Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Stimulants drugs are substances that increase activity in the body, resulting in an increased level of energy, alertness, and focus. From coffee and tea to cocaine and methamphetamine, these drugs have been used and abused for their stimulating effects for centuries. But what are the risks involved with stimulant drug use? In this article, we’ll explore the different types of stimulants, their effects, and the potential consequences of using them.
- How To Use Stimulant Drugs?
- Talk to your doctor about your symptoms to determine if a stimulant drug is right for you.
- Read the directions carefully and follow instructions.
- Take the prescribed dosage as directed.
- Monitor how you feel while taking the drug and tell your doctor if you experience any side effects.
| Stimulant Drugs | Caffeine |
|---|---|
| Type | Psychoactive Drug |
| Effects | Increases alertness and energy |
| Side Effects | Anxiety, restlessness, insomnia |
Contents
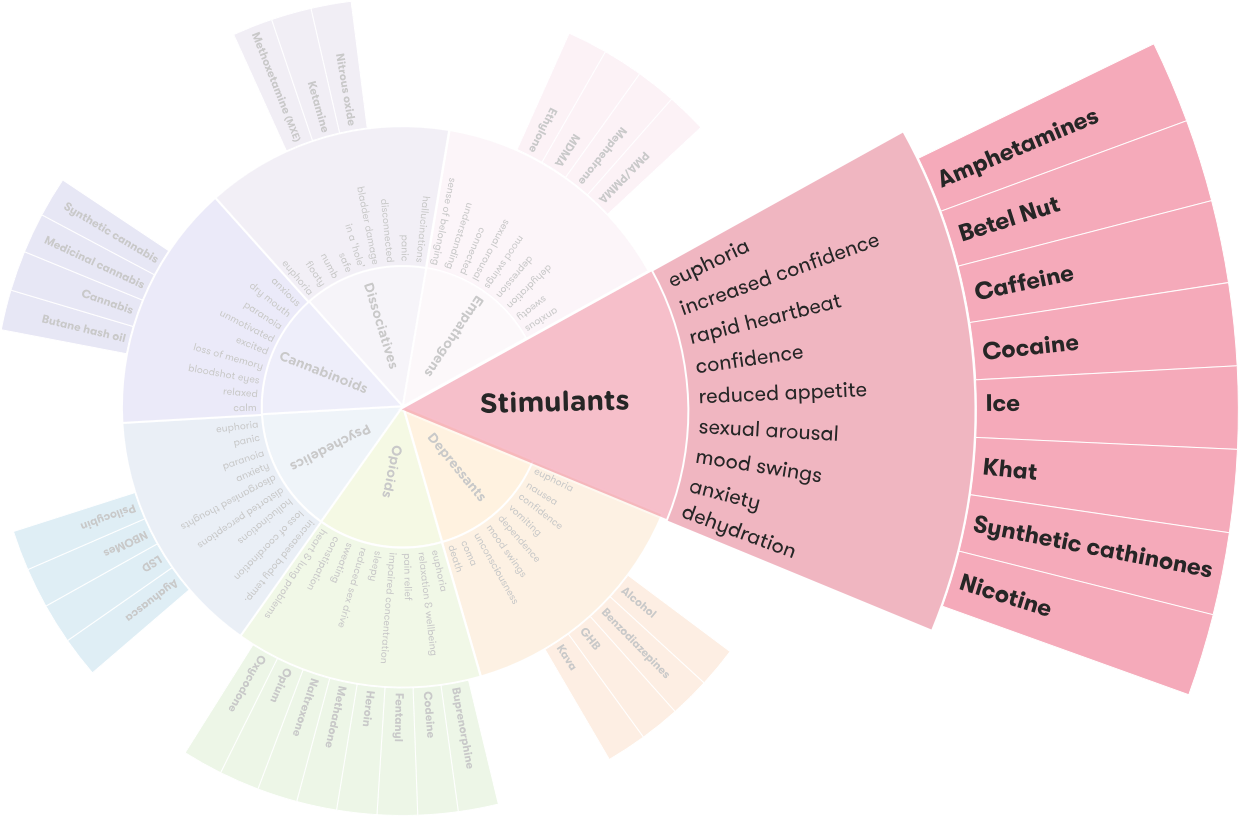
What Are Stimulants and How Do They Work?
Stimulant drugs are psychoactive drugs that increase alertness, energy and activity levels, and produce euphoria. Stimulants are central nervous system (CNS) stimulants and can be used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Stimulants can be prescribed medications or can be taken recreationally.
The most commonly used stimulants are amphetamines, cocaine, caffeine, and nicotine. Stimulants increase the amount of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine. These chemicals are responsible for producing feelings of pleasure and providing energy. Stimulants can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, suppress appetite, and reduce the need for sleep.
When taken in small doses, stimulants can provide a person with increased energy and alertness. However, when taken in large doses or when taken over a long period of time, stimulants can have a number of adverse effects, such as increased risk of addiction, paranoia, and even death.
Types of Stimulant Drugs
Stimulant drugs can be classified into three main categories: amphetamines, cocaine, and nicotine.
Amphetamines
Amphetamines are a type of stimulant drug that is often prescribed to treat ADHD. Amphetamines work by increasing the amount of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain. Commonly prescribed amphetamines include Adderall, Ritalin, and Concerta.
Amphetamines can be habit-forming and can cause a number of side effects, including anxiety, insomnia, irritability, and hypertension. In some cases, long-term use of amphetamines can lead to addiction and dependence.
Cocaine
Cocaine is a stimulant drug that is often used recreationally. Cocaine works by increasing the amount of dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin in the brain. Cocaine can cause a number of side effects, including anxiety, paranoia, and hypertension. It can also lead to addiction and dependence.
Nicotine
Nicotine is a stimulant drug that is found in many tobacco products, such as cigarettes, cigars, and chewing tobacco. Nicotine works by increasing the amount of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the brain. Nicotine can be habit-forming and can cause a number of side effects, including increased heart rate and blood pressure, irritability, and insomnia.
Stimulant Use and Abuse
When taken as prescribed, stimulants can be beneficial for those who suffer from medical conditions. However, stimulants can be habit-forming and can lead to addiction and dependence. Stimulant abuse can have a number of adverse effects, including anxiety, paranoia, hypertension, and even death.
Signs of Stimulant Abuse
Stimulant abuse can be difficult to recognize, as many of the signs can be attributed to other causes. However, some common signs of stimulant abuse include increased heart rate and blood pressure, insomnia, loss of appetite, irritability, and anxiety.
Treatment for Stimulant Abuse
If you or someone you know is struggling with stimulant abuse, it is important to seek treatment right away. Treatment for stimulant abuse typically involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. Medication can be used to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms, while psychotherapy can help to address any underlying psychological issues that may be contributing to the addiction. Lifestyle changes, such as engaging in regular exercise and eating a balanced diet, can also help to reduce cravings and prevent relapse.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Stimulants Drugs?
Answer: Stimulants drugs are a type of psychoactive drug that works by increasing the activity of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine. This can produce a range of effects, including increased alertness, wakefulness, and focus, as well as increased energy and improved mood. Stimulants can also increase heart rate, respiration rate, and blood pressure, as well as reduce appetite. Stimulants are most commonly used to treat conditions such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, but they may also be abused recreationally.
What Are the Different Types of Stimulants?
Answer: The most commonly used stimulants are amphetamines, methylphenidate, and cocaine. Amphetamines are stimulant drugs that act on the central nervous system to increase alertness and energy levels. Methylphenidate is a prescription drug used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. Cocaine is an illegal stimulant drug that produces a feeling of euphoria. Other types of stimulants include caffeine, ephedrine, and nicotine.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Stimulants?
Answer: The short-term effects of stimulants vary depending on the type of stimulant and the amount consumed. Generally, stimulants produce feelings of alertness, increased energy, and improved focus. They may also cause a decrease in appetite, increased heart rate, and elevated blood pressure. Stimulants can also produce feelings of euphoria and increased sociability.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Stimulants?
Answer: Long-term use of stimulants can lead to a range of physical and psychological effects. These include insomnia, anxiety, irritability, aggression, and depression. Prolonged use of stimulants can also lead to tolerance, meaning that higher doses are needed to achieve the same effects. Stimulant abuse can also lead to addiction, which can have serious health consequences.
Are Stimulants Addictive?
Answer: Yes, stimulants can be addictive. Abuse of stimulants leads to tolerance, meaning that higher doses are needed to produce the same effects. This can lead to compulsive drug-seeking behavior and addiction. Those who are addicted to stimulants may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop using the drug, such as fatigue, depression, and irritability.
What Are the Treatment Options for Stimulant Addiction?
Answer: Treatment for stimulant addiction typically involves a combination of behavioral therapy, medications, and support groups. Behavioral therapy can help individuals learn new coping skills and strategies to reduce drug use. Medications such as methadone and buprenorphine can also be used to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Support groups can provide a safe and supportive environment for those who are recovering from stimulant addiction.
Stimulants Mnemonic for MCAT
Stimulants drugs have the potential to be used both therapeutically and recreationally, but it is important to understand the risks and adverse effects associated with them. Stimulants can be dangerous when taken in high doses or for long periods of time, so it is important to be aware of the potential consequences. With careful consideration and proper medical supervision, stimulants drugs can be an effective way to treat certain conditions and can provide an enjoyable recreational experience.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts