Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
As an opioid epidemic continues to ravage the United States, it is essential to understand why people withdraw from opiates. Withdrawal from opiates can be an incredibly difficult process, and it can often be wrought with a variety of physical and psychological symptoms. In this article, we’ll explore the reasons why individuals withdraw from opiates, and the best ways to ensure a successful recovery.
Why Opiate Withdrawal is Necessary
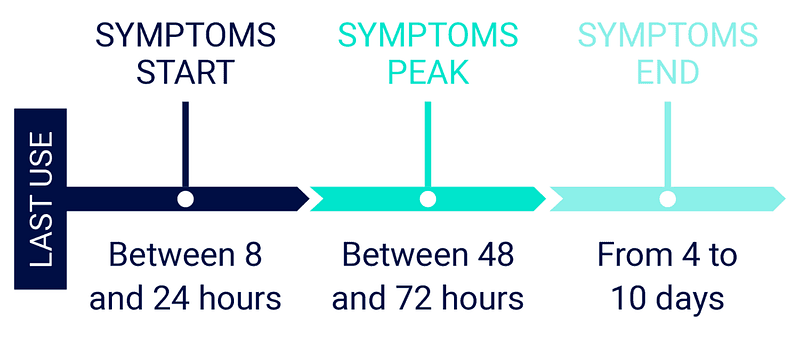
Opiate withdrawal is the physical and psychological process of the body’s reaction to the sudden absence of a drug, such as heroin or prescription painkillers. Opiate withdrawal occurs when the body attempts to rid itself of the substance and has to adjust to functioning without it. For individuals who have become dependent on opioids, opiate withdrawal can be uncomfortable, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe. It is necessary to withdraw from opiates in order to overcome addiction and reclaim one’s life.
The physical and psychological impact of opiate withdrawal can be overwhelming and dangerous. Common physical symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps, increased heart rate and blood pressure, and muscle aches and pains. Psychological symptoms can include depression, anxiety, irritability, and cravings for the drug. Other withdrawal symptoms may include insomnia, restlessness, chills, and sweating. Withdrawal can also cause a person to become agitated and disoriented, as well as having a lack of appetite and difficulty concentrating.
Opiate withdrawal can be a difficult process, but it is necessary to overcome addiction and restore health and well-being. Withdrawing from opiates without medical supervision can be dangerous and potentially life-threatening. It is important to seek medical help when withdrawing from opiates, as it can be a long and difficult process. Medical detox provides a safe and supportive environment to help individuals manage the physical and psychological symptoms of opiate withdrawal.
The Benefits of Opiate Withdrawal
When individuals decide to withdraw from opiates, they are taking the first step towards recovery and reclaiming their lives. Withdrawal can be uncomfortable and challenging, but it is a necessary step in the recovery process. Withdrawal from opiates can provide individuals with numerous physical and mental health benefits.
The physical benefits of opiate withdrawal include improved overall health and well-being. When individuals stop using opiates, their physical health will improve as the body begins to heal. Opiate withdrawal can also help individuals improve their sleeping habits and reduce their risk of developing a substance use disorder.
The psychological benefits of opiate withdrawal are just as important. Withdrawal can help individuals to regain control of their lives and reduce their risk of relapse. They may also experience improved mental clarity and an increased sense of self-worth. As individuals progress through the opiate withdrawal process, they will begin to experience more positive emotions and improved overall mental health.
Treatment Options for Opiate Withdrawal
Medical detox is the safest and most effective way to withdraw from opiates. Detox is a medically supervised process that helps individuals manage the physical and psychological symptoms of opiate withdrawal. During detox, individuals will be monitored by medical professionals and provided with medications to help ease the process. Detox also helps individuals develop healthier coping skills and strategies for managing cravings.
In addition to medical detox, there are a variety of other treatment options available for opiate withdrawal. These may include residential treatment programs, support groups, individual and family therapy, and medication-assisted treatment. These treatments can help individuals cope with the physical and psychological symptoms of opiate withdrawal and provide them with the tools they need to stay sober.
Conclusion
Opiate withdrawal is a necessary process for individuals who are trying to overcome their addiction. Withdrawal can be uncomfortable and difficult, but the physical and mental health benefits make it worth the effort. It is important to seek medical help when withdrawing from opiates, as it can be a long and difficult process. Medical detox provides a safe and supportive environment to help individuals manage the physical and psychological symptoms of opiate withdrawal. In addition to medical detox, there are a variety of other treatment options available for opiate withdrawal, such as residential treatment programs, support groups, individual and family therapy, and medication-assisted treatment. With the right support and guidance, individuals can successfully withdraw from opiates and reclaim their lives.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Opiates?
Opiates are a class of drugs that are derived from the poppy plant and are used medically to reduce pain, as well as recreationally for their euphoric effects. Common opiates include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone. These drugs can be found in many prescription medications and can also be illegally acquired.
What Are the Side Effects of Opiate Use?
There are a variety of side effects associated with opiate use, including nausea, constipation, drowsiness, confusion, and slowed breathing. Long-term use can also lead to dependence, tolerance, and addiction. Additionally, overdoses are possible, and can be fatal.
What Are the Signs of Opiate Addiction?
Signs of opiate addiction include a tolerance for the drug, cravings for the drug, difficulty controlling use, and spending large amounts of time and money trying to acquire the drug. Other signs may include changes in mood, behavior, and sleeping patterns, as well as withdrawal symptoms when not taking the drug.
What Is Withdrawal From Opiates?
Withdrawal from opiates is a natural, physical response to the body’s inability to function without the drug, and occurs when someone with an addiction suddenly stops taking the drug. Symptoms of withdrawal can include nausea, sweating, shaking, and insomnia.
What Are the Benefits of Withdrawing From Opiates?
Withdrawing from opiates can have a number of benefits. It can help to reduce cravings and symptoms of withdrawal, while also allowing the individual to regain control of their life. Additionally, it can help to reduce the risk of overdose, as well as physical and psychological dependence on the drug.
What Are the Steps Involved in Withdrawing From Opiates?
The process of withdrawing from opiates can vary depending on the individual, but typically includes steps such as tapering off the drug, managing withdrawal symptoms, and attending therapy or support groups. It is important to seek help from a professional if possible, as they can provide guidance and support throughout the process.
Opiates can be a powerful and dangerous tool, and when misused they can lead to serious health problems that can be difficult to overcome. Withdrawing from opiates is a difficult process, but it can be done with the right support, professional guidance, and dedication. The long-term benefits of quitting opiates outweigh the short-term benefits, and with proper guidance, you can find a healthier way to cope with the issues that led you to use opiates in the first place. Don’t let opiates control your life; take control of your own life and make the necessary steps to get off of them for good.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts