Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Drug addiction can have a profound impact on an individual’s life, and many wonder if this affliction is caused by genetics or by other factors. While it is difficult to provide an exact answer, there is evidence to suggest that genetics can play a role in drug addiction.
Answer: Yes, drug addiction can be genetic.
Contents
Is Drug Addiction Genetic Or Environmental
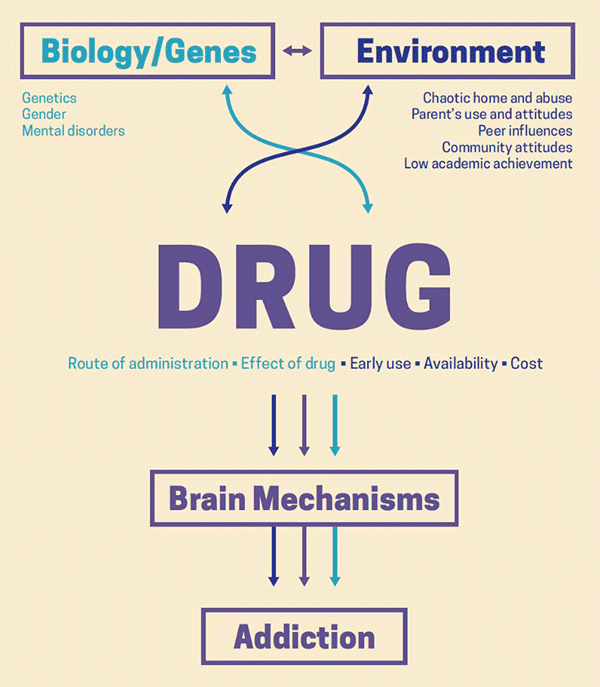
Drug addiction is a complex issue that has been studied extensively by researchers in order to determine the potential causes of this condition. While there is much debate about whether drug addiction is primarily caused by genetic or environmental factors, there is evidence to suggest that it is a combination of both.
Genetic factors are believed to play a significant role in the development of drug addiction. Studies have found that people with a family history of addiction are more likely to become addicted to drugs themselves. Additionally, research has identified certain genes that may increase the risk of addiction, such as those that are associated with changes in neurotransmitter pathways in the brain.
Environmental factors, such as stress, trauma, and peer influence can also contribute to the development of drug addiction. Studies have shown that people who experience significant stress or trauma, such as being exposed to violence, are more likely to become addicted to drugs. Additionally, those who grow up in environments where drug use is commonplace are more likely to develop an addiction to drugs.
Overall, while there is no single cause of drug addiction, it is likely a combination of both genetic and environmental factors. In order to reduce the risk of developing an addiction to drugs, it is important to be aware of potential risk factors and to take steps to prevent drug use. This can include avoiding environments where drug use is prevalent, seeking help for stress or trauma, and finding healthy ways to cope with challenging situations.
Addiction Genetic Predisposition
Yes, drug addiction can have a genetic component, and it is well documented that addiction can run in families. Scientific research has demonstrated that genetic factors can influence an individual’s vulnerability to addiction. A family history of addiction can increase the risk of developing a substance use disorder, as can certain genetic variations. It is believed that genes account for 40 to 60 percent of a person’s likelihood of developing drug or alcohol addiction.
Studies have shown that there is a clear link between genetic predisposition and addiction. Genes can affect a person’s response to drugs, increasing the chance of developing an addiction. For example, people with a certain variation of the dopamine receptor gene are more prone to developing an addiction to drugs or alcohol. Other genetic variations that have been associated with addiction include variations in the serotonin transporter gene, the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor gene, and the opioid receptor gene.
In addition to genetic factors, environmental factors such as stress, peer pressure, and trauma can contribute to the development of addiction. People with a family history of addiction are more at risk of developing an addiction, but the environment plays an important role as well. Therefore, it is important to consider both genetic and environmental factors when assessing the risk of developing an addiction.
How Do Drugs Affect Genetics
Drug addiction can be a complex condition that has both environmental and genetic components. Research has found that genetics plays a role in about half of a person’s vulnerability to drug addiction. For example, when one identical twin has an addiction, the other twin is more likely to also have an addiction than a fraternal twin. This indicates that the genetic component is stronger when the twins share the same genes.
Genetic influences on addiction include changes in brain chemistry that can make it more difficult for a person to control their impulses and make good decisions. Studies have also found that certain genes may increase a person’s risk of becoming addicted to drugs. For example, a person with a particular variant of the DRD2 gene may be more likely to become addicted to drugs than someone without the variant.
In addition to genetic influences, environmental factors can also play a role in drug addiction. These factors include exposure to drug use at a young age, mental health issues, peer pressure, and trauma. People who have experienced trauma, such as abuse or neglect, may be more likely to develop an addiction. These environmental factors can interact with genetic factors to increase the risk of addiction even further.
What Percentage Of Addiction Is Genetic
It is widely accepted that addiction has genetic roots, although the exact percentage of how much is genetic is unknown. Multiple studies have shown that genetics plays a role in addiction, yet the exact contribution of genetic factors is not fully understood.
Studies suggest that individuals who are genetically predisposed to addiction are more likely to develop a substance use disorder in response to environmental triggers. For instance, a person with a family history of addiction is more likely to become addicted than someone without such a history. Furthermore, a person with a particular gene variant may be more vulnerable to environmental influences, such as peer pressure or a stressful life event, that can lead to addiction.
The exact genetic contribution to addiction is still being studied, but it is believed to range from 40 to 60 percent. The remaining factors are believed to be environmental, such as exposure to drugs, social influences, and family dynamics. Thus, while there is a genetic component to addiction, it is not the only factor. Understanding the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to addiction can provide valuable insight into the development of more effective treatment and prevention strategies.
What Is The Addiction Gene Called
The connection between genetics and drug addiction has long been studied. It is believed that certain genetic factors make some people more vulnerable to addiction than others. The scientific name for the addiction gene is DRD2, a gene that codes for the dopamine receptor D2. This dopamine receptor plays an important role in the reward system of the brain, which is linked to addiction.
Studies have shown that people with certain variants of the DRD2 gene may be more likely to become addicted to drugs. This may be due to the fact that the dopamine receptor D2 is involved in the reward system of the brain, which is connected to addiction. People with these genetic variants may have a greater sensitivity to the reward of drugs, making it more difficult to resist the urge to take them. Furthermore, there may be a link between genetic variants of the DRD2 gene and the development of withdrawal symptoms when a person stops using drugs.
Overall, research suggests that drug addiction may be linked to genetics in some cases. The scientific name for the gene that is believed to be connected to addiction is DRD2. People with certain variants of this gene may be more likely to become addicted to drugs, as they may have a greater sensitivity to the reward of drugs. Further research is needed to better understand the genetic factors that may be associated with addiction.
Can Drugs Cause Genetic Mutations
Drug addiction can be a complex and devastating illness that can have a major impact on an individual’s life as well as their family and friends. It is a chronic condition that is characterized by compulsive drug-seeking and use, despite the potential for negative consequences. Evidence indicates that drug addiction is partly influenced by genetics; according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, about 40 to 60 percent of an individual’s risk for addiction is related to their genetic makeup.
Genetic mutations can be caused by a wide variety of factors, including exposure to certain chemicals and radiation. While the effects of drug abuse on genetics are not completely understood, there is some evidence to suggest that certain drugs can increase the risk of certain genetic mutations. For example, research has found that alcohol, nicotine, and certain other drugs can cause changes in DNA, which can lead to long-term health issues. Additionally, certain drugs have been linked to mutations in the genes that control cell growth and division, which can lead to cancer. While the exact mechanism by which drugs can cause genetic mutations is not yet clear, it appears that certain drugs can alter the way in which genes are expressed, which can lead to genetic mutations.
Genetic Model Of Addiction
The genetic model of addiction suggests that genetic factors play an important role in the development of drug addiction. Research studies have demonstrated that individuals with a family history of addiction are more likely to become addicted to drugs and alcohol than those without such a history. This suggests that genetic predispositions may be involved in the development of substance use disorder.
One of the most important findings in the field of addiction genetics is that multiple genes may be involved in the development of addiction. Studies have identified several different genes associated with addiction, including those involved in the reward pathways of the brain, as well as those involved in stress response and impulsivity. While there is still much to be learned about the specific genetic components of addiction, this research has provided valuable insights into the potential genetic underpinnings of drug and alcohol addiction.
In addition to identifying genetic contributions to addiction, research has also demonstrated that environmental factors can play a role in the development of substance use disorder. Factors such as stress, trauma, poverty, and access to drugs can all increase an individual’s risk of developing addiction. Therefore, a combination of genetic and environmental factors is likely to be involved in the development of drug addiction.
The Role Of Genes In Drug Addiction
The role of genes in drug addiction has been the subject of scientific research for many years. It is widely accepted that there is a genetic factor involved in drug addiction, and research suggests that up to 50% of the risk of addiction can be attributed to genetics. However, it is important to note that addiction is a complex behavioral disorder and that genetics are just one factor in its development.
Research indicates that genetic factors can play a role in how an individual responds to drugs, with some people being more susceptible to addiction. Those with a family history of addiction are more likely to develop an addiction themselves, as genes can influence how the brain responds to drugs and alcohol. Additionally, certain genetic variations are associated with an increased risk of addiction, such as variations in dopamine transporter genes, or genes associated with the reward system. Furthermore, certain ethnicities and cultures are at higher risk for addiction, which suggests that there is a genetic component to addiction.
Ultimately, the role of genetics in drug addiction is complex, and more research is needed to understand the role of genetics in addiction. However, it is clear that genetic factors can play an important role in the development of addiction, and that those with a family history of addiction should take extra caution when it comes to abusing drugs and alcohol.
From Genes to Addiction: How Risk Unfolds Across the Lifespan | Dr. Danielle Dick | TEDxRVA
In conclusion, although the exact cause of drug addiction is still unknown, it is clear that genetics play a large role. Research suggests that people with a family history of addiction are more likely to become addicted to drugs themselves. Therefore, it is important to understand the implications of addiction and to take any necessary steps to prevent it from happening in the first place. With the right kind of support and understanding, it may be possible to break the cycle of addiction and to develop healthier coping strategies.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts