Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Nicotine is a powerful drug found in the leaves of certain plants, most notably tobacco. It has a long history of use as a recreational drug and has grown in popularity in recent years due to its widespread availability and potential for addiction. But how does nicotine actually work? In this article, we’ll explore the effects of nicotine on the body, its potential health benefits, and the dangers of nicotine addiction.
- How to quit using Nicotine?
- Identify the triggers that make you want to use nicotine.
- Develop a plan to avoid those triggers.
- Find activities to distract yourself from wanting to use nicotine.
- Reach out to family and friends for support.
- Talk to your doctor about medications to help you quit.
| Nicotine vs Non-Nicotine | |
|---|---|
| Nicotine | Stimulates the release of dopamine, causes addiction, increases heart rate, respiration and alertness. |
| Non-Nicotine | Does not contain nicotine, does not cause addiction, does not increase heart rate, respiration and alertness. |
Contents
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is an addictive stimulant found in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. It is a colorless liquid that is also found in plants like tobacco, potatoes, and tomatoes. It acts on the brain and central nervous system to give a feeling of pleasure and alertness. Nicotine is also found in some foods and drinks, including tea, coffee, and chocolate.
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance and can have serious health risks. It has been linked to an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other conditions. Long-term use of nicotine can lead to addiction, which can make it difficult to quit.
How Does Nicotine Work?
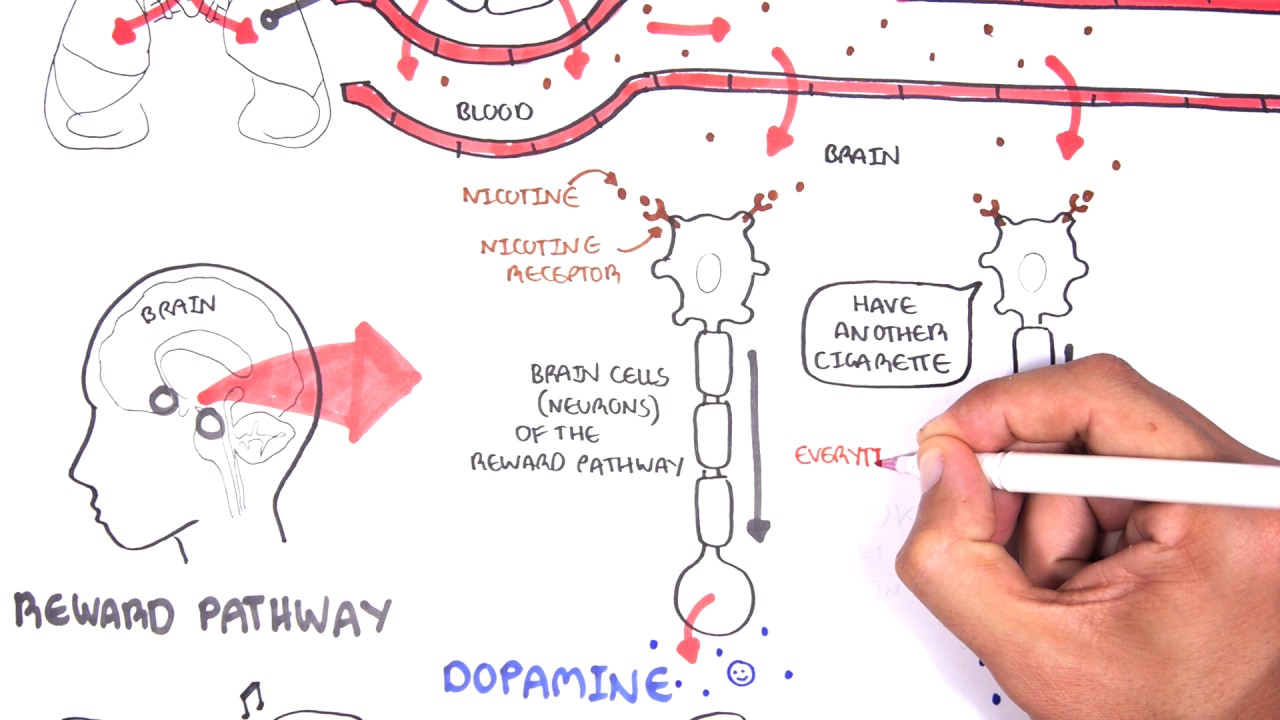
When nicotine enters the body, it causes a release of adrenaline, which increases heart rate and blood pressure. Nicotine also stimulates the release of dopamine, a chemical that produces a sense of pleasure. This is why people often experience a feeling of relaxation and pleasure when they use nicotine.
Nicotine acts on the brain by binding to receptors. This triggers a cascade of events that can lead to an increase in alertness and concentration. Over time, the nicotine receptors become less sensitive and the user needs to take in more nicotine to achieve the same effect. This is why smokers often need to smoke more cigarettes over time to get the same amount of satisfaction.
Nicotine Addiction
Nicotine is highly addictive and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. People who are addicted to nicotine may experience cravings and withdrawal symptoms when they try to quit. Common withdrawal symptoms include irritability, insomnia, anxiety, and depression.
Nicotine addiction is a serious condition and can be difficult to overcome. Quitting smoking can be a long and difficult process, and many people need help and support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals.
The Effects of Nicotine
Nicotine has both short-term and long-term effects on the body. In the short-term, it can cause increased heart rate, higher blood pressure, and constricted blood vessels. This can lead to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Long-term use of nicotine can lead to a number of health problems, including cancer, heart disease, and other conditions. Nicotine also increases the risk of developing mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
Health Risks of Nicotine
Nicotine is a highly addictive substance and can have serious health risks, including cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Long-term use of nicotine can also increase the risk of developing mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety.
Cancer Risks
Smoking is the most common way of taking in nicotine, and smoking is linked to an increased risk of many types of cancer, including lung, throat, and mouth cancer. Even secondhand smoke can increase the risk of cancer.
Heart Disease Risks
Nicotine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can lead to an increased risk of heart attack and stroke. Smoking is also linked to an increased risk of coronary heart disease.
Conclusion
Nicotine is an addictive stimulant found in cigarettes, cigars, and other tobacco products. It acts on the brain and central nervous system to give a feeling of pleasure and alertness. Nicotine is highly addictive and can have serious health risks, including cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Quitting smoking can be a long and difficult process, and many people need help and support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is a colorless, odorless, and highly addictive chemical stimulant found in tobacco products such as cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, snuff, and chewing tobacco. It is the main component of tobacco that causes addiction, and it is also found in some e-cigarettes and other nicotine delivery products. Nicotine is a stimulant that acts on the central nervous system and is one of the most widely used drugs in the world.
What are the Effects of Nicotine?
Nicotine affects the brain in several ways. It activates the release of dopamine, a brain chemical associated with pleasure, reward, and addiction. Nicotine also increases adrenaline, leading to increased heart rate and blood pressure. Short-term effects of nicotine include increased alertness, improved concentration, and increased energy. Long-term effects include increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and cancer.
How Does Nicotine Reach the Brain?
Nicotine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream through the lining of the lungs, mouth, and esophagus when inhaled or ingested. It then travels to the brain where it binds to nicotine receptors located in the brain’s reward system. This binding activates the brain’s reward system and triggers the release of dopamine, leading to feelings of pleasure and relaxation.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Body?
Nicotine affects the body in many ways. In the short-term, nicotine increases heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration, and can cause nausea and dizziness. Over time, nicotine use can lead to addiction and can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and cancer. Nicotine can also affect the development of the unborn child in pregnant women who use nicotine products.
What Are the Dangers of Nicotine?
Nicotine can be dangerous if used in large amounts or for long periods of time. Long-term use of nicotine can lead to addiction and can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and cancer. Nicotine can also be harmful to the developing fetus in pregnant women who use nicotine products. Additionally, nicotine use can lead to behavior problems, such as aggressive behavior and impulsivity, in children and teens.
Is Nicotine Addictive?
Yes, nicotine is highly addictive. The effects of nicotine on the reward system in the brain can lead to addiction. Nicotine addiction is similar to other forms of addiction, such as alcohol and drugs, in that it can lead to compulsive use, even despite negative health consequences. Nicotine addiction can be difficult to overcome and may require medical treatment.
How does nicotine work
In conclusion, nicotine is a powerful stimulant and a highly addictive substance that affects the body both physically and psychologically. Nicotine is absorbed quickly and can have a variety of effects on the body, including increased heart rate, constricted blood vessels, increased alertness, and increased blood pressure. Nicotine can also cause addiction, as it activates receptors in the brain that are associated with pleasure and reward. Nicotine has been linked to a variety of health issues, including heart and lung diseases, cancer, and stroke, and should be avoided if possible.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts