Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Opioids, or opiates, are powerful drugs that can have a major impact on a person’s life. They are derived from the poppy plant and are used to treat pain, coughs, and diarrhea. While they can be beneficial when used properly, they can also be dangerous and addictive if abused. In this article, we’ll explore which drugs are considered opiates, as well as their potential risks and benefits.
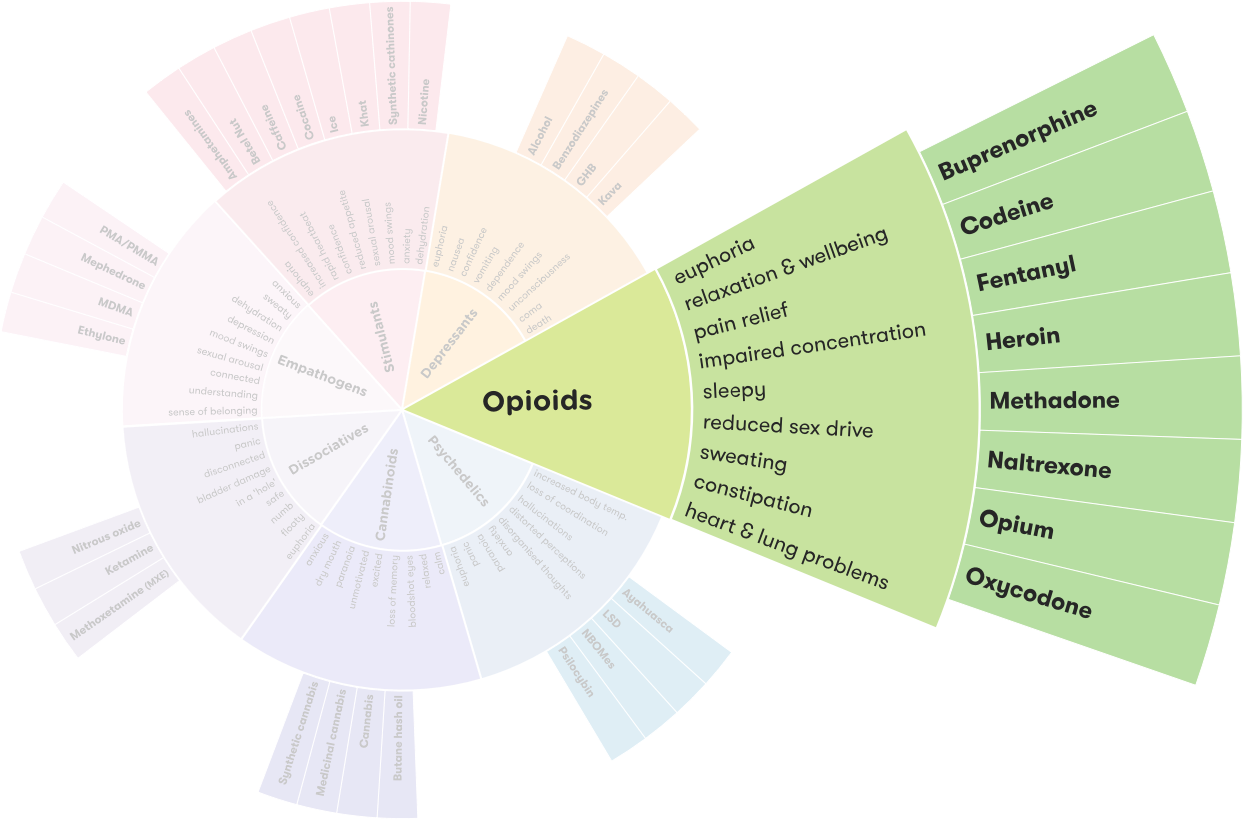
Opiates are a class of drugs that are derived from the poppy plant and include drugs like morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and heroin. Opiates are used to treat severe pain, but they can also be abused, leading to addiction and other health problems.
What Are Opiates?
Opiates are drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant, which is native to Asia and the Middle East. Opiates are used as painkillers and to treat various medical conditions such as addiction, depression, and anxiety. The most common type of opiate is morphine, but there are many other types of opiates, including codeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and fentanyl. Opiates are highly addictive and can cause serious health problems if misused.
What Are the Different Types of Opiates?
Morphine is the most commonly used opiate and is used to treat severe pain. It is commonly prescribed by doctors to treat cancer or post-operative pain. Codeine is another type of opiate that is used to treat mild to moderate pain and is also used to treat coughs, colds, and diarrhea. Hydrocodone is an opiate that is used to treat moderate to severe pain and is often prescribed for chronic pain. Oxycodone is another type of opiate that is used to treat severe pain and is often prescribed for chronic pain. Fentanyl is a powerful synthetic opiate that is used to treat severe pain and is often prescribed for cancer patients.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiates?
Opiate use can cause a range of side effects, including physical and psychological dependence, tolerance, and in some cases, even death. Common side effects include nausea, drowsiness, confusion, constipation, and respiratory depression. Long-term use can also lead to an increased risk of infections, liver and kidney damage, and changes in mood and behavior.
Are Opiates Addictive?
Yes, opiates are highly addictive. They act on the brain’s reward system, causing a feeling of euphoria and a strong craving for the drug. Regular use of opiates can lead to physical and psychological dependence, and withdrawal symptoms can include nausea, vomiting, insomnia, and depression.
How Are Opiates Misused?
Opiates are commonly misused by taking them in higher doses than prescribed, taking them more often than prescribed, or taking them without a prescription. They are also often taken in combination with other drugs, such as alcohol or other sedatives, which can increase the risk of overdose and other serious health problems.
What Are the Consequences of Opiate Misuse?
Misuse of opiates can lead to a range of physical and psychological consequences. Physically, it can lead to liver and kidney damage, respiratory depression, and an increased risk of infections. Psychologically, it can lead to changes in mood and behavior and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Opiate misuse can also lead to an increased risk of overdose and death.
What Are the Treatment Options for Opiate Misuse?
The most effective way to treat opiate misuse is through a combination of medication and counseling. Medications such as buprenorphine, naltrexone, and methadone can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms and can be used in combination with counseling and other forms of therapy.
What Are the Alternatives to Opiates?
There are a number of non-opiate pain medications that can be used in lieu of opiates for the treatment of pain. These include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, and topical analgesics. Non-opiate pain medications are generally considered to be safer and less addictive than opiates.
Related Faq
What Are Opiates?
Opiates are a type of drug derived from the opium poppy plant. They can be used for both medical and recreational purposes. They are commonly prescribed to treat pain, but they can also be abused and lead to addiction. Opiates act on the central nervous system and can cause feelings of euphoria, sedation, and relaxation. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, and heroin.
What Are the Effects of Opiates?
Opiates act on the central nervous system, which can cause a variety of effects. These effects can range from feelings of relaxation and euphoria to drowsiness and confusion. Opiates can also cause respiratory depression, which can be dangerous and even fatal in some cases. Long-term use of opiates can lead to physical dependence and addiction.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiates?
The most common side effects of opiates include drowsiness, confusion, constipation, nausea, and vomiting. Opiates can also cause respiratory depression, which can be dangerous and even fatal in some cases. Long-term use of opiates can lead to physical dependence and addiction.
Are Opiates Addictive?
Yes, opiates are highly addictive. Opiates act on the brain to produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation, which can be very difficult to stop once you start. Long-term use of opiates can lead to physical dependence and addiction.
What Are the Signs of Opiate Abuse?
The signs of opiate abuse can vary depending on the individual. Common signs of opiate abuse include changes in behavior, such as increased secrecy and social isolation, changes in sleep patterns, changes in appetite, and mood swings. Other signs of opiate abuse include physical changes such as constipation, nausea, and vomiting.
How Is Opiate Addiction Treated?
Opiate addiction is a complex disease that requires comprehensive treatment. Treatment for opiate addiction typically includes a combination of medications and behavioral therapies. Medications such as methadone and buprenorphine can help reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy and contingency management, can help people learn new coping skills and strategies to help them manage their addiction.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates are one of the most powerful and potentially dangerous drugs available to the public. It is important to understand the effects of these drugs, as well as the risks associated with using them. Knowing which drugs are considered opiates can help people make informed decisions when it comes to using them. It is important to remember that these drugs should only be used as prescribed and with the guidance of a doctor.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts