Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Stimulants are drugs that affect the central nervous system and can have a wide range of effects on the body. But how do they affect the brain? In this article, we’ll explore the neuroscience behind stimulants, and discuss their impact on the brain’s chemistry, performance, and overall health. We’ll also look at the potential short- and long-term effects of stimulant use, and what precautions people should take if they choose to use stimulants. So, let’s dive into the details of how stimulants affect the brain.
Stimulants, such as caffeine and amphetamines, affect the brain by increasing alertness and energy levels. They can also increase focus and concentration, as well as heart rate and blood pressure. In the short-term, stimulants can make a person feel more awake, alert, and energetic. In the long-term, however, they can lead to addiction, increased risk of stroke and heart attack, and even psychosis. It is important to use stimulants responsibly, and with medical supervision, to avoid these potential risks.
How Do Stimulants Impact the Brain?
Stimulants are powerful drugs that can have a profound effect on the brain. They act on specific neurotransmitters, like dopamine and norepinephrine, to enhance alertness, improve focus, and increase energy levels. With regular use, stimulants can have lasting effects on the brain and central nervous system. In this article, we’ll explore how stimulants work, the potential risks and benefits, and how to reduce the risk of long-term side effects.
What Are Stimulants?
Stimulants are a class of drugs that act on the central nervous system to increase alertness, focus, and energy levels. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, and cocaine. Stimulants are often used to treat attention disorders, narcolepsy, and other conditions. However, because of their potential for abuse and addiction, stimulants are highly regulated and require a prescription for medical use.
How Do Stimulants Work?
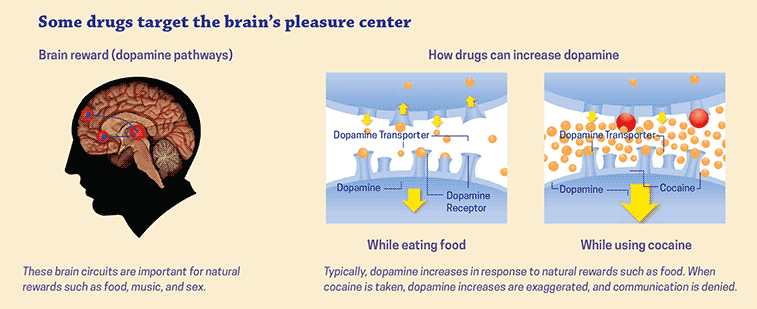
Stimulants work by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. These chemicals are responsible for controlling mood, perception, and reward-seeking behavior. When stimulants are taken, they bind to receptors in the brain and increase the activity of these neurotransmitters. This leads to an increase in alertness, focus, and energy levels.
Potential Benefits and Risks
Stimulants can have both positive and negative effects on the brain. On the positive side, they can be used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and other conditions. Stimulants can also improve energy levels and focus, which can be beneficial for athletes, students, and people with demanding jobs.
At the same time, stimulants can have some serious side effects. Long-term use of stimulants can lead to addiction, insomnia, and anxiety. Additionally, stimulants can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be dangerous for some people. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking any stimulant medication.
Reducing the Risk of Side Effects
The key to reducing the risk of long-term side effects from stimulants is to use them responsibly. It’s important to take the medication as directed and to not exceed the recommended dose. Additionally, it’s important to get regular check-ups, as stimulants can have long-term effects on the heart and other organs.
Considering Alternatives
Stimulants can be an effective treatment for certain conditions but they come with potential risks and side effects. For some people, there may be safer alternatives to stimulants. Non-stimulant medications, such as atomoxetine, can be used to treat ADHD. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as getting regular exercise and eating a healthy diet, can help improve focus and energy levels.
Seeking Professional Help
If you’re considering taking a stimulant or already taking one, it’s important to seek professional help. A healthcare provider can help you understand the potential risks and benefits of stimulants and provide guidance on how to use them safely. They can also help you explore other treatment options and determine if a stimulant is right for you.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Stimulants?
Stimulants are a class of drugs that act on the central nervous system and can increase alertness, attention, and energy. Stimulants can be either legal or illegal. Examples of legal stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, and prescription medications such as Adderall and Ritalin. Illegal stimulants include cocaine, methamphetamine, and MDMA (ecstasy).
How Do Stimulants Affect the Brain?
Stimulants act on the brain by increasing levels of dopamine and norepinephrine. This can lead to increased alertness and energy, improved focus, and improved mood. Stimulants can also lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate, increased respiration, and increased body temperature. In some cases, stimulants can lead to feelings of euphoria and an increased risk of addiction.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Stimulants?
The short-term effects of stimulants depend on the type and amount used. Generally, short-term effects can include increased alertness, energy, and focus; improved mood; increased heart rate and blood pressure; and increased body temperature. Stimulants can also lead to feelings of euphoria and an increased risk of addiction.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulants?
The long-term effects of stimulants depend on the type and amount used. Generally, long-term effects can include increased risk of addiction, increased risk of cardiovascular problems, increased risk of mental health problems such as depression, and increased risk of seizures. Stimulants can also lead to insomnia, irritability, and decreased appetite.
Are There Any Risks in Taking Stimulants?
Yes, there are risks associated with taking stimulants. Stimulants can lead to addiction, increased risk of cardiovascular problems, increased risk of mental health problems, and increased risk of seizures. Stimulants can also lead to insomnia, irritability, and decreased appetite.
What Are Some Ways to Reduce the Risk of Taking Stimulants?
To reduce the risk of taking stimulants, it is important to practice caution when using them. Talk to your doctor or healthcare provider to determine if stimulants are right for you. It is also important to take stimulants as prescribed and to not take more than the recommended dose. Additionally, avoid taking stimulants with alcohol or other drugs, and avoid taking stimulants in large doses or for extended periods of time.
How do drugs affect the brain? – Sara Garofalo
In conclusion, it is clear that stimulants have a profound effect on the brain. They can improve focus and alertness, as well as increase energy and heart rate. However, it is important to remember that these drugs can also be addictive and have dangerous side effects if used improperly. It is important to understand the risks and benefits associated with taking stimulants and consult your doctor before beginning any new treatment.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts