Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Alcohol has been a part of human culture for centuries, and its effects on our health and bodies continue to be studied and debated. But what about its molecular makeup? Is alcohol polar? In this article, we’ll explore the scientific evidence and look at what it means for the way we consume and interact with alcohol.
Yes, Alcohol is Polar. Alcohols are molecules that contain a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. The oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group has a partial negative charge, while the hydrogen and carbon atoms have partial positive charges. These charges cause the molecule to be polar, meaning it has both a positive and a negative side.
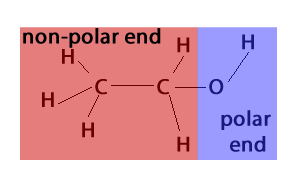
Is Alcohol a Polar Molecule?
Alcohol is a type of polar molecule, meaning it has an uneven distribution of electrons. This uneven distribution of electrons causes alcohol to have partial positive and partial negative charges, which make it a polar molecule. Alcohol is also a type of organic compound, meaning it is composed of both carbon and hydrogen atoms, as well as other elements. Alcohol molecules are composed of several carbon-hydrogen bonds, which are also polar.
Alcohol molecules have a highly polar nature due to their ability to form hydrogen bonds with other molecules. Hydrogen bonds are formed when hydrogen atoms in one molecule are attracted to the electronegative atoms in another molecule. This type of bond is much weaker than other types of bonds, but it is still strong enough to cause a partial positive and partial negative charge on each molecule, making them polar molecules.
The degree of polarity among alcohol molecules can vary depending on the structure and composition of the molecule. For example, ethanol molecules are slightly more polar than methanol molecules. This is due to the fact that ethanol molecules have more hydrogens than methanol molecules, which increases their ability to form hydrogen bonds. Additionally, the distance between the hydrogens and the electronegative atom in ethanol molecules is slightly shorter than in methanol molecules, which further increases their polarity.
Factors that Influence the Polar Nature of Alcohol
The polarity of an alcohol molecule can be affected by a variety of factors. The number of hydrogens and electronegative atoms in the molecule, as well as the distance between them, can all affect the degree of polarity. Additionally, the type of bond between the hydrogens and the electronegative atoms can also affect the polarity of the molecule. For example, single bonds tend to be more polar than double or triple bonds.
The polarity of an alcohol molecule can also be affected by the type of solvent it is dissolved in. For example, a polar solvent such as water will increase the polarity of an alcohol molecule, while a nonpolar solvent such as hexane will decrease its polarity. Additionally, the presence of other molecules in the solution can also affect the polarity of an alcohol molecule.
Uses of Polar Alcohol Molecules
Polar alcohol molecules have a variety of uses in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. For example, they can be used as solvents, which are liquids that are capable of dissolving other substances. Additionally, some polar alcohol molecules can also be used as surfactants, which are molecules that reduce the surface tension of a liquid. Polar alcohol molecules can also be used as detergents, which are molecules that help to clean and remove dirt from surfaces.
In addition to their industrial applications, polar alcohol molecules can also be used in the medical field. For example, they can be used as antiseptics, which are molecules that help to prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms. Additionally, some polar alcohol molecules can be used as anesthetics, which are molecules that help to reduce pain and induce sleep.
Physical Properties of Polar Alcohol Molecules
Polar alcohol molecules have a variety of physical properties that make them useful in many different applications. For example, they have a high boiling point, which means they can be used as solvents at high temperatures. Additionally, polar alcohol molecules also have a relatively low freezing point, which makes them useful in cryogenic applications.
Polar alcohol molecules also have a relatively low viscosity, which means they can flow easily through narrow spaces. This makes them useful for applications such as lubrication and cooling. Additionally, polar alcohol molecules have a relatively low surface tension, which means they can be used as surfactants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alcohol is a type of polar molecule that has an uneven distribution of electrons, which causes it to have partial positive and partial negative charges. The degree of polarity among alcohol molecules can vary depending on the structure and composition of the molecule, as well as the type of solvent it is dissolved in. Polar alcohol molecules have a variety of uses in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, as well as the medical field. Additionally, they have a variety of physical properties that make them useful in many different applications.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Alcohol?
Alcohol is an organic compound with the general formula CnH2n+1OH. It is the generic name for a range of chemical compounds that can be divided into two main categories: ethanol, which is found in alcoholic beverages, and methanol, which is a toxic substance. The most commonly consumed alcohol is ethanol, which is produced by fermentation of sugars by yeast or through a distillation process.
Is Alcohol Polar?
Yes, alcohol is a polar compound. This is because the oxygen atom in the alcohol has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen atoms. This causes the oxygen atom to attract electrons from the hydrogen atoms, creating a partially negative charge around the oxygen atom and a partially positive charge around the hydrogen atoms. This polarity gives alcohol its solubility properties, as it is soluble in water.
What is Polarity?
Polarity is the unequal distribution of electrons in a molecule. This unequal distribution creates a partial positive and partial negative charge in the molecule, giving it a net dipole moment. This dipole moment is the measure of the polarity of a molecule.
What are the Properties of Polar Compounds?
Polar compounds have several properties, including solubility in water, boiling point, and surface tension. Polar compounds are generally more soluble in water than nonpolar compounds. They also have higher boiling points than nonpolar compounds, due to the increased interactions between the molecules. Lastly, polar compounds have higher surface tension than nonpolar compounds, due to the increased interactions between the molecules.
What are the Benefits of Polar Compounds?
Polar compounds have many benefits, including increased solubility in water and increased boiling points. These properties make polar compounds ideal for use in many industries, including pharmaceuticals and food production. Additionally, polar compounds are often used in cleaning products, as they are more effective at removing dirt and grease than nonpolar compounds.
What is the Difference Between Polar and Nonpolar Compounds?
The main difference between polar and nonpolar compounds is the unequal distribution of electrons in the molecule. In polar compounds, the electrons are unequally distributed, creating a partial positive and partial negative charge. This gives polar compounds a net dipole moment, making them able to interact with water molecules. Nonpolar compounds do not have this unequal distribution of electrons, so they are not able to interact with water molecules.
Why is alcohol more polar than water?
In conclusion, alcohol is a polar molecule. It has a positively charged end and a negatively charged end, allowing it to dissolve in water and other polar solvents. Alcohols are highly reactive, making them useful for a variety of applications. Understanding the polarity of alcohols is important in order to use them safely and effectively.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts