Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the use of stimulants to increase dopamine, the neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of pleasure and reward. Stimulants such as caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines are known to increase dopamine levels in the brain and are commonly used to treat conditions like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. But do stimulants actually increase dopamine levels in the long term, and if so, what are the potential risks and benefits? In this article, we will explore the effects of stimulants on dopamine levels, and how they might affect our mental and physical health.
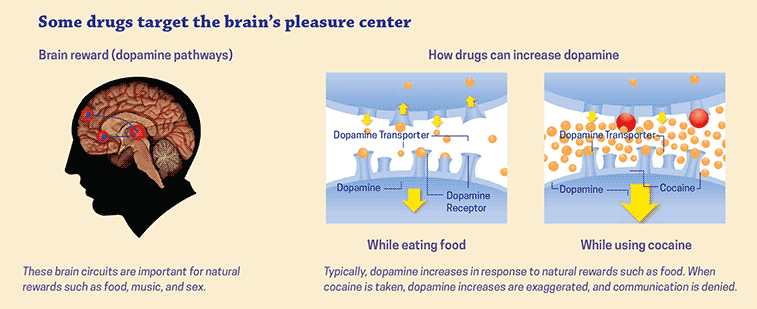
Yes, stimulants like cocaine, methamphetamine, and Adderall increase dopamine levels in the brain. This can lead to a temporary feeling of euphoria and an improved mood. However, long-term use of these drugs can lead to addiction and a range of negative health effects.
Does Stimulant Use Increase Dopamine Levels?
Stimulants are a class of psychoactive drugs that are used to enhance mental and physical performance, and to treat certain medical conditions. They act on the brain by stimulating the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is involved in alertness, motivation, attention, and reward-seeking behavior. The question arises: do stimulants increase dopamine levels?
Studies have shown that stimulant use can increase dopamine in the brain. One study found that when given amphetamine, a stimulant, the release of dopamine in the brain was significantly increased. Another study found that when given modafinil, another stimulant, dopamine release in the brain was increased over a period of time.
However, it is important to note that the effects of stimulants on dopamine levels vary between individuals. Some people may have a greater response to stimulants than others, and some may not experience any increase in dopamine at all. Additionally, the effects of stimulants on dopamine levels are not permanent, and may dissipate over time.
How Do Stimulants Increase Dopamine Levels?
Stimulants increase dopamine levels by acting on the brain in two different ways. First, they can act directly on the dopamine neurons in the brain, stimulating the release of dopamine. Secondly, they can act indirectly, by increasing the amount of dopamine available in the brain.
The direct action of stimulants is thought to be the primary mechanism for increasing dopamine levels. By stimulating the release of dopamine, stimulants can increase the amount of the neurotransmitter available to the brain. This can lead to an increase in alertness, attention, and motivation.
The indirect action of stimulants is thought to be less significant, but can still play a role in increasing dopamine levels. Stimulants can block the reuptake of dopamine, which is when the neurotransmitter is reabsorbed by the neurons that released it. This can lead to a higher concentration of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to increased alertness, attention, and motivation.
Are Stimulants Safe?
Stimulants can be effective at increasing dopamine levels in the brain and can have a positive effect on mental and physical performance. However, it is important to note that stimulants can have potential side effects, such as insomnia and anxiety. Therefore, it is important to discuss any potential risks with a healthcare professional before taking a stimulant.
Additionally, stimulants can be addictive and can lead to dependence. People who take stimulants regularly may develop a tolerance, meaning they will need to take higher doses to achieve the same effect. Therefore, it is important to use stimulants safely and responsibly.
Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Use
The long-term effects of stimulant use on dopamine levels are not yet clear. Some studies have suggested that long-term use of stimulants can lead to a reduction in dopamine receptors, which can lead to a decrease in dopamine levels. However, more research is needed to confirm this.
Additionally, there is evidence that long-term use of stimulants can lead to changes in the brain’s reward system. This can lead to changes in behavior, such as increased risk-taking and impulsive behavior. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the potential long-term risks of stimulant use.
Conclusion
Studies have shown that stimulant use can increase dopamine levels in the brain. However, the effects of stimulants on dopamine levels vary between individuals and are not permanent. Additionally, stimulants can have potential side effects and can be addictive. Therefore, it is important to use stimulants safely and responsibly.
Related Faq
Q1. What is dopamine?
A1. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain that plays a key role in reward and motivation, as well as in cognition, attention, and movement. Dopamine is also involved in memory, mood, and learning. It is released by the brain when we experience something rewarding, such as eating a delicious meal or getting a good grade on an exam. This release of dopamine helps to reinforce the behavior that led to the reward, thus motivating us to repeat it.
Q2. What are stimulants?
A2. Stimulants are substances that increase activity in the body. This can include increasing alertness, focus, and physical activity. Stimulants are often used to treat conditions such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and depression. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, and prescription medications such as Adderall and Ritalin.
Q3. How do stimulants work?
A3. Stimulants work by stimulating the release of neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters help to increase alertness, focus, and physical activity. Stimulants can also affect appetite and mood.
Q4. Do stimulants increase dopamine?
A4. Yes, stimulants can increase dopamine levels in the brain. Stimulants increase the release of dopamine, and they can also block the reuptake of dopamine, resulting in a buildup of dopamine in the brain. This increase in dopamine can lead to feelings of euphoria and increased alertness and focus.
Q5. What are the potential risks of taking stimulants?
A5. Stimulants, when taken in large doses or for long periods of time, can lead to addiction and other serious health problems. Stimulants can also increase blood pressure and heart rate, and they can cause anxiety, insomnia, and restlessness. Stimulants should only be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Q6. Are there alternatives to taking stimulants?
A6. Yes, there are alternatives to taking stimulants for conditions such as ADHD and narcolepsy. These include lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and healthy eating, as well as cognitive behavioral therapy and relaxation techniques. Other alternatives include certain supplements and medications, such as omega-3 fatty acids and modafinil.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Amphetamine
In conclusion, there is a strong link between the use of stimulants and increased dopamine levels. Stimulants not only increase dopamine production in the brain, but they also increase the amount of dopamine that can be released by neurons. This increase in dopamine is thought to be responsible for the alertness and focus associated with the use of stimulants. While these effects can be beneficial, long-term use of stimulants can have serious consequences. It is important to understand the risks and benefits associated with the use of stimulants before deciding to use them.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts