Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Drug tests are a common tool used to confirm the presence of various substances in a person’s system. One of the most commonly tested substances is opiates, which are a group of drugs derived from the opium poppy plant. Unfortunately, while drug tests can be a useful tool, they are not foolproof and can sometimes yield false positives. In this article, we will explore what can give a false positive for opiates and how to avoid this issue.
Contents
- What Can Cause False Positive Opiate Results?
- Related Faq
- What Substances Can Give a False Positive for Opiates?
- What is a False Positive?
- How Can False Positives be Avoided?
- What are the Consequences of a False Positive?
- What Types of Drug Tests are Prone to False Positives?
- What Should be Done if a False Positive Occurs?
- Can certain foods, drinks, and meds cause a false positive on a drug test?
What Can Cause False Positive Opiate Results?
A false positive opiate result occurs when a drug test incorrectly indicates that a person has taken an opiate, even though they have not. False positives are relatively rare, but they can occur in certain circumstances. In this article, we will discuss the potential causes of a false positive opiate result.
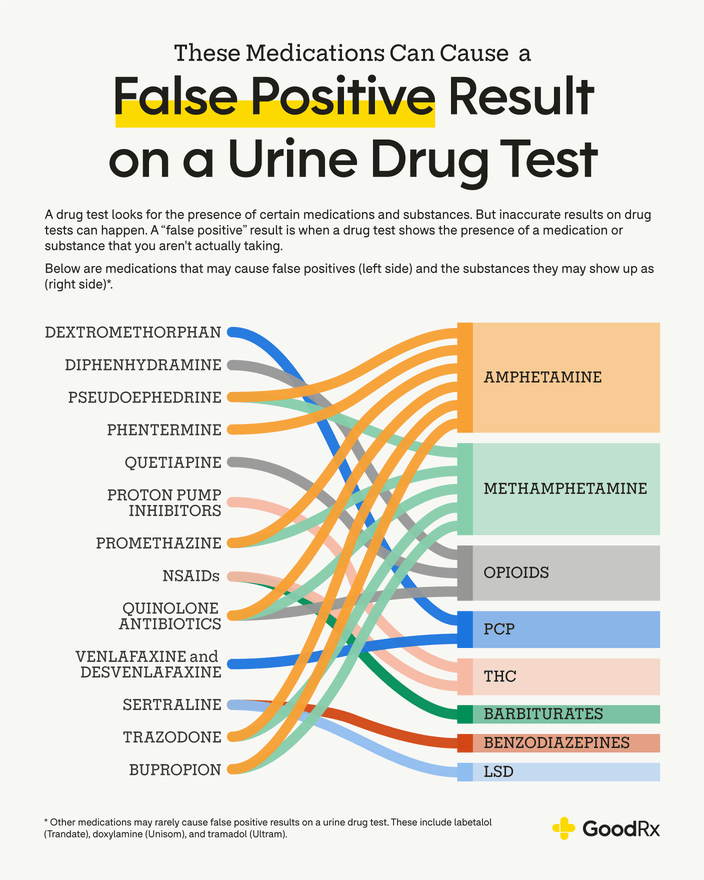
False positives can occur if a person has taken a medication that contains a compound similar to an opiate. This is known as cross-reactivity, and it can cause the test to show a positive result even though no opiate was taken. Certain cold medications, such as dextromethorphan, can also cause cross-reactivity. In addition, poppy seeds, which contain trace amounts of opiates, can result in a false positive.
Medications
A number of medications can lead to a false positive opiate result. These include certain antibiotics, antifungals, and antipsychotics. Some of the medications that may cause a false positive result include codeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and methadone. In addition, some antidepressants and antihistamines can also cause a false positive result.
The amount of medication needed to cause a false positive result varies from person to person. In some cases, even a small amount of medication can cause a false positive result. It is important to discuss any medications that you are taking with your doctor before taking a drug test.
Contaminated Samples
In some cases, a false positive result can occur due to a contaminated sample. This can occur if the sample is not collected properly, or if the sample is contaminated with another substance. For example, if the sample is contaminated with another substance that contains a compound similar to an opiate, it can lead to a false positive result.
It is important to make sure that the sample is collected properly and that it is not contaminated with any other substances. This can help to ensure that the results are accurate.
Improperly Calibrated Tests
In some cases, a false positive result can occur due to an improperly calibrated test. If the test is not calibrated properly, it may not be able to detect the presence of an opiate accurately. This can lead to a false positive result.
It is important to make sure that the test is calibrated properly before it is used. This can help to ensure that the results are accurate.
Lab Errors
In some cases, a false positive result can occur due to a lab error. This can occur if the lab technician makes a mistake when processing the sample. It is important to make sure that the lab technician is properly trained and that the sample is processed correctly.
Cross-Reactivity
Cross-reactivity occurs when a drug test incorrectly detects the presence of an opiate when none was taken. This can occur if a person has taken a medication that contains a compound similar to an opiate. Cold medications and poppy seeds are two common causes of cross-reactivity.
It is important to make sure that any medications that you are taking do not contain compounds that are similar to opiates. In addition, it is important to avoid eating poppy seeds before taking a drug test.
Related Faq
What Substances Can Give a False Positive for Opiates?
Answer: There are a number of substances that can give a false positive for opiates. These include certain over-the-counter medications, such as cold and flu medications, as well as certain prescription medications, such as quinolone antibiotics, methadone, and even some dietary supplements. Other potential false positives include poppy seeds, which contain natural opiates, and ibuprofen, which can cause a false positive for opiates due to its chemical structure.
What is a False Positive?
Answer: A false positive is a test result that suggests a particular condition or substance is present when it is not. Specifically, a false positive for opiates is a positive result on a drug test that is not due to the presence of opiates in the sample. False positives can occur due to a variety of reasons, such as the presence of certain medications, dietary supplements, or substances that are chemically similar to opiates.
How Can False Positives be Avoided?
Answer: False positives can be avoided by taking a few steps prior to a drug test. First, it is important to disclose all medications, supplements, and other substances that may be taken prior to a drug test. This will allow the medical professional administering the test to take these into consideration and to use additional tests to confirm the results. Additionally, certain techniques may be used by the laboratory to help avoid false positives, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
What are the Consequences of a False Positive?
Answer: The consequences of a false positive can be significant. Depending on the jurisdiction, a false positive may result in the individual being subjected to criminal penalties or other sanctions, such as loss of employment. For this reason, it is important to take steps to avoid false positives, such as disclosing all medications and supplements prior to the drug test.
What Types of Drug Tests are Prone to False Positives?
Answer: All types of drug tests are prone to false positives, although some are more prone than others. Immunoassay tests, such as urine or saliva tests, are more prone to false positives than other testing methods, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. This is because immunoassay tests are less precise and have a higher rate of false positives.
What Should be Done if a False Positive Occurs?
Answer: If a false positive occurs, it is important to take steps to confirm the results. This may include additional tests, such as a more advanced test, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Additionally, it is important to contact the laboratory that performed the test and explain the potential causes of the false positive. If the cause of the false positive is confirmed, the individual may be able to take steps to correct the situation and avoid any potential consequences.
Can certain foods, drinks, and meds cause a false positive on a drug test?
In conclusion, there are a number of substances which can lead to a false positive result for opiates. These substances include poppy seeds, certain over-the-counter cold medications, and certain prescription medications. It is important to be aware of these substances and to understand the potential consequences of a false positive result. If you are concerned that you may be at risk of a false positive, it is important to speak to a medical professional.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts