Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Alcohol is often thought of as a depressant, but this isn’t always the case. In fact, certain types of alcohol are considered to be stimulants, with the ability to increase energy, alertness and even mood. In this article, we’ll explore what alcohol is a stimulant, and how it can affect your body and mind. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of the potential benefits and risks of drinking alcohol as a stimulant.
Alcohol is a depressant, not a stimulant. It is a central nervous system depressant that slows down the body’s processes. Although alcohol can make people feel more relaxed, energized, and less inhibited, it is not a stimulant. Stimulants, such as caffeine and amphetamines, speed up the body’s processes and give a person a burst of energy. Drinking alcohol can lead to dehydration, fatigue, and depression, which can all contribute to feelings of tiredness.
Contents
- What Types of Alcohol are Stimulants?
- What Are the Health Benefits of Alcohol Stimulation?
- The Bottom Line
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What Alcohol is a Stimulant?
- What Are the Stimulating Effects of Alcohol?
- What Are the Risks of Consuming Stimulant Alcohol?
- How Can I Tell If Alcohol is Acting as a Stimulant?
- How Can I Reduce the Stimulating Effects of Alcohol?
- What Are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Alcohol?
- Truth Time! Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant?
What Types of Alcohol are Stimulants?
Alcohol is a drug that can have a range of effects on the body, including both depressant and stimulant effects. Stimulants are substances that increase alertness, focus, and energy. Alcohol can be classified as a stimulant, depending on the type and amount consumed.
Most commonly, beer and wine are considered to be stimulants. Beer and wine typically contain lower levels of alcohol than spirits, so the stimulant effect tends to be milder. The effects of beer and wine are often described as more of a feeling of relaxation and well-being than an energizing effect.
Spirits, such as whiskey, vodka, and gin, are more likely to cause a stimulating effect. These types of alcohol contain higher levels of alcohol and are more likely to produce feelings of alertness, focus, and energy. Drinking too much of these types of alcohol can lead to feelings of agitation, restlessness, and anxiety.
How Does Alcohol Stimulate the Brain?
Alcohol stimulates the brain by increasing the availability of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is responsible for feelings of pleasure, motivation, and reward. When alcohol is consumed, it increases the levels of dopamine in the brain, which can lead to feelings of pleasure, reward, and stimulation.
Alcohol also affects the release of other neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating mood, anxiety, and stress levels. Consuming alcohol can lead to an increase in serotonin and GABA, which can lead to feelings of relaxation, calmness, and well-being.
What Are the Risks of Alcohol Stimulation?
Although alcohol can have stimulating effects, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with consuming too much alcohol. Consuming too much alcohol can lead to alcohol poisoning, which can be fatal. Additionally, long-term excessive alcohol consumption can lead to serious health problems, such as liver damage, heart disease, and depression.
Alcohol can also lead to impaired judgment, which can lead to risky or dangerous behaviors. Alcohol can also lead to dehydration, which can cause headaches, dizziness, and fatigue. Finally, drinking too much alcohol can lead to addiction, which can have serious consequences on physical, mental, and emotional health.
What Are the Health Benefits of Alcohol Stimulation?
Although excessive alcohol consumption can be dangerous, moderate consumption of alcohol can have some health benefits. Moderate consumption of alcohol can reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and some types of cancer. Additionally, moderate consumption of alcohol can help to reduce stress and anxiety levels.
Alcohol can also act as a social lubricant, helping to reduce social anxiety and increase confidence in social situations. Finally, moderate consumption of alcohol can help to improve cognitive functioning, including memory, problem-solving, and decision-making.
What is Moderate Alcohol Consumption?
Moderate alcohol consumption is defined as up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men. A drink is defined as 12 ounces of beer, five ounces of wine, or one and a half ounces of liquor. It is important to note that these amounts are for individuals over the age of 21 and that drinking should not be done in excess.
What Are the Effects of Alcohol Withdrawal?
When an individual who has been consuming alcohol regularly stops drinking, they may experience withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can range from mild to severe and can include anxiety, depression, irritability, headaches, fatigue, and insomnia. More severe symptoms can include seizures, hallucinations, and delirium tremens.
The Bottom Line
Alcohol can have both stimulant and depressant effects on the body. Beer and wine are more likely to produce a milder, more relaxed effect, while spirits are more likely to produce a stimulating effect. It is important to be aware of the risks of excessive alcohol consumption and to drink in moderation. Moderate consumption of alcohol can have some health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke and improving cognitive functioning.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Alcohol is a Stimulant?
Answer: Alcohol is a depressant drug that is often misconstrued as a stimulant. It is estimated that up to 20% of drinkers experience stimulating effects from drinking alcohol, while the remaining 80% experience depressive effects. Stimulating effects of alcohol are generally short-lived and diminish with continued consumption.
What Are the Stimulating Effects of Alcohol?
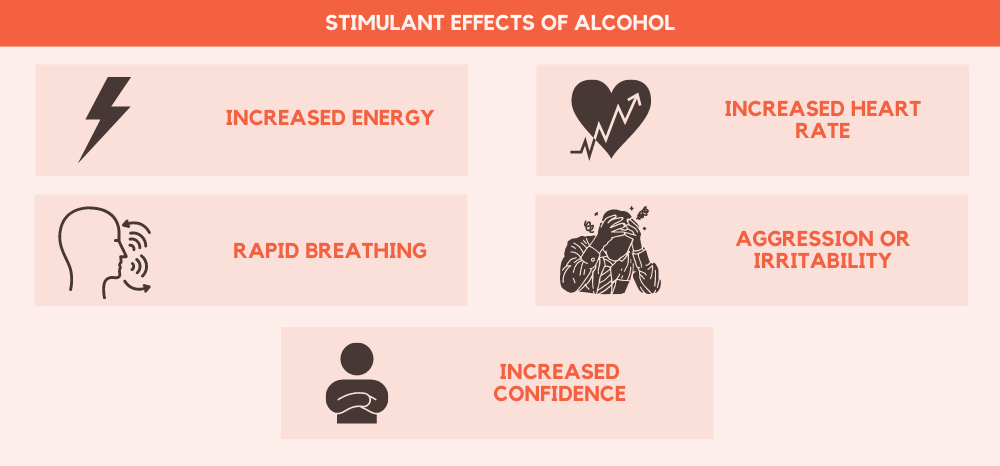
Answer: The stimulating effects of alcohol are generally short-lived and diminish with continued consumption. Stimulating effects of alcohol can include increased energy, increased alertness, increased sociability, and increased confidence. However, these stimulating effects can also be accompanied by side effects, such as impaired judgment, impaired motor coordination, and increased risk of harm.
What Are the Risks of Consuming Stimulant Alcohol?
Answer: The risks of consuming stimulant alcohol can include impaired judgment, impaired motor coordination, and increased risk of harm. These risks can be amplified when combined with other drugs, such as prescription medications, illegal drugs, or over-the-counter medications. Additionally, drinking alcohol in excess can lead to alcohol poisoning, which can be life-threatening.
How Can I Tell If Alcohol is Acting as a Stimulant?
Answer: Generally, if you experience a feeling of increased energy, alertness, sociability, or confidence after consuming alcohol, it is likely acting as a stimulant. However, it is important to remember that these effects are generally short-lived and diminish with continued consumption.
How Can I Reduce the Stimulating Effects of Alcohol?
Answer: To reduce the stimulating effects of alcohol, it is important to drink in moderation and understand your own individual tolerance. Additionally, drinking slower, alternating alcoholic beverages with non-alcoholic drinks, eating before and during drinking, and avoiding mixing alcohol with other drugs can help reduce the stimulating effects of alcohol.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulant Alcohol?
Answer: Long-term effects of stimulant alcohol can include increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder, increased risk of physical and mental health issues, and increased risk of injury and death. Additionally, drinking alcohol in excess can lead to alcohol poisoning, which can be life-threatening. It is important to understand the risks associated with drinking alcohol and to drink responsibly.
Truth Time! Is Alcohol a Stimulant or Depressant?
Alcohol, like other drugs, can be both a stimulant and a depressant. While alcohol is often seen as a depressant, it can also act as a stimulant when consumed in excess. This can lead to increased aggression, overconfidence, and impaired judgment. It is important to remember that alcohol is a powerful drug and should be consumed with caution. If you or someone you know is struggling with an alcohol addiction, please reach out for help.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts