Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Drug addiction has become a global epidemic, impacting individuals, families, and communities around the world. For many, the question of whether drug addiction is an illness or a choice is an ongoing debate. On one hand, many believe that addiction is a matter of personal responsibility and self-control. On the other, there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that addiction is a disease of the brain, much like any other chronic medical condition. In this article, we will explore the complexities of the debate and delve into the science behind drug addiction to determine if it is, in fact, a disease.
Drug Addiction as a Disease
Drug addiction is a serious problem in many parts of the world. It affects individuals, families, and communities. The question of whether or not drug addiction is a disease is a complex one and is the subject of much debate. There are many different theories on this subject, but one thing is clear: drug addiction is a serious problem that needs to be addressed.
The first argument in favor of drug addiction being a disease is that it has many of the same characteristics as other diseases. Drug addiction is a chronic disorder that is characterized by compulsive drug use despite negative consequences. This is similar to other chronic diseases such as diabetes or hypertension, which also have no known cure. Additionally, drug addiction is often accompanied by other physical and mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, and insomnia.
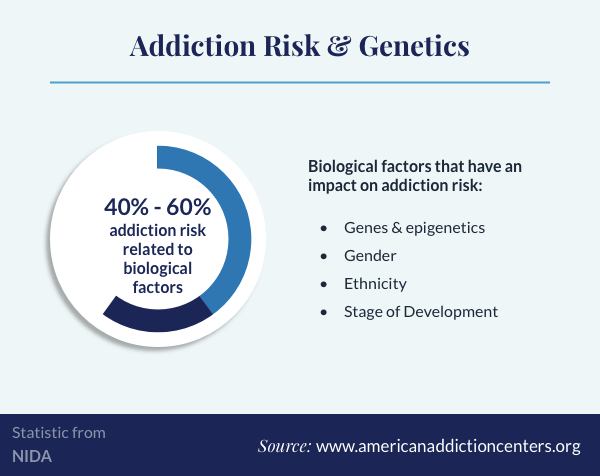
The second argument in favor of drug addiction being a disease is that it is caused by a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Drug addiction is caused by changes in the brain’s chemistry, which can be caused by genetic predisposition, environmental factors such as trauma, or even social factors such as peer pressure. These changes can lead to compulsive drug use and addiction, which can have devastating consequences on the individual’s life.
The Impact of Drug Addiction
The impact of drug addiction on an individual’s life can be significant. It can lead to physical and psychological issues, as well as financial and legal problems. Drug addiction can cause a person to lose their job, their home, and their relationships. It can also lead to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety, and can even lead to suicide in extreme cases.
Drug addiction can also have a significant impact on society. It can lead to increased crime rates, higher healthcare costs, and decreased economic productivity. It can also lead to strained relationships between family members, friends, and members of the community.
Treatment for Drug Addiction
The good news is that drug addiction is treatable. Treatment programs typically involve a combination of pharmacological, psychological, and educational components. Medications such as methadone and buprenorphine can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while psychotherapy and counseling can help individuals deal with underlying issues. Education and support groups can also help individuals learn how to cope with their addiction and live a healthy, productive life.
Addiction as a Disease of the Brain
Recent research has shown that drug addiction is a disease of the brain. This means that it is a physical disorder, not a moral failing. It is caused by changes in the brain’s chemistry, which can be caused by genetic predisposition, environmental factors, or even social factors. This means that drug addiction must be treated like any other chronic disease, with a combination of pharmacological, psychological, and educational components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, drug addiction is a serious problem that affects individuals, families, and communities. It is a chronic disorder that is caused by changes in the brain’s chemistry and has devastating effects on the individual’s life. However, with proper treatment and support, individuals can learn to cope with their addiction and live a healthy, productive life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is Drug Addiction a Disease?
A1. Yes, drug addiction is considered a disease. According to the American Society of Addiction Medicine, drug addiction is a chronic, relapsing brain disorder characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences. Drug addiction is a complex condition that affects the reward, motivation and memory circuits of the brain. This disease is caused by changes in brain structure and function due to repeated drug use, which can cause addiction-related behaviors, such as compulsive drug seeking and use, that persist even in the face of extremely negative consequences.
Q2. What are the Causes of Drug Addiction?
A2. The exact cause of drug addiction is not known, but it is believed that a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors play a role. Biological factors can include a family history of addiction, genetic predisposition, and brain chemistry. Psychological factors can include poor coping skills, low self-esteem, and a history of trauma. Environmental factors can include peer pressure, access to drugs, and a lack of support from family and friends.
Q3. What are the Symptoms of Drug Addiction?
A3. The symptoms of drug addiction can vary depending on the type of drug being abused and the individual’s unique circumstances. Common signs and symptoms of drug addiction include changes in behavior, cravings for the drug, physical changes, social withdrawal, and neglect of responsibilities. Some people may also suffer from physical dependence, meaning they experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop using the drug.
Q4. What are the Consequences of Drug Addiction?
A4. Drug addiction can have serious and long-lasting consequences on an individual’s physical and mental health, as well as their relationships and financial situation. Some of the potential consequences of drug addiction include an increased risk of developing chronic health conditions, such as liver and heart disease; psychological problems, such as depression and anxiety; and social issues, such as marital strife and difficulty finding and keeping employment.
Q5. How is Drug Addiction Treated?
A5. Drug addiction is a treatable condition and there are a variety of evidence-based treatments available for individuals struggling with this disease. The most effective treatment for drug addiction typically involves a combination of medication, counseling, and lifestyle changes. Medications can help reduce cravings and reduce the risk of relapse, while counseling and therapy can help individuals develop coping skills and learn to manage their triggers and cravings.
Q6. What are the Risks of Relapse?
A6. The risk of relapse is always present for those who have struggled with addiction, as cravings and triggers can resurface at any time. To reduce the risk of relapse, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, build strong social supports, and participate in ongoing therapy and counseling. Additionally, it is important to be aware of potential triggers and take steps to prevent or manage them, such as avoiding certain people or places.
Why Is Addiction A Disease?
Drug addiction is a complex, multi-faceted condition that affects individuals in many different ways. It is clear that drug addiction is a disease, one that can have serious consequences for the individual and those around them. While there is no single, one-size-fits-all solution to the issue, it is essential that we continue to explore the best ways to help those suffering from addiction and support them in their recovery. Only with a holistic, compassionate approach to this devastating condition can we truly make a difference in the lives of those struggling with addiction.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts