Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Alcohol is a drug with a long and complex history of use in human society. From religious ceremonies to social gatherings, alcohol has always been a popular choice for many. But what kind of drug is it? Is it a depressant or a stimulant? In this article, we’ll explore the effects of alcohol on the body and mind, and answer the question: Is alcohol a depressant or stimulant drug?
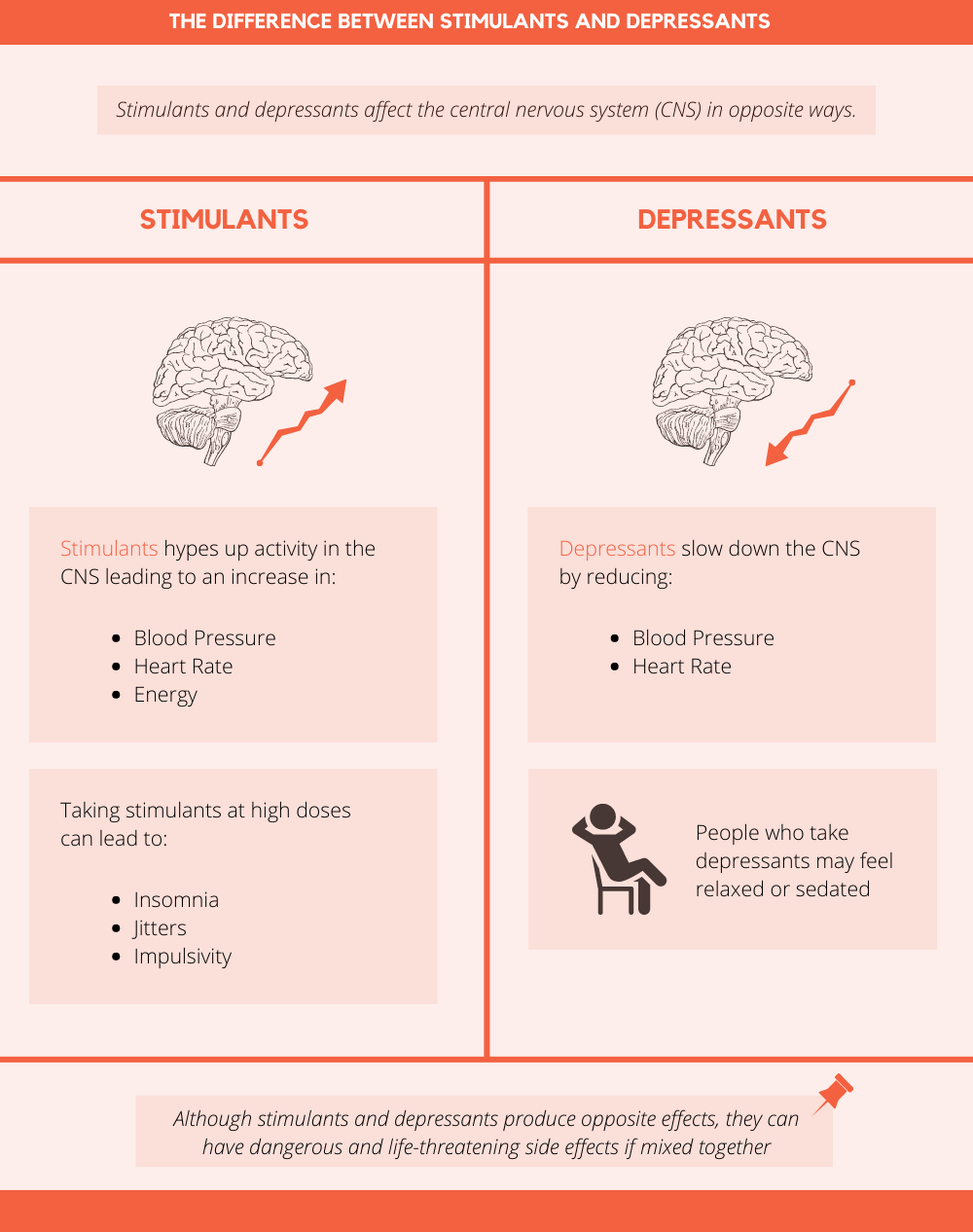
Alcohol is a depressant drug. It slows down the communication between the brain and the body, resulting in a decrease in physical and psychological performance. It can also cause a decrease in inhibitions, resulting in increased risk-taking behavior. In high doses, it can lead to depression, anxiety, and addiction. It can also cause physical harm, such as liver damage, heart problems, and weakened immune system.
Contents
- What is Alcohol?
- Alcohol as a Stimulant
- Short-Term Effects of Alcohol
- Conclusion
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- Question 1: What is a depressant drug?
- Question 2: Is alcohol a depressant drug?
- Question 3: What are the effects of alcohol on the body?
- Question 4: What is a stimulant drug?
- Question 5: Is alcohol a stimulant drug?
- Question 6: Are there any long-term risks associated with drinking alcohol?
- Truth Time! Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant?
What is Alcohol?
Alcohol, also known as ethanol, is a chemical compound found in beverages like beer, wine, and hard liquor. It is produced by fermenting the sugars in grains, fruits, or other plants. When consumed, alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it can have depressant or stimulant effects on the body.
Alcohol as a Depressant
Alcohol is classified as a central nervous system depressant, meaning it slows down functions in the brain and body. When consumed, alcohol can reduce inhibitions, making it easier to relax or socialize. It can also decrease coordination, reaction time, and memory. In large doses, it can cause drowsiness, slurred speech, and even unconsciousness.
Risk of Alcohol Abuse
The effects of alcohol can vary greatly from person to person, and even small amounts can be dangerous. Heavy drinking can lead to addiction and an increased risk of health problems. Long-term abuse of alcohol can lead to liver damage, heart disease, depression, and other serious conditions.
Alcohol as a Stimulant
Despite being classified as a depressant, alcohol can also have stimulant effects on the body. In small doses, alcohol can increase energy, improve mood, and reduce anxiety. It can also increase sociability and make people feel more confident.
Risks of Alcohol as a Stimulant
Although alcohol can have positive effects in the short term, long-term use can be dangerous. Drinking too much can lead to addiction, which can put a strain on relationships and lead to health problems. It can also increase the risk of risky behaviors like driving while intoxicated or engaging in unprotected sex.
Short-Term Effects of Alcohol
The effects of alcohol can vary depending on the amount consumed, the individual’s size, weight, and tolerance, and any other drugs or medications they may be taking. In general, alcohol can cause dizziness, drowsiness, slurred speech, impaired coordination, and slowed reaction time. In large doses, it can cause vomiting, unconsciousness, and even death.
Long-Term Effects of Alcohol
Heavy and long-term drinking can have serious negative effects on the body and mind. It can lead to liver damage, heart disease, weakened immune system, depression, and other health problems. It can also lead to addiction, which can cause financial, legal, and relationship troubles.
Conclusion
Alcohol can have both depressant and stimulant effects on the body, depending on the amount consumed. In small doses, it can have positive effects, but these are often outweighed by the potential risks of heavy drinking. It is important to be aware of the potential risks of alcohol and to practice responsible drinking.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What is a depressant drug?
A depressant drug is a type of psychoactive substance that depresses the activity of the central nervous system, resulting in decreased alertness, slower heart rate, and slower breathing. This type of drug affects the brain by decreasing the activity of neurons and neurotransmitters, which can lead to feelings of relaxation, drowsiness, and sleepiness. Common depressant drugs include alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, barbiturates, and cannabis.
Question 2: Is alcohol a depressant drug?
Yes, alcohol is a depressant drug. It depresses the activity of the central nervous system, resulting in decreased alertness, slower heart rate, and slower breathing. Alcohol affects the brain by decreasing the activity of neurons and neurotransmitters, which can lead to feelings of relaxation, drowsiness, and sleepiness.
Question 3: What are the effects of alcohol on the body?
The effects of alcohol on the body depend on the amount consumed. In small doses, alcohol can act as a stimulant and can cause people to feel energized, talkative, and relaxed. In larger doses, however, alcohol can lead to impaired judgment, slowed reflexes, and poor coordination. Long-term excessive drinking can lead to liver damage, heart disease, and other serious health conditions.
Question 4: What is a stimulant drug?
A stimulant drug is a type of psychoactive substance that increases the activity of the central nervous system, resulting in increased alertness, faster heart rate, and faster breathing. This type of drug affects the brain by increasing the activity of neurons and neurotransmitters, which can lead to feelings of euphoria, increased energy, and improved concentration. Common stimulant drugs include amphetamines, cocaine, ecstasy, and nicotine.
Question 5: Is alcohol a stimulant drug?
No, alcohol is not a stimulant drug. It depresses the activity of the central nervous system, resulting in decreased alertness, slower heart rate, and slower breathing. Alcohol affects the brain by decreasing the activity of neurons and neurotransmitters, which can lead to feelings of relaxation, drowsiness, and sleepiness.
Question 6: Are there any long-term risks associated with drinking alcohol?
Yes, there are long-term risks associated with drinking alcohol. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, heart disease, and other serious health conditions. It can also lead to an increased risk of developing certain types of cancers, such as mouth, esophagus, and liver cancer. Additionally, long-term excessive drinking can lead to psychological problems, such as depression and anxiety.
Truth Time! Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant?
In conclusion, alcohol is both a depressant and a stimulant drug, depending on the amount and type consumed. In small amounts, alcohol can act as a stimulant, while in larger amounts, it acts as a depressant. As a depressant, alcohol can impair judgment and cause significant physical and psychological damage. Therefore, it is important to consume alcohol in moderation and seek help if you or someone you know is struggling with an alcohol addiction.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts