Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Opiates are among the most commonly prescribed medications in the world. They are used to treat a variety of ailments, including pain, anxiety, and depression. But what exactly are opiates? This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the different types of opiates, their effects, and potential side effects. We’ll also discuss the importance of talking to your doctor before taking any opiate medication. So read on to learn more about opiates and the medications that are considered opiates.
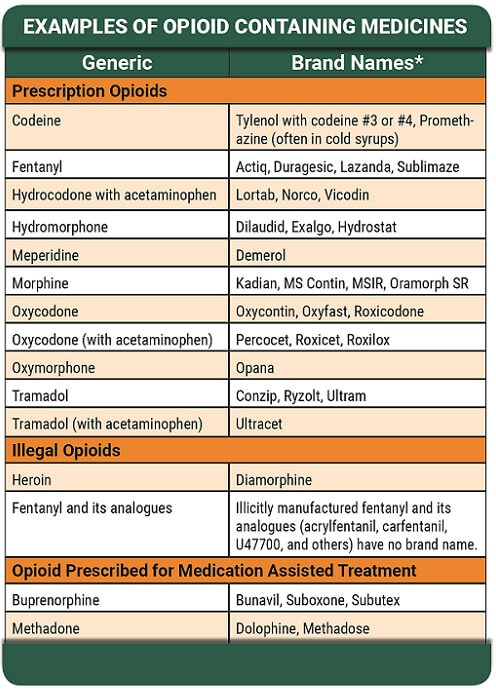
Opiates are a type of medication used to reduce pain, and they can be natural or synthetic. Common natural opiates include morphine, codeine, and thebaine; while common synthetic opiates are methadone, fentanyl, and oxycodone.
Contents
- What are Opiates?
- What are the Risks of Opiates?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What Are Opiates?
- What are Some Commonly Used Opiate Medications?
- What Are the Side Effects of Opiate Medications?
- Are There Non-Opiates Medications Available?
- What are the Risks of Taking Opiate Medications?
- What Should I Do if I Think I’m Addicted to Opiates?
- This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
What are Opiates?
Opiates are a class of drugs derived from opium, which is an extract from the poppy plant. They are sometimes referred to as narcotics, and they have a variety of effects on the body, including pain relief, sleepiness, and euphoria. Opiates have been used for centuries for medical and recreational purposes, but they can be very dangerous and are highly addictive.
Opiates work by binding to certain receptors in the brain, blocking the transmission of pain signals and creating a feeling of euphoria or relaxation. Opiates can be found in both prescription and illegal forms, and they are typically used to treat pain, insomnia, and other medical conditions.
The most commonly used opiates are morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and codeine. Other commonly used opiates include fentanyl, hydromorphone, and buprenorphine.
What are the Risks of Opiates?
Opiates are highly addictive and can be dangerous if abused. Some of the risks associated with opiate abuse include: physical dependence, overdose, and death. Opiate abuse can also lead to psychological and emotional problems, such as depression and anxiety.
Physical dependence occurs when a person becomes tolerant to the drug, meaning they need to take more of the drug to achieve the same effects. Over time, the body can become dependent on the drug and withdrawal symptoms can occur if the drug is stopped.
Overdose is a serious risk associated with opiate abuse. Opiate overdoses can be life-threatening and can result in coma or death. Opiates can also interact with other drugs or alcohol, increasing the risk of overdose.
What are the Symptoms of Opiate Abuse?
The symptoms of opiate abuse can vary depending on the type of drug being used, the amount being taken, and the user’s individual body chemistry. Common symptoms of opiate abuse include: changes in sleep patterns, changes in appetite, mood swings, and cravings for the drug. Other signs of opiate abuse include confusion, impaired coordination, and dilated pupils.
What are the Treatments for Opiate Abuse?
The most effective treatment for opiate abuse is a combination of medication and behavioral therapy. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is the use of approved medications, such as buprenorphine or methadone, to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms and make it easier for individuals to stay in treatment. Behavioral therapy can help individuals understand the root causes of their addiction and develop healthy coping strategies to help them stay sober.
Inpatient or outpatient treatment centers can provide a safe environment for individuals to get the care they need to overcome their addiction. Treatment centers can also provide access to medications and therapies that can help individuals manage their addiction.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Opiates?
Opiates are a type of drug that is derived from the poppy plant. These drugs are used to treat pain, as well as to produce a feeling of euphoria. They can be either natural or synthetic, and include heroin, morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, buprenorphine, and fentanyl. Opiates are highly addictive, and can produce physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms when stopped.
What are Some Commonly Used Opiate Medications?
Some of the most commonly used opiates are oxycodone, hydrocodone, codeine, morphine, and fentanyl. Oxycodone and hydrocodone are commonly prescribed to treat pain, while codeine and morphine are used to treat coughs, diarrhea, and other conditions. Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that is often used in pain management, and is considered to be much more potent than other opiates.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiate Medications?
The most common side effects of opiate medications include nausea, vomiting, constipation, drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and respiratory depression. Long-term use of opiates can also lead to tolerance, physical dependence, and addiction. Other side effects can include dry mouth, decreased appetite, sweating, and sexual dysfunction.
Are There Non-Opiates Medications Available?
Yes, there are many non-opiate medications available to treat pain. Some of these medications include acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, and celecoxib. Non-opiate medications are often safer and less addictive than opiates, and can be used for long-term pain management.
What are the Risks of Taking Opiate Medications?
The risks of taking opiate medications include tolerance, physical dependence, addiction, and overdose. Taking opiates can also interfere with the body’s natural ability to regulate pain, and can lead to a decrease in pain tolerance. Taking opiates can also lead to increased risk of falls and injuries due to drowsiness and dizziness.
What Should I Do if I Think I’m Addicted to Opiates?
If you think you may be addicted to opiates, it is important to seek professional help. Treatment for opiate addiction typically includes a combination of counseling, medication-assisted treatment, and other therapies. It is also important to avoid using opiates, as well as other drugs or alcohol, and to seek support from friends and family.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates are a type of medication that is commonly used to treat pain, but can also be highly addictive. While there are many types of opiates, some of the most commonly prescribed are morphine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and codeine. It is important for those taking opiates to be aware of the potential for addiction and to be monitored closely by their doctor. With the proper care and attention, opiates can be beneficial in providing relief from pain.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts