Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that can cause severe and even life-threatening damage to the body. It affects millions of people across the globe and can be difficult to manage. One of the most pressing questions surrounding lupus is what drugs can cause it? In this article, we’ll explore some of the medications that may be linked to lupus, as well as the potential risks and benefits of taking them. We’ll also look at alternative treatments and how to reduce your risk of developing lupus.
There is no single drug that causes lupus. However, certain medications can trigger or worsen the symptoms of lupus, such as antimalarials, certain antibiotics, and certain drugs used to treat heartburn, high blood pressure, and arthritis.
- Antimalarials – These drugs, such as hydroxychloroquine, are commonly prescribed to treat lupus symptoms. They can help prevent joint damage and reduce flares.
- Antibiotics – Certain antibiotics, such as sulfonamides, can trigger lupus symptoms. They should be avoided if possible.
- Drugs for heartburn, high blood pressure, and arthritis – Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and some drugs used to treat heartburn, high blood pressure, and arthritis can worsen lupus symptoms.
Contents
What Medications May Trigger Lupus?
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder that causes inflammation throughout the body. The cause of lupus is not completely understood, but some medications may trigger or worsen the condition. Understanding which drugs can cause lupus may help people to avoid them or take them with caution.
The most common medications that can trigger lupus are certain antibiotics, anti-seizure medications, and certain drugs used to treat heart conditions. These medications may cause a person to develop lupus symptoms or worsen existing symptoms. It is important to note that not everyone who takes the medications will experience lupus-like symptoms.
Antibiotics
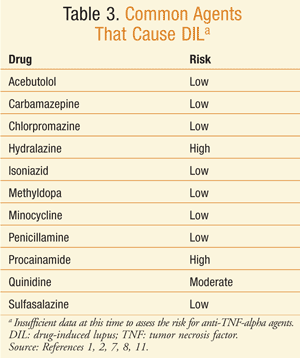
Antibiotics are one of the most common medications that can trigger lupus. The most commonly reported antibiotics are sulfonamides, which are used to treat bacterial infections. Other antibiotics that may trigger lupus include minocycline, chlorpromazine, and nitrofurantoin.
It is important to remember that not all antibiotics can trigger lupus. However, it is important to be aware of the potential for lupus symptoms when taking any antibiotic. People should speak with their doctor about any concerns they have about taking antibiotics.
Anti-Seizure Medications
Anti-seizure medications, or anticonvulsants, are another class of medications that may trigger lupus. These medications are used to treat epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and other conditions. The most commonly reported anticonvulsants are phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital.
It is important to note that not everyone who takes anticonvulsants will develop lupus. However, it is important to be aware of the potential for lupus symptoms when taking any anticonvulsant. People should speak with their doctor about any concerns they have about taking anticonvulsants.
Heart Medications
Certain heart medications may also trigger lupus. These medications are used to treat heart conditions such as high blood pressure and heart failure. The most commonly reported heart medications are ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
It is important to remember that not everyone who takes heart medications will experience lupus-like symptoms. However, it is important to be aware of the potential for lupus symptoms when taking any heart medication. People should speak with their doctor about any concerns they have about taking heart medications.
Diagnosing Lupus After Drug Use
When lupus symptoms develop after taking a certain medication, it is important to speak with a doctor about the possibility of lupus. Doctors may diagnose lupus using a combination of physical exams, blood tests, and imaging tests.
In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to treat lupus. These medications may include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and immunosuppressants. It is important to take these medications as prescribed by a doctor.
Managing Lupus Symptoms
In addition to medications, there are lifestyle changes that may help to manage lupus symptoms. For example, it is important to get enough rest, exercise regularly, and practice stress management. Eating a healthy diet and avoiding triggers such as sun exposure and certain medications may also help.
Seeking Support
Living with lupus can be challenging, and it is important to seek support. People living with lupus may benefit from joining a lupus support group or talking to a counselor. These resources can help people to cope with the challenges of living with lupus.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Lupus?
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues and organs. It can cause inflammation and tissue damage in the joints, skin, kidneys, heart, lungs, blood vessels, and brain. Symptoms of lupus can include fatigue, joint pain, fever, skin rashes, and kidney problems. Lupus can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms can be similar to those of other diseases. There is no cure for lupus, but treatments can help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
What Drugs Cause Lupus?
Certain drugs have been known to cause lupus-like symptoms or make existing lupus worse. These drugs include certain antibiotics, seizure medications, blood pressure medications, and immunosuppressants. Other drugs that have been linked to lupus include quinidine, procainamide, hydralazine, and isoniazid. It is important to talk to your doctor about any medications you are taking and their potential side effects.
How is Lupus Diagnosed?
Lupus is diagnosed based on a combination of physical exam findings, lab tests, and patient history. Lab tests may include a complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, antinuclear antibody test, and urine analysis. Your doctor may also order imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to help diagnose lupus. Your doctor may also ask about your family history and any medications you are taking.
How is Lupus Treated?
The treatment of lupus depends on the severity of the disease, the organs involved, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment may include oral medications such as anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, antimalarial drugs, and immunosuppressants. Other treatments may include physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and surgery to correct any damage caused by lupus.
What are the Complications of Lupus?
Lupus can cause a variety of complications, including skin problems, kidney failure, blood clotting disorders, and heart and lung problems. It can also cause inflammation of the brain and nervous system, leading to seizures, confusion, and memory loss. Other complications may include anemia, osteoporosis, and infertility.
Are There Any New Treatments for Lupus?
Yes, there are new treatments for lupus being developed. Researchers are looking into new ways to treat the disease, such as using stem cell therapy and gene therapy. Other new treatments being explored include the use of monoclonal antibodies and biologic drugs to target specific proteins in the body that are involved in lupus.
Lupus is a complex and often misunderstood autoimmune disorder that can affect many different aspects of an individual’s life. Knowing what drugs can cause lupus is critical for those who are at risk or already suffer from the condition. While there is no single drug known to cause lupus, certain medications can increase the risk of developing the condition. It is important to discuss any potential risks with a doctor before taking any medications, and be alert to any symptoms of lupus. With the right medical care and lifestyle modifications, those living with lupus can manage the disorder and live a full and healthy life.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts