Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands...Read more
Benzodiazepines, or “benzos,” are a class of prescription medications commonly used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and other conditions. While they can be helpful in some situations, they can also be highly addictive. In this article, we’ll explore why benzodiazepines can be so addictive and what steps can be taken to avoid addiction.
Benzodiazepines are highly addictive medications commonly prescribed to treat anxiety, seizures, and insomnia. They work by increasing the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain, which is a neurotransmitter that reduces the activity of nerve cells in the central nervous system. When used as prescribed, benzodiazepines can be beneficial; however, when used for long periods of time or in high doses, they can be highly addictive.
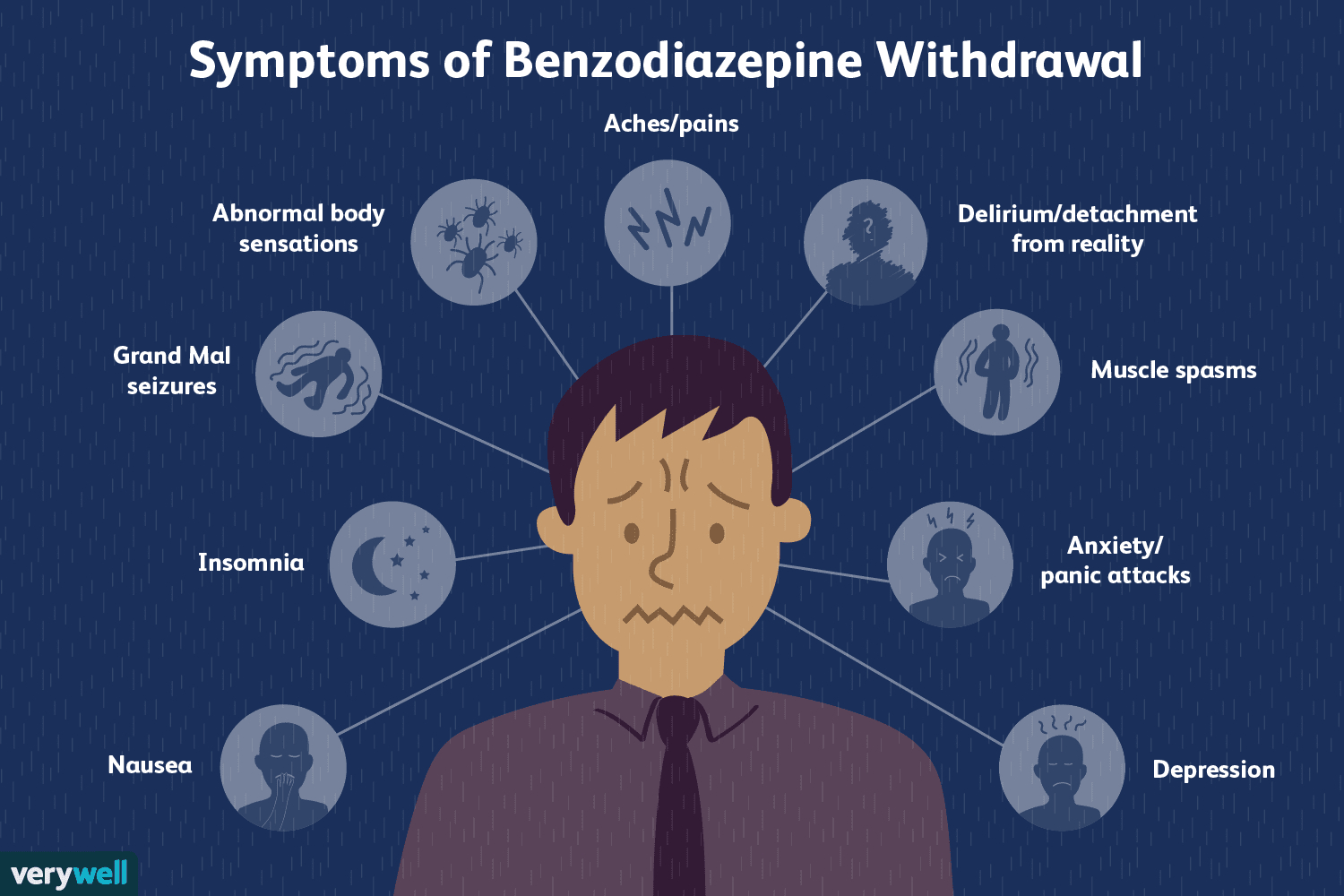
Individuals who take benzodiazepines for long periods of time may experience physical and psychological dependence. Physical dependence occurs when the body adapts to the drug and requires more of it to achieve the same effects. Psychological dependence occurs when an individual finds that the drug is necessary for them to feel normal or relaxed. Withdrawal symptoms can occur when an individual suddenly stops taking benzodiazepines.
People who are addicted to benzodiazepines may attempt to obtain the drug from multiple doctors, take higher doses than prescribed, and take the drug for longer periods of time than prescribed. They may also experience cravings, slipping into compulsive behavior, and neglecting other aspects of life. It is important to speak to a doctor if you or someone you know is addicted to benzodiazepines.
Contents
Introduction to Benzodiazepine Addiction
Benzodiazepines are drugs that are commonly prescribed to treat a variety of conditions, including anxiety, insomnia, seizures, muscle spasms, and alcohol withdrawal. They are also used to produce a calming effect and to help people relax. While benzodiazepines can provide short-term relief from symptoms, they can also be highly addictive when used for extended periods of time. In this article, we will discuss why benzodiazepines are addictive and what the risks of addiction are.
Reasons for Benzodiazepine Addiction
Brain Changes
When benzodiazepines are used for long periods of time, they can cause changes in the brain. These changes can alter the way the brain responds to certain stimuli, resulting in a physical dependence on the drug. People who are addicted to benzodiazepines may experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop taking the drug. These symptoms can range from mild to severe and can include anxiety, insomnia, tremors, sweating, and confusion.
Tolerance and Dependence
When benzodiazepines are taken for a long time, the body can become tolerant to the drug, meaning that the person needs to take larger doses in order to achieve the same effect. This can lead to dependence on the drug, as the person may feel that they need to take the drug in order to function normally. People who are dependent on benzodiazepines may also find it difficult to stop taking the drug, even if they want to.
Misuse and Abuse
Benzodiazepines can be misused or abused by taking them in larger doses than prescribed or taking them without a prescription. When benzodiazepines are misused or abused, they can cause serious side effects, including impaired coordination and judgment, confusion, and memory problems. People who misuse or abuse benzodiazepines may also be at risk of addiction.
Risks of Benzodiazepine Addiction
Health Risks
Long-term use of benzodiazepines can have serious health risks, including liver damage, depression, and respiratory depression (slowed breathing). Abruptly stopping benzodiazepines can also cause withdrawal symptoms, which can include seizures, hallucinations, and delirium.
Social and Financial Risks
Benzodiazepine addiction can also have social and financial consequences. People who are addicted to benzodiazepines may struggle to keep up with their obligations at work or school and may have difficulty maintaining relationships. They may also become involved in criminal activities in order to obtain the drug. In addition, addiction to benzodiazepines can be expensive, as people may need to buy the drug on the street or pay for expensive treatment programs.
Conclusion
Benzodiazepines can be effective for treating a variety of conditions, but they can also be highly addictive when used for extended periods of time. People who are addicted to benzodiazepines may experience physical, mental, and financial consequences. It is important to use benzodiazepines only as prescribed and to seek help from a medical professional if addiction is suspected.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Benzodiazepine?
Benzodiazepines are a class of medications known as central nervous system depressants that are prescribed to treat a variety of conditions, including anxiety disorders, seizures, muscle spasms, alcohol withdrawal, and insomnia. They are typically taken orally, but can also be injected. Common benzodiazepine medications include Xanax, Valium, Klonopin, and Ativan.
What makes Benzodiazepine addictive?
Benzodiazepines are considered addictive because they are habit-forming and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. When taken for a long period of time or in high doses, benzodiazepines can cause the body to become tolerant to the drug, meaning it will require higher doses to achieve the same effects. This can lead to a phenomenon known as “rebound anxiety,” which is a heightened experience of anxiety symptoms when the drugs wear off. Additionally, benzodiazepines can produce feelings of pleasure and relaxation, which can make them difficult to stop taking.
What are the signs of addiction to Benzodiazepines?
Common signs of benzodiazepine addiction include an increase in tolerance, taking higher doses than prescribed, taking the drug more often than prescribed, and withdrawal symptoms when attempting to stop taking the drug. Other signs include difficulty sleeping, increased irritability, changes in mood, and preoccupation with obtaining and using the drug.
What are the risks of taking Benzodiazepine?
There are several risks associated with taking benzodiazepines, including the potential for addiction, an increased risk of depression, impaired thinking and judgment, drowsiness, memory problems, and an increased risk of falls and fractures in elderly individuals. Additionally, benzodiazepines can interact with other medications and should not be mixed with alcohol or other drugs.
What are the treatment options for Benzodiazepine addiction?
Treatment for benzodiazepine addiction typically includes behavioral therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy and contingency management, as well as medications to help manage withdrawal symptoms and reduce cravings. In some cases, medications such as antidepressants may be prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms. Additionally, support groups and counseling can help individuals who are struggling with benzodiazepine addiction.
What are the long-term effects of Benzodiazepine addiction?
Long-term effects of benzodiazepine addiction can include depression, memory problems, impaired thinking and judgment, difficulty sleeping, and an increased risk of falls and fractures in elderly individuals. Additionally, individuals who are addicted to benzodiazepines may experience withdrawal symptoms when attempting to stop taking the drug. These symptoms can include anxiety, restlessness, nausea, muscle cramps, sweating, and seizures.
Benzodiazepines are powerful drugs that can be highly addictive if not taken responsibly. Their sedative and anxiolytic properties can be effective in treating a variety of medical conditions, but the risk of addiction is too great to ignore. When taken correctly, they can be beneficial, but it is important to be aware of the potential for addiction and consult with a doctor before taking them. With proper supervision and guidance, individuals can benefit from benzodiazepines without the danger of becoming addicted.
Mark Halsey is a licensed therapist, founder, and chief editor of Clean Break Recovery. With over a decade of addiction treatment experience, Mark deeply understands the complex needs of those struggling with addiction and utilizes a comprehensive and holistic approach to address them. He is well-versed in traditional and innovative therapies, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and mindfulness-based interventions.
More Posts