Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Drugs can be classified based on their effects on the body, and stimulants are among the most widely used. Stimulants are drugs that can increase alertness and energy, and can also have a range of other effects on the body. In this article, we will explore what drugs are classified as stimulants, how they work, and the potential dangers associated with their use.
Contents
What are Stimulant Drugs?
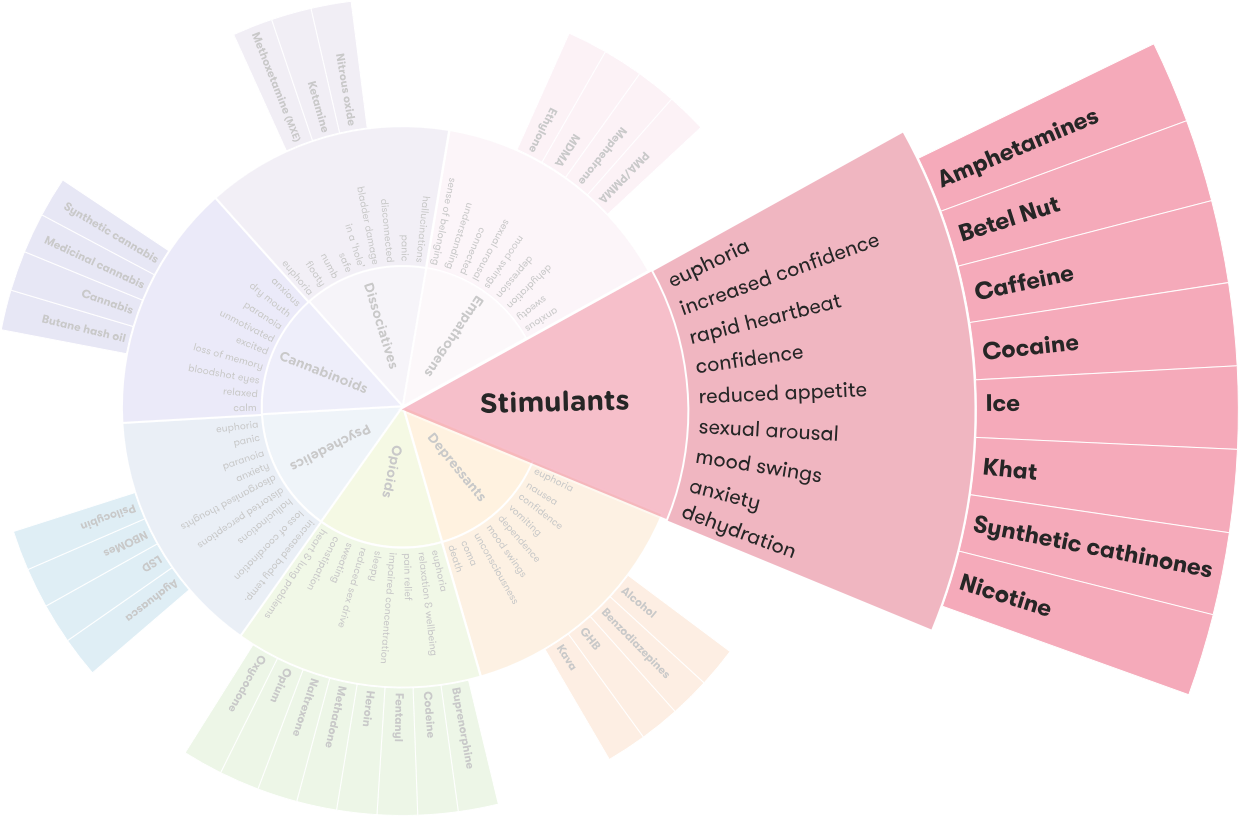
Stimulants are drugs that act on the central nervous system and increase activity in the body. They can enhance alertness, attention, and energy, as well as elevate heart rate and blood pressure. Stimulants are commonly used to treat attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity, but can also be used recreationally. Examples of stimulants include caffeine, amphetamines, cocaine, and nicotine.
Stimulants can be divided into two main categories: psychostimulants, which are prescription medications, and illicit stimulants, which are illegal drugs. Psychostimulants are typically prescribed to treat a variety of conditions, and their effects are generally milder than those of illicit stimulants. Illicit stimulants can have more powerful, and potentially dangerous, effects.
Effects of Stimulant Drugs
The effects of stimulants can vary depending on the type of drug and the individual using them. Generally, stimulants increase alertness, attention, and energy, as well as elevate heart rate and blood pressure. They can also lead to feelings of euphoria, increased self-confidence, and decreased appetite. Some stimulants can also lead to increased risk-taking behavior and aggressive behavior.
Short-term side effects of stimulants include insomnia, anxiety, irritability, and restlessness. Long-term use of stimulants can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Stimulants can also be dangerous when mixed with other drugs or alcohol, as they can increase the risk of overdose.
Prescription Stimulants
Amphetamines
Amphetamines are psychostimulants that are commonly prescribed to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. They work by increasing levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to improved alertness, attention, and concentration. Commonly prescribed amphetamines include Adderall, Dexedrine, and Vyvanse.
Side effects of amphetamines can include insomnia, anxiety, and irritability. Long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Amphetamines can also be dangerous when mixed with other drugs or alcohol.
Methylphenidate
Methylphenidate is another psychostimulant that is commonly prescribed to treat ADHD. It works by increasing levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to improved alertness, attention, and concentration. Commonly prescribed methylphenidates include Ritalin, Concerta, and Daytrana.
Side effects of methylphenidate can include insomnia, anxiety, and irritability. Long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Methylphenidate can also be dangerous when mixed with other drugs or alcohol.
Illicit Stimulants
Cocaine
Cocaine is an illicit stimulant that is derived from the coca plant. It works by increasing levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to feelings of euphoria and increased energy. Cocaine is highly addictive and can cause serious health problems, such as heart attack and stroke.
Side effects of cocaine can include insomnia, anxiety, and irritability. Long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Cocaine can also be dangerous when mixed with other drugs or alcohol.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine is an illicit stimulant that is similar to amphetamines. It works by increasing levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which can lead to feelings of euphoria and increased energy. Methamphetamine is highly addictive and can cause serious health problems, such as heart attack and stroke.
Side effects of methamphetamine can include insomnia, anxiety, and irritability. Long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence, as well as an increased risk of addiction. Methamphetamine can also be dangerous when mixed with other drugs or alcohol.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Stimulant Drugs?
Stimulant drugs are a class of psychoactive substances that increase the activity of the brain and central nervous system. Stimulants can have a variety of effects on the body, including increasing alertness, attention, and energy, producing euphoria, and reducing fatigue. These drugs are commonly used to treat a variety of conditions, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and depression. Stimulants can also be abused, leading to serious health consequences.
What Types of Drugs Are Stimulants?
Common types of stimulant drugs include amphetamines, such as Adderall and Ritalin; methylphenidate, such as Concerta and Daytrana; and modafinil, such as Provigil and Nuvigil. Stimulants can also be found in varying forms, such as tablets, capsules, and liquids. Additionally, some over-the-counter medications can contain stimulants, such as caffeine and ephedrine.
What are the Effects of Stimulant Drugs?
The effects of stimulant drugs vary depending on the type of drug and dose taken. Generally, stimulants increase alertness, attention, and energy, produce feelings of euphoria, reduce fatigue and appetite, and increase heart rate and blood pressure. When taken in large doses or abused, stimulants can lead to dangerous side effects, such as delusions, paranoia, and psychosis.
How Are Stimulant Drugs Used?
Stimulant drugs are typically prescribed for medical conditions, such as ADHD, narcolepsy, and depression. These drugs can also be used off-label for other conditions, such as sleep apnea, chronic fatigue syndrome, and obesity. Additionally, some stimulants are abused recreationally for their euphoric and energizing effects.
What are the Risks of Stimulant Drugs?
The risks of stimulant drugs depend on the type of drug, dose taken, and individual factors. Generally, stimulants are considered safe when taken as prescribed, but they can be dangerous if abused or taken in large doses. Stimulants can lead to physical and psychological dependence, and they can also have serious side effects, such as psychosis, cardiovascular complications, and kidney damage.
How Can Stimulant Abuse be Treated?
The treatment of stimulant abuse typically involves a combination of medications, such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, and mood stabilizers, in addition to psychotherapy. Additionally, the use of cognitive-behavioral therapy can help individuals identify and address the underlying causes of their stimulant use. In some cases, residential treatment centers or inpatient rehabilitation programs may be necessary for successful recovery from stimulant abuse.
Psychoactive drugs: Stimulants | Processing the Environment | MCAT | Khan Academy
Stimulant drugs can be an effective way to improve focus and alertness, but it is important to remember that these medications can have serious side effects and should be used with caution. When used responsibly, stimulants can help people with a variety of medical and psychological conditions, but should never be taken without consulting a doctor first. With careful consideration and medical supervision, stimulant drugs can be a useful tool in improving focus and alertness, allowing people to lead ultimately healthier and more productive lives.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts