Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Smoking is a habit that affects millions of people around the world, yet many are unaware of the exact effects that nicotine has on their body. One of the most common questions asked is “What is nicotine classified as?” Nicotine is an addictive drug found in cigarettes and other tobacco products, and it’s important to understand the classification of this substance so that you can make informed decisions about your health. In this article, we will explore the classification of nicotine and the potential health effects it can have.
Contents
What is Nicotine Classified As?
Nicotine as a Stimulant
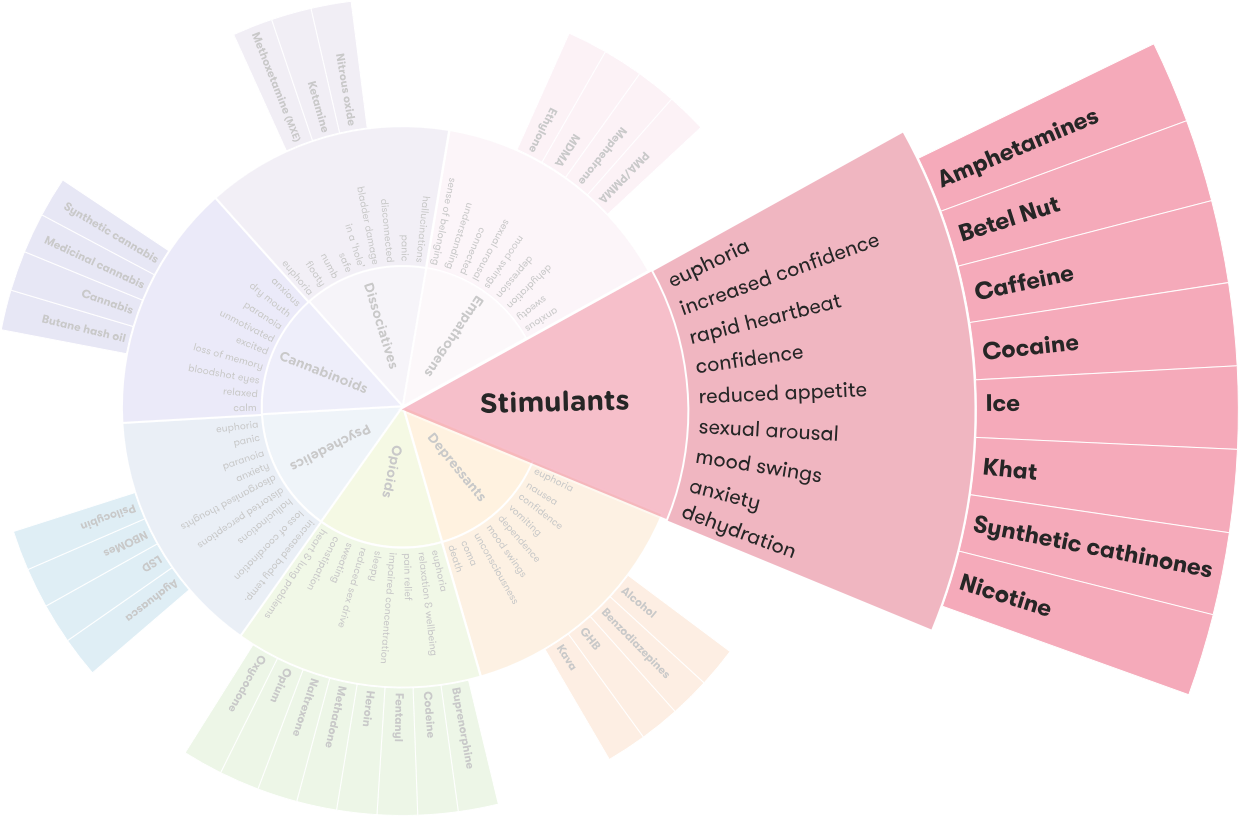
Nicotine is classified as a stimulant. It is a chemical found in tobacco and other plants of the nightshade family. It acts on the central nervous system, producing effects such as increased alertness, increased heart rate, and increased blood pressure. Nicotine is highly addictive and can be habit forming. It can also cause withdrawal symptoms when one stops using it. Nicotine can also be found in some e-cigarettes, although it is not as common as it is in tobacco products.
The main effects of nicotine are caused by the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter in the brain. Acetylcholine is responsible for the release of dopamine, which is associated with pleasure and reward. This is why nicotine is so addictive and why people who use it often crave more.
In terms of its classification, nicotine is considered to be a stimulant because it stimulates the central nervous system and increases alertness, heart rate, and blood pressure. Nicotine is also classified as a respiratory stimulant, as it can stimulate the respiratory system, leading to an increase in breathing rate.
Nicotine as a Poison
Nicotine is considered to be a poison, as it can have serious effects on the body if used in high doses. Nicotine is toxic and can cause serious health problems, including death. It is important to note that even small amounts of nicotine can be dangerous.
Nicotine is also considered to be a poison because of the way it affects the body. Nicotine can increase blood pressure and heart rate, which can lead to heart disease and stroke. It can also cause respiratory problems, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Nicotine can also cause nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
The long-term effects of nicotine can also be serious. Nicotine has been linked to cancer, heart disease, and other serious health conditions. It can also damage the lungs and other organs, leading to a decreased quality of life.
Nicotine as a Drug
Nicotine is also classified as a drug, as it is used to treat certain medical conditions. For example, it is used to treat Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), as it can help to improve focus and concentration.
Nicotine is also used to treat smoking cessation, as it can help to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. It can also be used to help with weight loss, as it can suppress appetite.
However, it is important to note that nicotine should not be used without medical supervision, as it can be dangerous if used in high doses. It can also lead to addiction and other serious health problems.
Nicotine as a Psychoactive Substance
Nicotine is also classified as a psychoactive substance, which means that it can alter one’s mental state and affect the way they think and feel. Nicotine is known to have both stimulant and depressant effects, as it can make one more alert and focused, but it can also cause feelings of relaxation and sedation.
The effects of nicotine on the brain can be both positive and negative. On one hand, it can help to improve concentration, focus, and memory. On the other hand, it can lead to addiction and other serious mental health problems.
Nicotine can also have a negative effect on physical health. It can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and cancer. It can also lead to respiratory problems, such as coughing and wheezing.
Nicotine as an Addictive Substance
Nicotine is classified as an addictive substance because it is highly addictive and can be habit forming. People who use nicotine often find it difficult to stop, as it can lead to withdrawal symptoms when one stops using it.
Nicotine can also lead to physical dependence, as one’s body can become used to having nicotine in their system. This can lead to cravings and increased tolerance, which can make it difficult to stop using nicotine.
It is important to note that nicotine should not be used without medical supervision, as it can be dangerous and lead to addiction. It is also important to be aware of the potential health risks associated with nicotine use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nicotine is classified as a stimulant, poison, drug, psychoactive substance, and addictive substance. It can have serious effects on the body, such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased risk of cancer and heart disease. It can also lead to addiction and other serious mental health problems. Nicotine should not be used without medical supervision and it is important to be aware of the potential health risks associated with its use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine Classified as?
Answer: Nicotine is classified as a stimulant, psychoactive, and addictive drug. It is found in tobacco leaves, as well as in many products such as cigarettes, cigars, e-cigarettes, and smokeless tobacco. Nicotine acts on the central nervous system and has stimulant, sedative, and euphoric effects.
What Types of Products Contain Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine is most commonly found in cigarettes, cigars, e-cigarettes, and smokeless tobacco. It is also found in some other products such as nicotine patches and gums. In addition, nicotine is sometimes used as an ingredient in certain medicines, such as nasal sprays and inhalers.
What Are the Effects of Nicotine?
Answer: Nicotine acts on the central nervous system and has several effects. It can produce a feeling of alertness and energy, as well as a sense of relaxation and pleasure. It can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, and cause a dry mouth and throat. Nicotine is highly addictive, and long-term use can lead to physical and psychological dependence.
What Are the Risks of Using Nicotine?
Answer: The use of nicotine carries many risks. It can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. It can also lead to nicotine dependence and addiction, which can be difficult to overcome. Additionally, nicotine can have negative effects on the developing brain of adolescents and young adults, and can also increase the risk of other mental health disorders.
Is Nicotine Legal?
Answer: Nicotine is legal in many countries, but its use is regulated in some places. In the United States, nicotine is legal for adults to use when it is obtained from a legal source. However, in some states, it is illegal to sell nicotine products to anyone under the age of 21.
What Are the Alternatives to Nicotine?
Answer: There are a variety of alternatives to nicotine that may help people quit smoking or reduce their nicotine use. These include nicotine replacement therapies such as patches, gum, and inhalers, as well as medications that can help reduce cravings. Additionally, non-nicotine products such as electronic cigarettes and heated tobacco devices may be helpful for some people. There are also a variety of behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, that are effective in helping people quit smoking.
Tobacco Addiction: Nicotine and Other Factors, Animation
In conclusion, Nicotine is classified as an alkaloid, which is a type of naturally occurring organic compound. It is found in various plants that are related to nightshades, including tobacco, and is the primary psychoactive ingredient in cigarettes. Nicotine has both stimulant and relaxant effects on the body, and can be both beneficial and detrimental to health depending on the dose and the way it is administered.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts