy coping skills. Individual counseling can help individuals identify triggers and develop strategies to cope with cravings and manage stress. Group counseling can provide a supportive environment for individuals to share their experiences and receive feedback from other group members.
Alternative Treatments for Opioid Addiction
In addition to medication-assisted treatment and counseling, there are several alternative treatments that can be used to treat opioid addiction. Exercise, yoga, and meditation can help individuals reduce stress and cope with cravings. Acupuncture, massage, and biofeedback can also help to reduce stress and improve mental health.
Exercise, Yoga, and Meditation
Exercise, yoga, and meditation are effective ways to reduce stress and cope with cravings. Exercise can help to release endorphins, which can reduce stress and improve mood. Yoga helps to improve flexibility and reduce stress, while meditation can help to clear the mind and reduce anxiety.
Acupuncture, Massage, and Biofeedback
Acupuncture, massage, and biofeedback are alternative treatments that can be used to reduce stress and improve mental health. Acupuncture can help to reduce stress and relieve pain, while massage can help to relax tense muscles and reduce stress. Biofeedback can help individuals become aware of their body’s reactions to stress and learn to control them.
Supportive Resources
In addition to professional medical treatment, there are a number of supportive resources available to individuals with opioid addiction. Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous, can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to share their experiences and receive support from others in similar situations. There are also online resources and helplines that can provide information and support for individuals with opioid addiction.
Related Faq
1. What is opioid addiction?
Opioid addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder where a person compulsively seeks and uses opioids, despite the harm it causes to their life and relationships. Opioid addiction is caused by changes in the brain’s reward and motivation systems, which are caused by the misuse of opioids. Opioids are a class of drugs that include prescription pain relievers, such as oxycodone, hydrocodone, codeine, and morphine, as well as illegal drugs like heroin.
2. What are the signs of opioid addiction?
The signs of opioid addiction can vary from person to person, but some common signs include: taking higher doses of opioids than prescribed; taking opioids for longer than prescribed; spending large amounts of money on opioids; lying about opioid use; and taking risks, such as driving under the influence of opioids. Other signs of opioid addiction include changes in mood or behavior, such as irritability or aggression, and withdrawal symptoms when the person stops using opioids.
3. What are the treatment options for opioid addiction?
The treatment options for opioid addiction include medication-assisted treatment (MAT), which combines medications and behavioral therapies to treat opioid addiction. MAT can be used to reduce opioid cravings and withdrawal symptoms, as well as to stabilize mood. In addition to MAT, other treatment options for opioid addiction include counseling and individual and group therapy. Counseling and therapy can help people with opioid addiction learn healthy coping skills and develop strategies for managing triggers and cravings.
4. How can family and friends help someone with opioid addiction?
Family and friends can help someone with opioid addiction by providing them with emotional support and understanding. Additionally, family and friends can help by providing practical support, such as helping the person find a treatment program or offering to go to counseling sessions with them. It is also important for family and friends to be aware of the signs of relapse and to encourage the person to seek help if they experience any of these signs.
5. What are the risks of opioid addiction?
The risks of opioid addiction include physical, psychological, and social harm. Physically, opioid addiction can lead to an increased risk of overdose, as well as cardiovascular, respiratory, and other health problems. Psychologically, opioid addiction can cause depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Socially, opioid addiction can lead to relationship problems, financial difficulties, and loss of employment.
6. What should I do if I think I might be addicted to opioids?
If you think you might be addicted to opioids, it is important to seek help as soon as possible. The first step is to talk to your doctor or a mental health professional about your concerns. They can evaluate your symptoms and recommend a treatment plan that is best suited to your needs. Treatment options include medication-assisted treatment, counseling, and individual and group therapy. It is also important to find social support, such as joining a support group or talking to family and friends.
Opioid addiction is a serious and potentially deadly health problem that requires proper diagnosis, treatment and ongoing support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals. Treatment should focus on helping the individual create a new lifestyle and learn how to cope with the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. With the right support and dedication, opioid addiction can be managed and ultimately overcome.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts