Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Adderall is a widely used prescription drug that is used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. But what exactly is Adderall, and is it considered a stimulant? In this article, we’ll explore the answer to this question and discuss the potential risks and benefits of Adderall. We’ll also discuss the different forms of Adderall and how it affects the body. By the end, you should have a better understanding of what Adderall is and whether it is considered a stimulant.
Yes, Adderall is a stimulant. It is a combination of two stimulant medications, dextroamphetamine and amphetamine, that increase activity in the brain. It is commonly used to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and other sleep disorders.
What is Adderall?
Adderall is a stimulant medication typically used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). It is composed of two main ingredients, amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which are believed to improve focus, concentration, and motivation. Adderall also has some off-label uses, such as treating narcolepsy and promoting weight loss.
History of Adderall
Adderall was first developed in the 1930s and was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the 1960s. It was initially prescribed to treat narcolepsy, but over the years it has become more widely used to treat ADHD. It is now one of the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD.
How Does Adderall Work?
Adderall works by increasing the levels of two neurotransmitters in the brain, dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating focus, concentration, and motivation. By increasing their levels, Adderall helps to improve these cognitive functions, making it easier for people with ADHD to focus and concentrate.
Is Adderall a Stimulant?
Yes, Adderall is a stimulant. Stimulants are a type of drug that increase alertness, attention, and energy. Other common stimulants include caffeine, cocaine, and amphetamines. Adderall is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA). This means that it has a high potential for abuse and dependence.
How is Adderall Used?
Adderall is typically prescribed in pill form, and can be taken orally or crushed and snorted. It is important to take Adderall as prescribed by a doctor, and not to take more than the recommended dose. Taking too much Adderall can lead to serious medical complications, including irregular heartbeat and seizures.
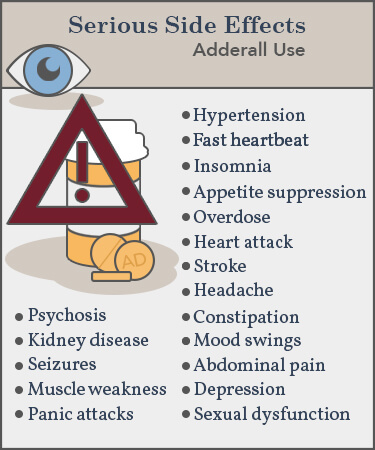
Potential Side Effects of Adderall
Like all medications, Adderall can cause side effects. Common side effects may include insomnia, headaches, loss of appetite, weight loss, and dry mouth. More serious side effects may include irregular heartbeat, chest pain, and changes in blood pressure. It is important to speak to a doctor about any side effects experienced while taking Adderall.
Conclusion
Adderall is a stimulant medication used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). It is composed of two main ingredients, amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, which help improve focus and concentration. Adderall is a Schedule II controlled substance, meaning it has a high potential for abuse and dependence. It is important to take Adderall as prescribed by a doctor, and to be aware of potential side effects.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Adderall?
Adderall is a prescription medication containing two drugs: amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. It is used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It works by affecting chemicals in the brain and nerves that contribute to impulse control and hyperactivity.
Is Adderall a Stimulant?
Yes, Adderall is a stimulant medication. Stimulants are drugs that increase alertness, attention, and energy. Adderall increases the amount of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can help improve concentration, focus, and attention.
What are the Side Effects of Adderall?
Common side effects of Adderall include dry mouth, headaches, loss of appetite, stomach pain, dizziness, restlessness, and trouble sleeping. More serious side effects can include changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar levels.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Adderall?
The long-term effects of Adderall can include addiction and dependence. It can also lead to depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues. Long-term use of Adderall can also cause physical health issues such as heart problems, high blood pressure, and changes in weight.
Can Adderall be Abused?
Yes, Adderall can be abused. It can be abused by taking larger doses than prescribed or taking it without a prescription. Adderall can also be crushed and snorted or injected, which can increase the risk of addiction and overdose.
What Should I Do if I Think I’m Abusing Adderall?
If you think you’re abusing Adderall, it’s important to seek help. Talk to your doctor or a mental health professional about your concerns. You can also get help from a support group or a substance abuse treatment program.
Ten facts about Adderall
Adderall is a stimulant that has become increasingly popular over the past few years. It has been used to treat many conditions such as ADHD and narcolepsy, but has also been abused by some people as a recreational drug. While Adderall can be an effective medication and treatment option, it is important to understand the potential risks and side effects associated with its use. Taking Adderall responsibly and under the guidance of a doctor can help ensure that it is used safely and effectively.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts