Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
The effects of opiates on the human body have been known since ancient times. While this class of drugs has been used for centuries to treat pain, it has also been abused, leading to a number of serious issues. But what drugs have opiates in them? In this article, we’ll take a look at the different types of opiates and their effects on the body. From over-the-counter painkillers to prescription drugs, we’ll cover it all so you can understand the potential dangers of opiates.
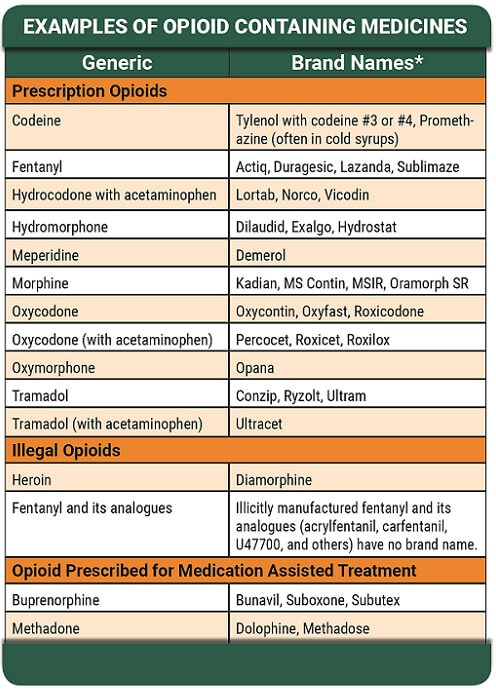
Opiate drugs include natural and semi-synthetic substances such as morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and hydromorphone. Some synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, pethidine, and methadone are also considered opiates. Natural opiates are derived from the opium poppy plant and include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. Semi-synthetic opiates are made from the natural opiates and include heroin, dihydrocodeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and hydromorphone. Synthetic opioids are made from chemicals and do not come from any natural source. Examples of synthetic opioids include fentanyl, pethidine, and methadone.
Contents
What Drugs Have Opiates?
Opiates
Opiate drugs are a type of narcotic analgesic drug derived from the opium poppy. They are used to treat pain, nausea, and other medical conditions. Opiates are highly addictive and can cause long-term physical and psychological damage. Common opiate drugs include morphine, codeine, and oxycodone.
Morphine
Morphine is a naturally occurring opiate and the primary active ingredient in opium. It is used to treat severe pain, such as that associated with cancer, and is often given in combination with other pain medications. Morphine is highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Codeine
Codeine is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from morphine. It is used to treat mild to moderate pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Codeine is usually combined with other medications, such as acetaminophen, to increase its effectiveness. Codeine is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Oxycodone
Oxycodone is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from thebaine. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Oxycodone is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Synthetic Opiates
Synthetic opiates are man-made drugs that act on the same brain receptors as natural opiates. They are used to treat moderate to severe pain and are available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Synthetic opiates are highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence. Common synthetic opiates include fentanyl, hydrocodone, and methadone.
Fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly powerful synthetic opiate that is up to 100 times stronger than morphine. It is used to treat severe pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Fentanyl is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from codeine. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Hydrocodone is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Semi-Synthetic Opiates
Semi-synthetic opiates are man-made drugs that are derived from natural opiate alkaloids. They are used to treat moderate to severe pain and are available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Semi-synthetic opiates are highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence. Common semi-synthetic opiates include hydromorphone, oxymorphone, and buprenorphine.
Hydromorphone
Hydromorphone is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from morphine. It is used to treat severe pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Hydromorphone is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Oxymorphone
Oxymorphone is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from oxycodone. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Oxymorphone is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is a semi-synthetic opiate derived from thebaine. It is used to treat moderate to severe pain and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. Buprenorphine is also highly addictive and can cause physical and psychological dependence.
Uses of Buprenorphine
Buprenorphine is used to treat moderate to severe pain, as well as to help manage opioid addiction. It is available in both short- and long-acting forms. Buprenorphine can be prescribed by a doctor or dispensed in a pharmacy.
Side Effects of Buprenorphine
Common side effects of buprenorphine include nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, headache, dry mouth, and itching. More serious side effects include shallow breathing, slowed heart rate, confusion, seizures, and coma. Buprenorphine can also interact with alcohol and other drugs, so it is important to speak to a doctor before starting or changing a medication.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What are Opiates?
Opiates are substances derived from the opium poppy plant, which can be either naturally occurring or synthetically created. Opiates are primarily used to reduce pain, but they can also be used to produce feelings of euphoria, relaxation and sedation. Examples of opiates include morphine, codeine, heroin and hydrocodone.
What are the Most Commonly Used Opiates?
The most commonly used opiates are morphine, codeine, oxycodone and hydrocodone. Morphine is a naturally occurring opiate that is used to treat moderate to severe pain. Codeine is a naturally occurring opiate that is used to treat mild to moderate pain. Oxycodone is a synthetically created opiate that is used to treat moderate to severe pain. Hydrocodone is a synthetically created opiate that is used to treat moderate to severe pain.
Are There Any Over-the-Counter Opiate Drugs?
Yes, there are some over-the-counter opiate drugs, such as certain cough syrups and cold medicines. These medicines contain codeine, which is an opiate, and are used to treat mild to moderate pain, as well as to reduce coughing.
What are Some of the Side Effects of Opiate Use?
The side effects of opiate use can vary depending on the type and amount of opiate used. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, constipation, drowsiness, confusion, depression, dizziness, itching and sweating. Long-term use of opiates can lead to physical and psychological dependence, and in some cases, even addiction.
Are Opiates Addictive?
Yes, opiates can be addictive. Regular use of opiates can cause the body to become physically dependent on the drug and can lead to addiction. Addiction is a chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior, despite the negative consequences it can have on one’s mental and physical health.
How is Opiate Addiction Treated?
Opiate addiction is typically treated through a combination of medication and behavioral therapy. Medications, such as methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone, can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms associated with opiate addiction. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, can help individuals identify and cope with the underlying causes of their addiction and develop healthier coping strategies.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates are a class of drugs that have been used for centuries to treat a variety of medical conditions. They are highly effective and can be found in many prescription and over-the-counter medications. Opiates are very powerful and should be used with caution and only under the supervision of a qualified medical professional. They can be highly addictive and should be used only as prescribed. Understanding the risks and benefits associated with opiate use is essential to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts